A Complete Guide to Oral Cancer: Risk Factors, Signs, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive overview highlights the causes, symptoms, and prevention of oral cancer. Identifying early signs can save lives, especially given rising tobacco and alcohol use. Learn about risk factors and how to detect early symptoms for effective intervention.
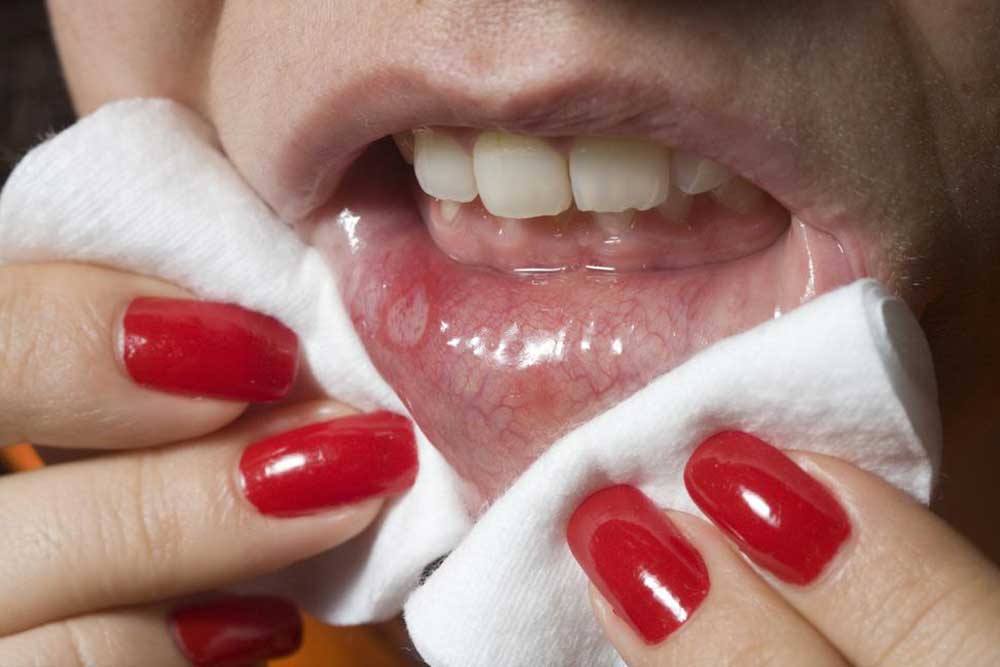

A Complete Guide to Oral Cancer: Risk Factors, Signs, and Prevention Strategies
Oral cancer impacts areas such as the lips, tongue, gums, and floor of the mouth. According to the American Cancer Society, nearly 50,000 Americans received an oral cancer diagnosis in 2017.
Causes and Risk Factors
This disease results from genetic alterations in mouth and lip cells, causing abnormal growths and tumors. It can invade adjacent tissues like the throat and neck. Common risk factors include smoking, chewing tobacco, heavy alcohol use, and sun exposure. Weakened immune systems and hereditary factors also contribute.
Early warning signs assist in timely detection. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for prompt diagnosis. Notable indicators include:
Thickened or rough patches inside the mouth
Loose teeth or dental instability
Persistent mouth sores that bleed or refuse to heal
Pain or stiffness in the jaw
Painful sensation in the tongue
Difficulty chewing or swallowing
Changes in voice or persistent sore throat
Ear pain
Unexpected weight loss
Continuous facial or neck pain with bleeding
White or red patches within the mouth
Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
Numbness or sensation loss in face or mouth
Persistent bad breath despite oral hygiene
With the increase in tobacco and alcohol consumption, early detection is essential for effective treatment and improved outcomes. Awareness is key to reducing oral cancer-related deaths.