Osteoporosis Explained: Causes, Risks, and Preventive Strategies
This article provides an overview of osteoporosis, highlighting its causes, risks, and prevention methods. It emphasizes the global prevalence, health impacts, and strategies to manage the condition effectively. Learn about ways to protect bone health and reduce fracture risks through lifestyle and medical interventions.
Osteoporosis Explained: Causes, Risks, and Preventive Strategies
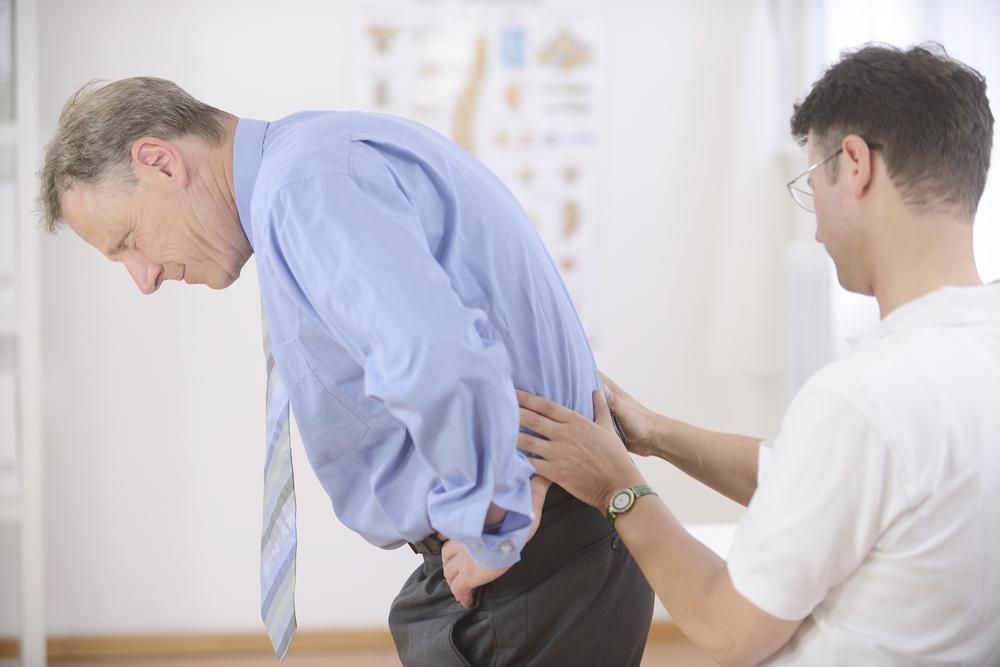
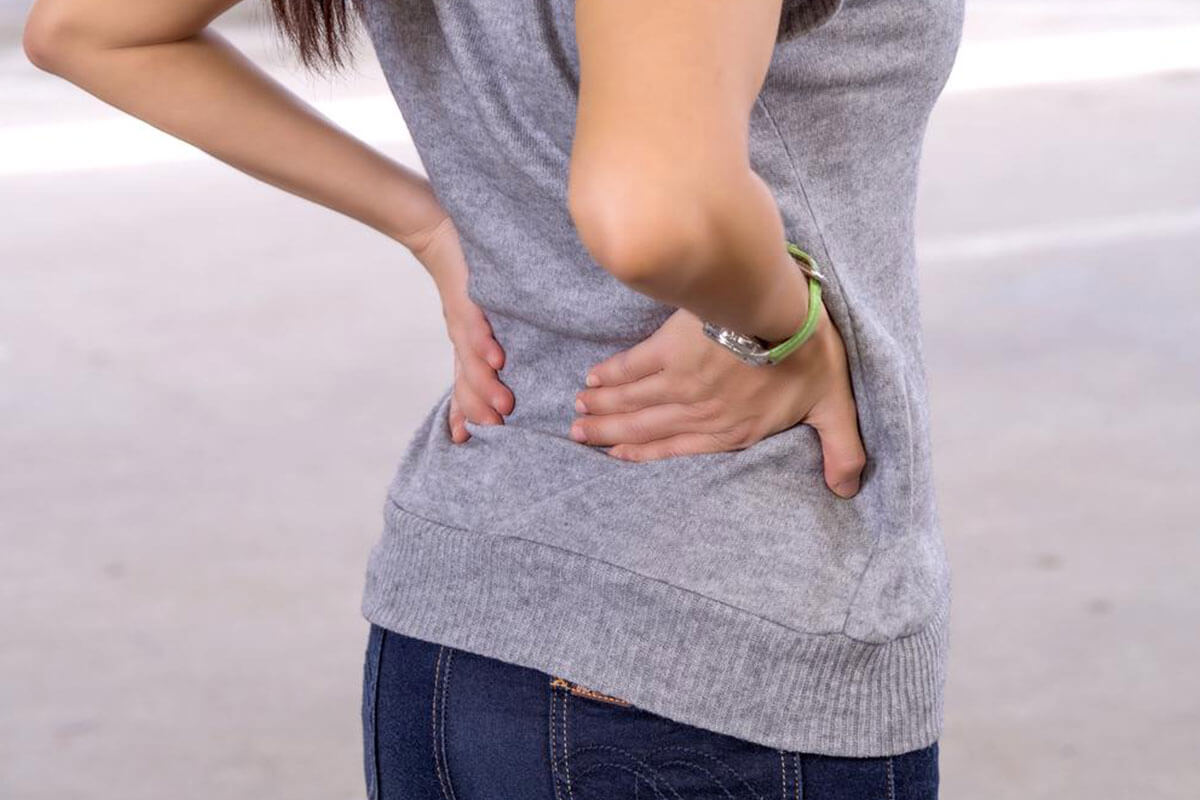
Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become brittle and porous, increasing the likelihood of fractures. The term translates to "porous bones," resulting from factors like lifestyle choices, diet, and genetic predispositions related to age, sex, and ethnicity.
Bone tissue is continuously renewed, but aging and other factors slow this process, causing bones to weaken and become more susceptible to injury.
In advanced stages, routine movements such as bending or coughing can lead to fractures, with hip fractures being among the most serious.
Global and National Impact
Over 200 million people worldwide are affected by osteoporosis, surpassing the prevalence of heart disease, strokes, and cancers.
In the United States, approximately 44 million individuals suffer from low bone mass or osteoporosis. Nearly half of women and about 7.5% of men over age 50 are affected.
The National Institutes of Health considers osteoporosis a critical public health issue.
Each year, around 1.5 million fractures occur due to osteoporosis, mainly impacting women over 50 and men over 60. This disease often results in lasting disability and increased mortality, especially following major fractures such as hips. Many patients struggle to regain full mobility, and about 20% die within a year after breaking a bone. However, with proper treatment, fall prevention, a balanced diet, and gentle exercises, individuals with osteoporosis can maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from qualified healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment options.