A Comprehensive Guide to Pulmonary Fibrosis: Key Insights and Management Strategies
Learn about pulmonary fibrosis, a serious lung disease characterized by scarring that impairs breathing. This article covers causes, symptoms, prevalence, and management strategies to improve patient outcomes. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to slow disease progression and maintain quality of life.

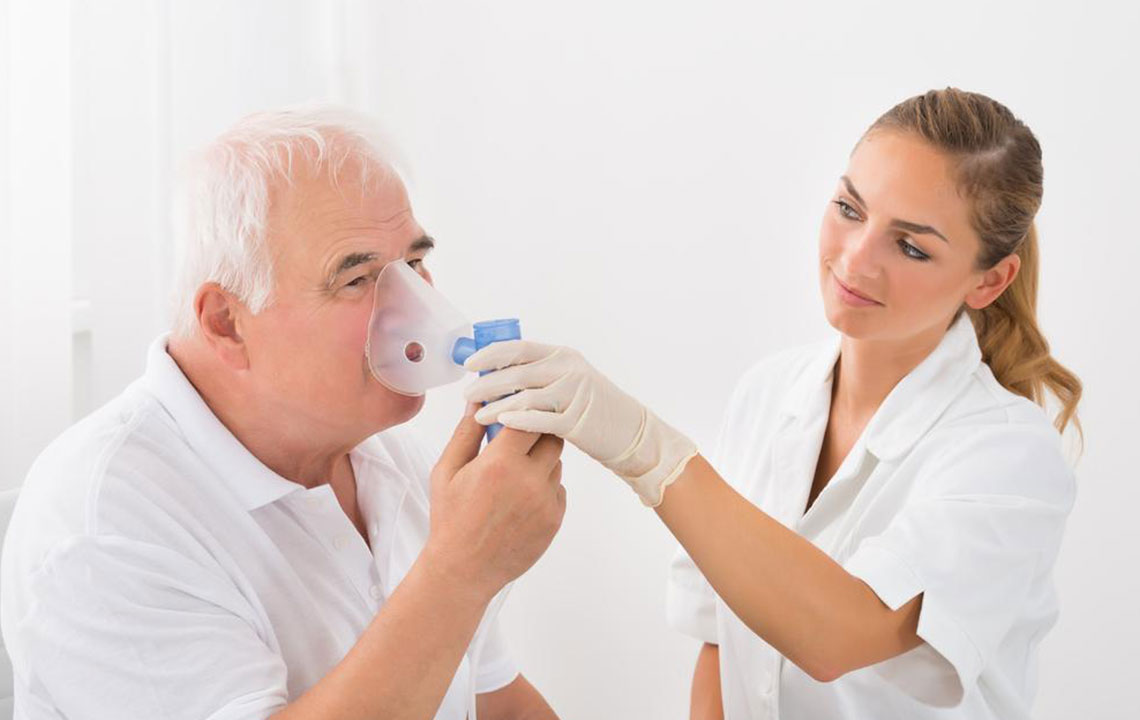
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious respiratory disorder marked by the formation of scar tissue within the lungs. The word "pulmonary" relates to the lungs, while "fibrosis" refers to tissue scarring. This condition causes the lungs' tiny air sacs to become thickened and rigid, impacting their ability to transfer oxygen effectively. Often progressing without obvious signs, pulmonary fibrosis can lead to breathing issues and exhaustion. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are vital for enhancing quality of life and slowing disease advancement. Here are essential facts to understand about this complex condition.
What is pulmonary fibrosis?
It involves the thickening and scarring of alveolar walls, decreasing lung flexibility. This makes lung expansion during breathing difficult, causing shortness of breath and fatigue, and requiring more energy for respiration.
Causes of pulmonary fibrosis
Includes exposure to hazardous materials such as silica, asbestos, and coal dust, along with certain medications and autoimmune conditions. Some cases are idiopathic, where the cause remains unknown. Genetic factors may also contribute.
Signs and symptoms
Common symptoms feature a persistent dry cough, breathlessness, tiredness, and reduced physical stamina. Symptoms may develop gradually over years or escalate quickly, making prompt medical evaluation essential for effective management.
Prevalence
Pulmonary fibrosis impacts approximately 50,000 people each year, mainly those over 50 and more often men. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis accounts for a significant share, with about 132,000 individuals affected across the country.
Available treatments
While no cure exists for reversing lung scarring, therapies focus on symptom relief and enhancing life quality. Ongoing clinical trials seek new options. Regular healthcare consultations are crucial for monitoring and adapting treatment plans. Early intervention can slow progression and help preserve lung function.
Report any worsening signs promptly and stay informed about emerging treatments. With appropriate care and lifestyle changes, patients can better maintain their health and independence despite this challenging condition.