Key Strategies for Effective Diabetes Management
This article highlights essential methods for managing diabetes effectively. It covers symptoms, causes, and risk factors, emphasizing early detection and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding these key aspects can help individuals control their condition and prevent complications.
Key Strategies for Effective Diabetes Management
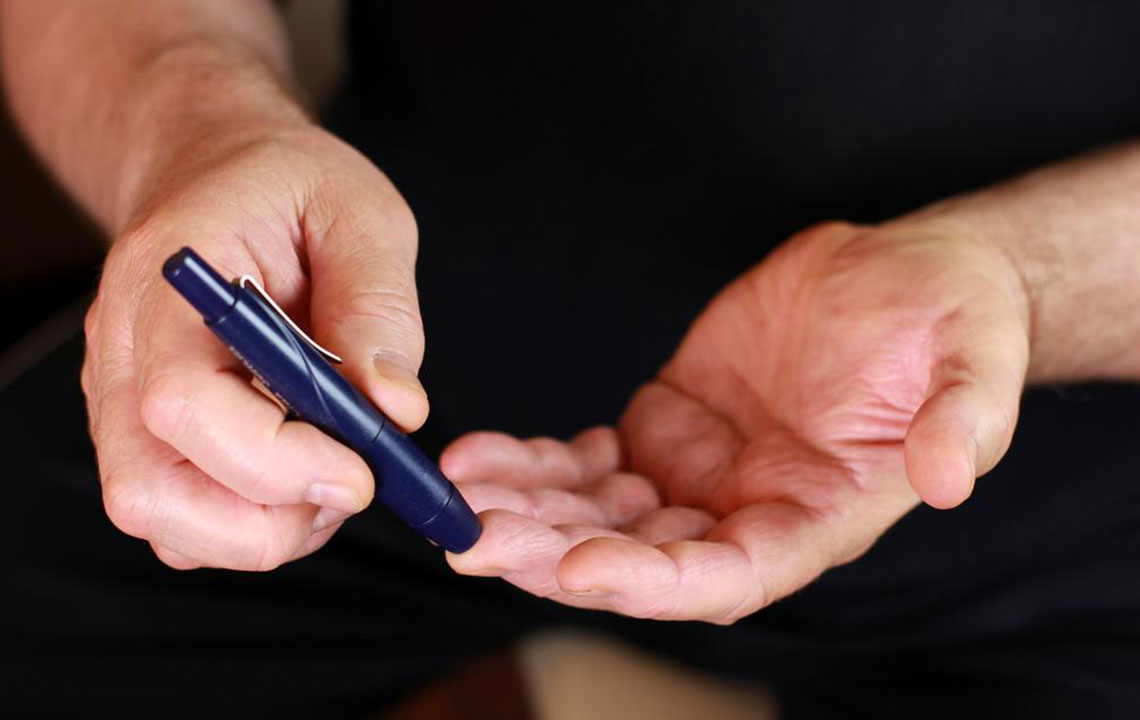
Diabetes is a condition where blood glucose levels are abnormally high, resulting from issues with insulin production or utilization. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps cells absorb glucose for energy. When the body cannot produce enough insulin or use it efficiently, glucose accumulates in the blood, leading to potential health problems.
While there is no cure for diabetes, recognizing symptoms and understanding risk factors are essential for control. Early detection enables better management and reduces complications.
Monitoring early symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and recurring infections helps in timely diagnosis. Different types of diabetes have distinct causes; type 1 involves immune destruction of insulin-producing cells, while type 2 results from insulin resistance and decreased production. Risk factors include genetics, lifestyle choices, obesity, age, and high blood pressure, all important for prevention and ongoing management.
Being aware of these factors allows individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles and seek medical guidance, improving quality of life with diabetes.


