Early Indicators and Symptoms of Leukemia to Watch For
Learn to identify the early signs of leukemia, including fatigue, unexplained bleeding, and lymph node swelling. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. This guide covers types of leukemia, common symptoms, and warning signs to watch for, helping you stay informed and proactive about your health.

Detecting Leukemia: Key Signs to Be Aware Of
Leukemia often presents with subtle symptoms that can be easy to overlook. Recognizing these early signs can lead to timely diagnosis and more successful treatment options.
What is leukemia?
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood that begins in the bone marrow, which produces blood cells. It causes the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells, disrupting normal blood functions. These cancerous cells multiply rapidly, eventually displacing healthy blood cells within the marrow.
While white blood cells are vital for fighting infections, when they malfunction due to leukemia, it can lead to bleeding, anemia, and increased infections. The disease can also spread to lymph nodes and other organs, causing pain and swelling.
Types of leukemia
Depending on how quickly symptoms appear, leukemia is classified as either acute or chronic. Acute leukemia develops rapidly with severe symptoms early on, while chronic leukemia progresses more slowly, often with few initial symptoms.
Leukemia is categorized based on which blood cell types are affected, primarily including:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Additional subtypes include hairy cell leukemia and specific variants like promyelocytic leukemia.
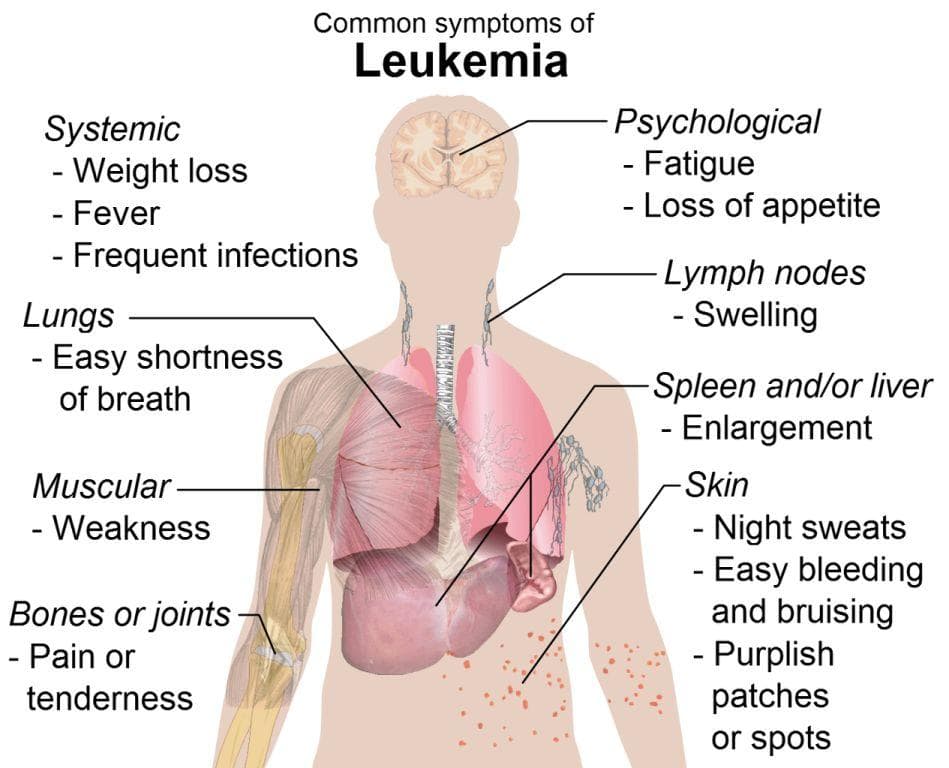
Recognizing early signs
Initially, leukemia symptoms may be faint or absent. As the disease advances, common and atypical signs become more evident. Watch out for these indicators:
Persistent tiredness and weakness without clear cause
Frequent fevers and chills
Bones or joint pain
Recurrent infections
Red spots on the skin (petechiae)
Unexplained bleeding from gums, nose, or rectum
Heavy periods
Headaches and night sweats
Shortness of breath
Unexpected weight loss or loss of appetite
Abdominal discomfort
Swelling or pain in the upper abdomen
Unexplained bruising
Other symptoms to monitor
Swollen lymph nodes: Swelling in the neck, armpits, or groin may signal lymphatic spread.
Anemia: Low red blood cell count can cause fatigue and breathlessness.
Leukopenia: Reduced white blood cells lead to higher infection risk.
Thrombocytopenia: Low platelet count can cause easy bruising and bleeding.
Organ enlargement: An enlarged liver or spleen can cause discomfort or fullness in the upper abdomen.
Persistent symptoms like fatigue, fever, or body aches might resemble cold or flu but should not be ignored if they last. Early medical evaluation is critical for diagnosis and can significantly improve treatment success.