Guide to Monitoring and Controlling Your Blood Sugar for Better Health
Learn how to effectively monitor and manage blood sugar levels to enhance overall health. This guide covers essential facts, normal ranges, and practical tips for stable blood glucose, emphasizing lifestyle choices and regular testing for prevention and control.
Guide to Monitoring and Controlling Your Blood Sugar for Better Health
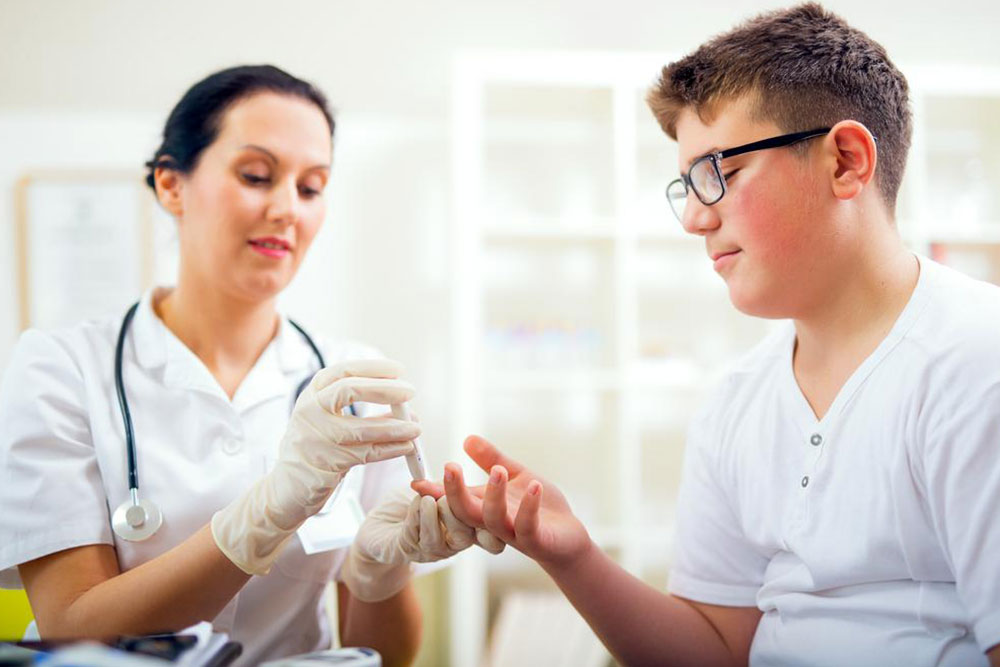
Blood glucose, commonly called blood sugar, supplies the energy necessary for bodily functions. Measuring the glucose circulating in your blood is essential for understanding your health status.
Insulin moves glucose from your digestive system into cells to generate energy. Typically, blood sugar levels are lowest in the early morning before meals and increase after eating. Consistent abnormal levels can pose health risks. Regular blood sugar checks are vital for maintaining wellness.
The common unit for blood sugar measurement is mmol/L.
Blood Sugar Variations
Abnormal blood sugar levels are classified as:
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): Excessively high blood glucose can cause complications like heart problems.
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Too low blood sugar may lead to dizziness, weakness, or insulin shocks. Maintaining balanced levels is crucial for health.
Multiple elements influence blood sugar levels.
For those without diabetes, fasting blood sugar typically ranges from 3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L (70-100 mg/dL). Normal levels average around 5.5 mmol/L, but can vary throughout the day. Non-fasting levels should stay below 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL). Diabetics should aim for pre-meal values between 5.0 and 7.2 mmol/L (90-130 mg/dL), with post-meal levels under 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL).
Managing blood sugar involves maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, staying hydrated, and following medical advice. Consuming vegetables like kale and spinach, legumes, nuts, green tea, and fiber-rich foods can help regulate blood glucose. Routine checkups and blood tests are essential for diabetics to keep blood sugar within a safe range.