Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
This comprehensive overview discusses the main types of lung cancer, their causes, warning signs, and preventive measures. Early detection and lifestyle changes are vital for better outcomes. Learn about risk factors such as exposure to toxins, symptoms like persistent cough and chest pain, and strategies for reducing risk. Proper awareness can lead to timely diagnosis and improved survival rates, making this guide an essential resource for understanding lung health and cancer prevention.
Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: Types, Causes, and Symptoms
The respiratory system's lungs are essential for oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release. Like all organs, lungs are vulnerable to diseases, especially lung cancer, which is the most prevalent cancer worldwide. Early detection and understanding the specific type of lung cancer are crucial for effective treatment and improved prognosis.
Lungs act as sponge-like organs facilitating gas exchange. Long-term exposure to harmful airborne toxins significantly increases lung cancer risk.
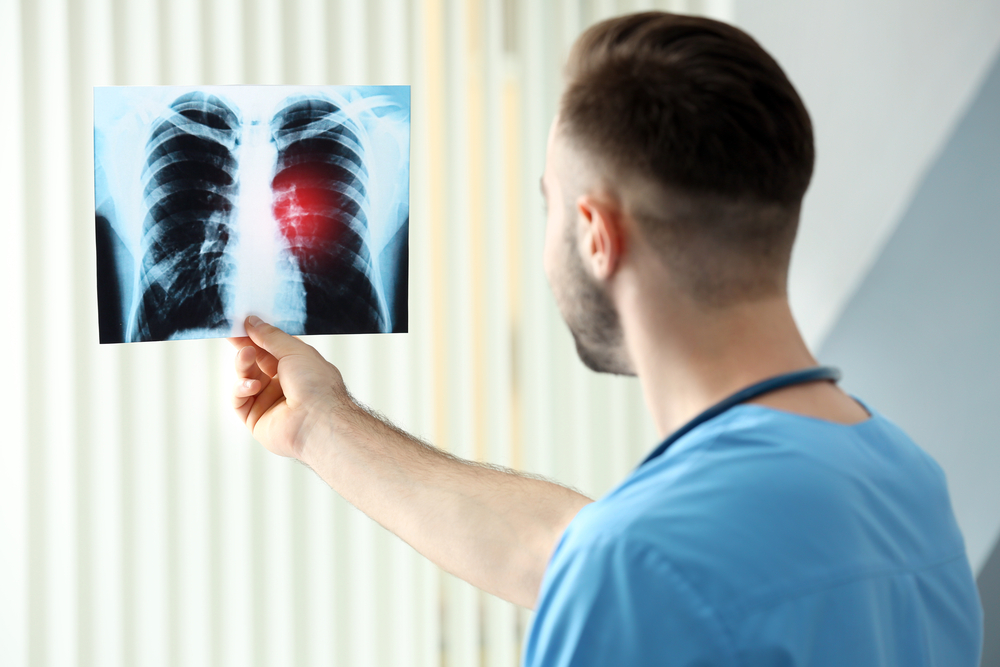
People regularly exposed to toxic fumes or gases face higher chances of developing lung cancer. This article explores key aspects such as types, causes, and early warning signs of the disease.
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is categorized mainly into two types, based on the appearance of cancer cells at diagnosis. The treatment strategy depends on the type and stage of the tumor.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
This is a fast-growing, aggressive form of cancer that tends to progress quickly if not detected early. It typically responds well to therapies like chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Includes various subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Symptoms often involve shortness of breath and a persistent cough.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of lung cancer remains uncertain. However, prolonged exposure to substances like radon, asbestos, arsenic, nickel, and chromium increases the risk. Family history and past radiation treatments also contribute to susceptibility.
Radon, a decay product of uranium in soil and water, can accumulate indoors, raising inhalation risks. Occupational contact with carcinogenic chemicals further heightens the likelihood. Sometimes, cases occur without identifiable risk factors.
Signs and Symptoms
Initially, lung cancer often shows no symptoms. As it advances, signs become more evident and include:
Persistent cough
Difficulty breathing
Headaches
Bone discomfort
Chest pain
Hoarseness
Additional symptoms include shortness of breath due to airway obstruction, pain from metastasis to bones or brain, coughing up blood, and fluid buildup in the chest. If untreated, it can spread and reduce survival chances, with a five-year survival rate around 26%. Prevention involves avoiding pollutants, leading a healthy lifestyle, and practicing breathing exercises to keep the lungs healthy.