Lupus Explained: Causes, Signs, and Treatment Strategies
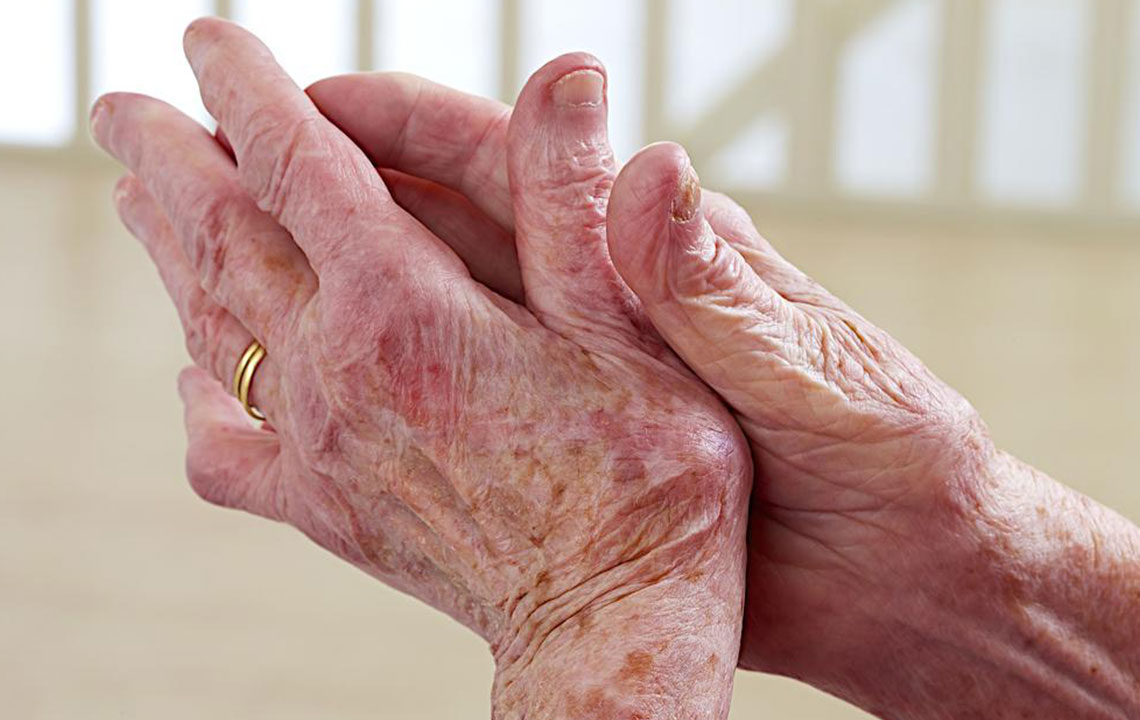
Lupus is a complex autoimmune condition affecting mainly young women, characterized by immune system attacks on healthy tissues. Symptoms like fatigue, skin rashes, and hair loss require early diagnosis for effective management. Although incurable, advances in treatment and lifestyle changes enable affected individuals to lead fulfilling lives. Understanding its causes and signs is crucial for timely intervention and controlling disease progression.
Lupus Explained: Causes, Signs, and Treatment Strategies
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly targets the body's own tissues. Instead of protecting against threats, it attacks healthy cells, causing widespread inflammation and damage. Although there is no cure currently, advances in treatment help control symptoms and improve quality of life. Lupus may also contribute to abnormal growths due to immune dysfunction. Symptoms can present subtly at first, typically in young women during adolescence or early adulthood. Common indicators include fatigue, mild fever, characteristic skin rashes, especially after sun exposure, and hair thinning. Accurate early diagnosis is essential since symptoms overlap with other conditions. Internal organ involvement can lead to serious health issues. Active management through medical care and lifestyle changes enables many patients to live productive lives, even with this complex disorder.
Autoimmune lupus manifests uniquely among individuals, with severity ranging from mild to severe flare-ups. It predominantly impacts women in their late teens to early thirties. Recognizing early symptoms such as fatigue, mild fever, specific skin rashes, and hair loss is vital for prompt diagnosis. Though incurable, lupus management through healthcare, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive care allows patients to maintain active, meaningful lives despite ongoing challenges posed by the disease.