Understanding Pulmonary Fibrosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This article provides a detailed overview of pulmonary fibrosis, covering its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. It highlights the impact of environmental toxins, lifestyle factors, and medical options like medication and transplantation. Ongoing research aims to improve prognosis for this challenging disease.
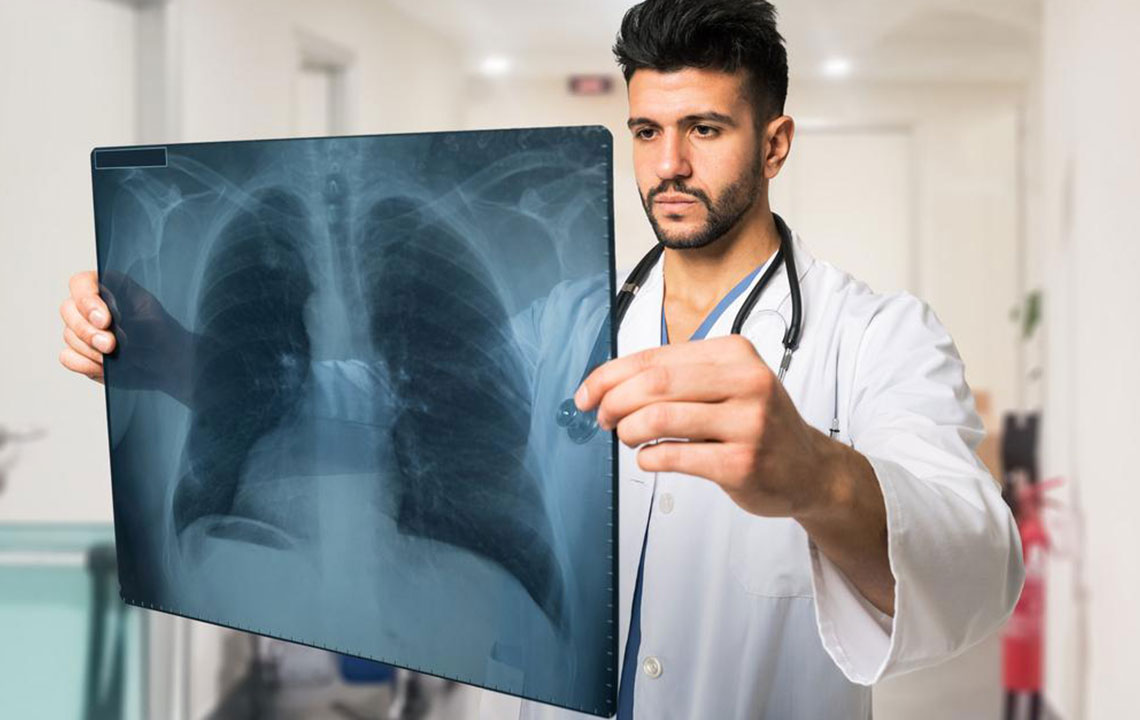
Pulmonary fibrosis is a long-term lung disorder involving the gradual buildup of scar tissue within the lungs, which hampers breathing ability. Its precise origin is often unknown, classified as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. External factors like inhaling asbestos, silica, coal dust, and heavy metals, as well as certain drugs and health conditions, increase risk. Lifestyle factors such as smoking and genetic predisposition also contribute. Common signs include ongoing shortness of breath, dry cough, fatigue, weight loss, and finger clubbing. Medications like pirfenidone and nintedanib help slow the decline, with lung transplants considered for advanced cases. Research continues to improve treatments, though the outlook remains difficult.
Pulmonary fibrosis
Chronic respiratory illness
Scar formation in lungs
Environmental hazards
Therapeutic options


