A Comprehensive Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
Explore the essentials of rheumatoid arthritis, including causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how lifestyle changes and medications can help manage this autoimmune disease effectively. A comprehensive overview for better understanding and living better with RA.

Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis
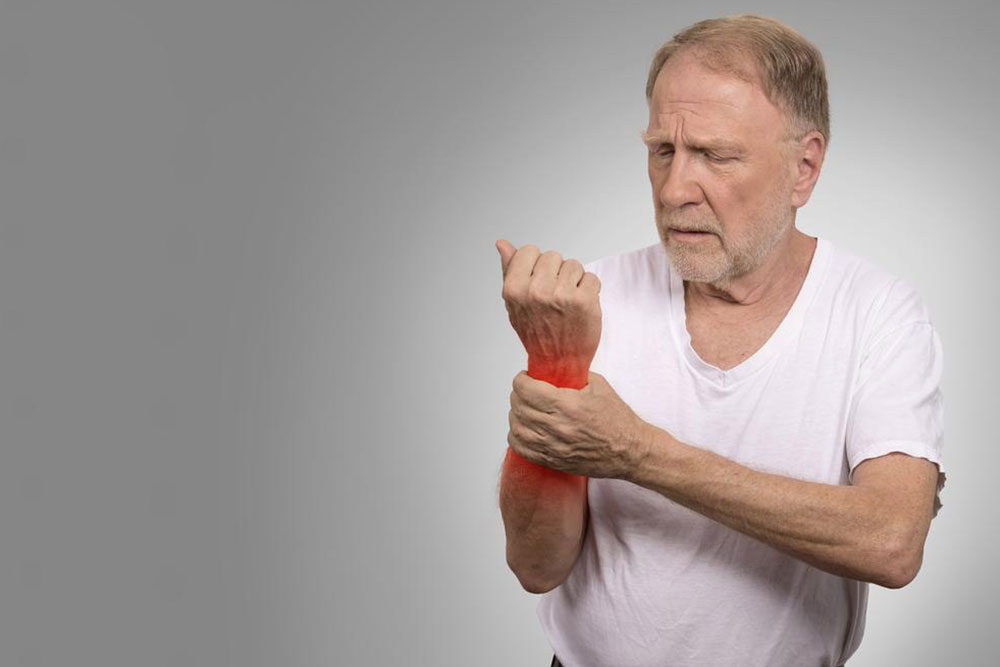
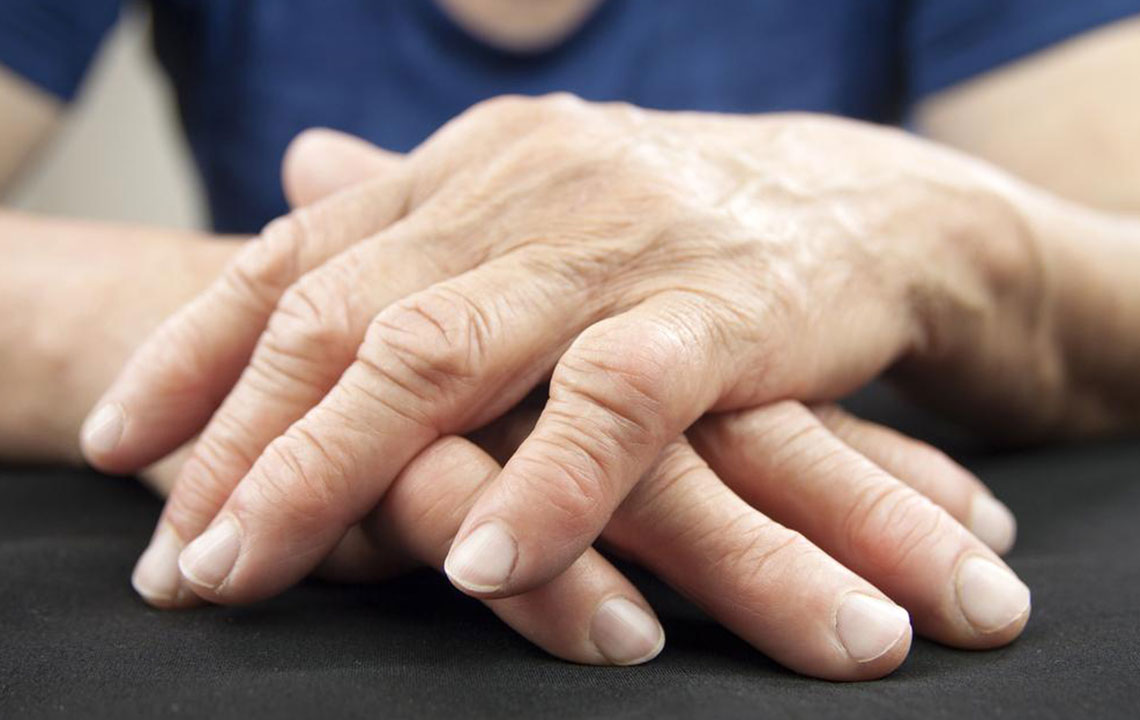
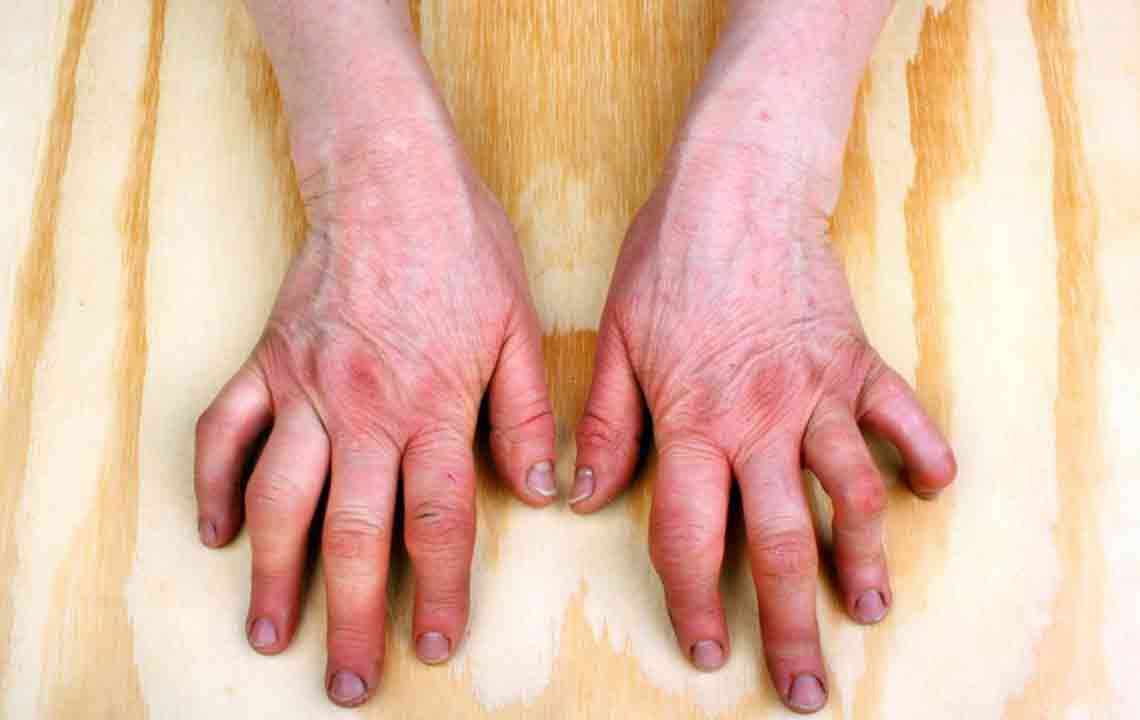
Arthritis encompasses over 200 different joint-related conditions, with common types including osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Rheumatic arthritis. Osteoarthritis results from long-term joint wear and tear, while Rheumatic arthritis often stems from bacterial infections like Streptococci, affecting joints and the heart, especially in children. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks joint tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. Genetics and environmental factors such as smoking and exposure to certain particles contribute to its development.
In RA, the immune system incorrectly targets synovial joint tissues, causing inflammation and deterioration. Genetic predispositions combined with environmental factors like smoking, infections, or silica exposure elevate risk. RA often affects joints symmetrically—if one side is involved, the opposite side likely is too. Diagnosis relies on patient history, physical assessments, blood tests such as Rheumatoid factor and anti–citrullinated protein antibody, along with imaging scans. While a cure remains elusive, treatments like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, methotrexate, and biologics including JAK inhibitors help control symptoms and slow progression.
Lifestyle and dietary choices can enhance symptom relief. Consuming omega-3 fatty acids from fish such as salmon and mackerel, along with turmeric’s anti-inflammatory properties, may alleviate discomfort. A diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, plus antioxidants like vitamins C, A, and E, selenium, and flavonoid-rich foods support overall health. Gentle activities like swimming, yoga, and stretching promote joint flexibility, strength, and mobility. Proper management allows RA patients to lead active, fulfilling lives.