Recognizing the Early Warning Signs of Leukemia
Leukemia is a blood cancer affecting white cells, with symptoms such as bleeding, anemia, swollen lymph nodes, infections, and fatigue. Early detection is critical, so awareness of these signs can prompt timely medical evaluation. Consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.

Leukemia is a cancer that originates in tissues responsible for blood production, such as the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It primarily affects white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting infections. Normally, these cells grow and multiply as needed, but leukemia causes abnormal cells to develop that do not function properly, leading to health complications.
Leukemia Incidence
Men tend to be more frequently diagnosed than women, with approximately 30,000 new cases reported each year in the country.
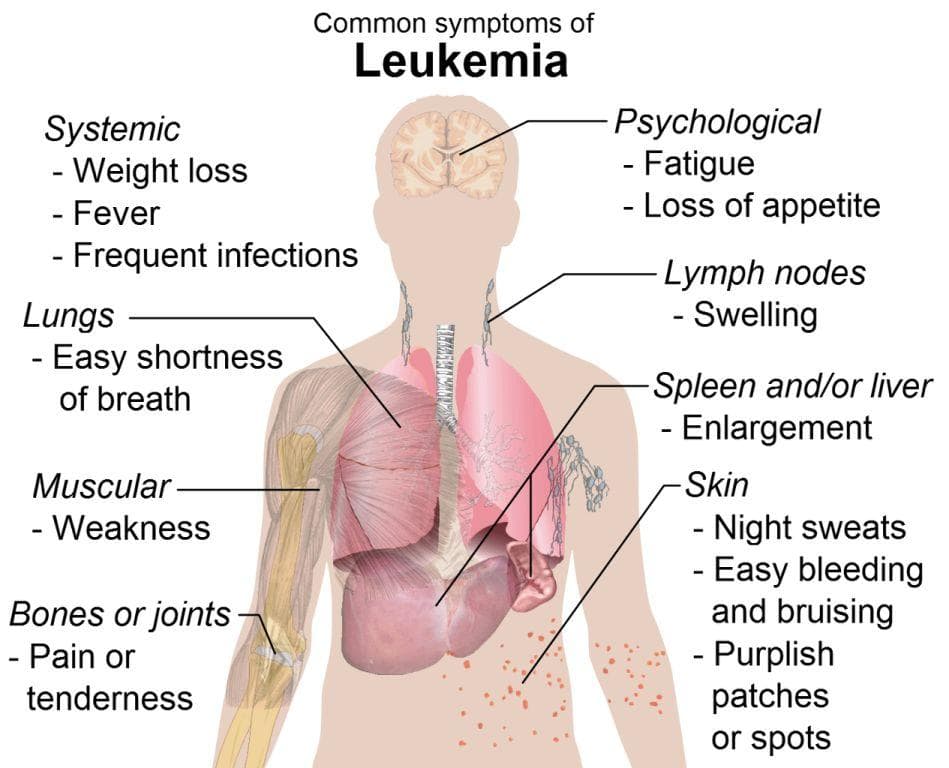
Common Symptoms of Leukemia
Initially, symptoms may be absent, but as the disease progresses, individuals might experience:
Excessive Bleeding and Bruising: Frequent nosebleeds, bleeding gums, blood in urine or stool, or easily bruised skin are common. Small red or purple spots called petechiae may also appear under the skin.
Anemia: Reduced red blood cells can cause fatigue, pallor, and decreased energy levels, due to less oxygen reaching tissues.
Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlargements in areas such as the neck, armpits, or groin happen because of abnormal lymphocyte accumulation.
Higher Susceptibility to Infections: Impaired immune defenses increase the risk of infections like sore throat, pneumonia, skin rashes, mouth sores, or fevers.
General Weakness and Unwellness: Symptoms include unintended weight loss, ongoing fatigue, discomfort in the upper abdomen, persistent fever, or night sweats.
Note: The information shared here is for educational use only. Always seek advice from licensed healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment. This content does not replace professional medical consultation.