Comprehensive Approach to Alleviating Fibromyalgia Symptoms
This article offers a detailed overview of fibromyalgia, encompassing symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Emphasizing early recognition and comprehensive management, it guides patients and healthcare providers towards effective symptom control and improved well-being.

Comprehensive Approach to Alleviating Fibromyalgia Symptoms
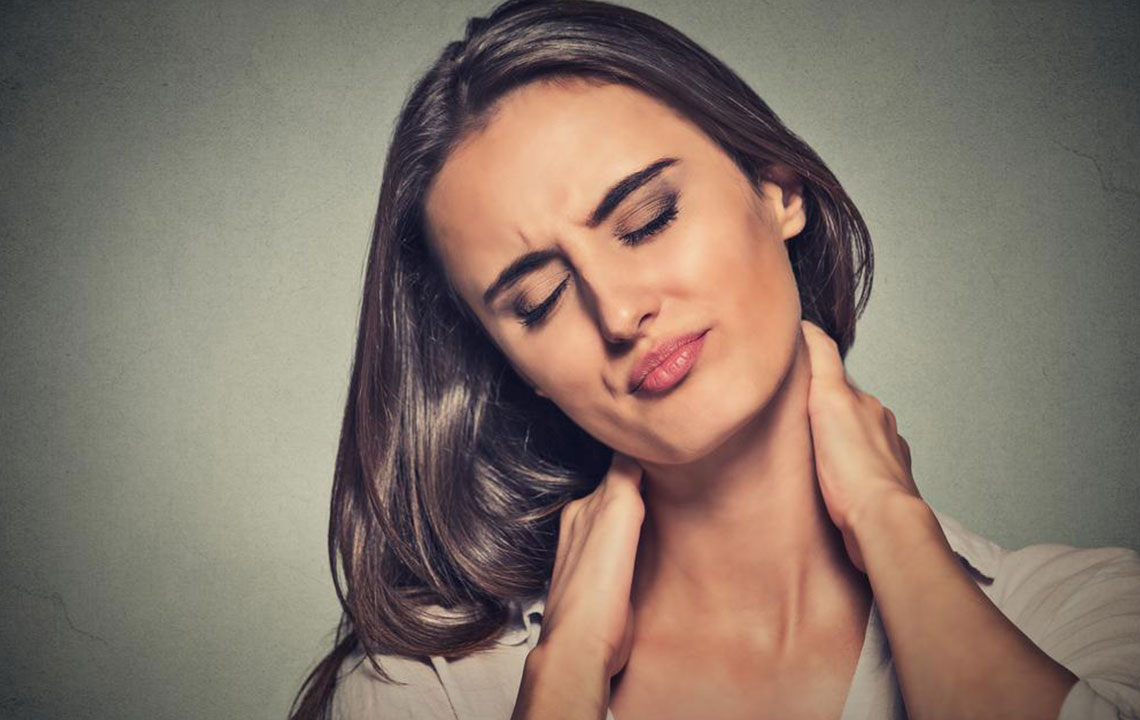
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition that currently lacks a definitive cure, but with proper management, its symptoms can be effectively minimized. It primarily impacts muscles and bones, leading to persistent discomfort.
This disorder manifests through widespread muscle and joint pain, fatigue, sleep issues, mood swings, and memory challenges. The brain's role in heightening pain perception contributes significantly, making symptoms more intense.
Symptoms can arise abruptly after physical or emotional stress, surgeries, or infections, or they may develop gradually without clear signs. Recognizing early symptoms is crucial for timely intervention, as many patients remain unaware of their worsening condition.
Women are more frequently affected by fibromyalgia than men. Associated issues include tension headaches, depression, anxiety, digestive troubles, TMJ syndrome, and increased sensitivity to stimuli like noise and bright lights.
Common Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
Key signs include:
Persistent muscle tightness and pain in muscles and joints
Muscle spasms and cramps
Unexplained fatigue varying from mild to severe
Sleep disruptions, including insomnia
Stiffness when changing positions or walking
Memory lapses, mood swings, difficulty focusing
Digestive problems such as nausea, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation
Headaches and migraines
Tender areas in the jaw and face
Sensitivity to foods, light, sounds, medications, and fragrances
Depression and mental health issues
Burning or tingling sensations in limbs and face
Frequent urination and urgency
Pain limits exercise capacity
Feelings of swelling without visible swelling
Causes of Fibromyalgia
Factors contributing to fibromyalgia include:
Physical or emotional trauma
Infections or illnesses weakening the body
Genetic factors
Diagnosis Techniques
As there is no specific test, doctors rely on physical examinations for tender points and blood tests like CBC, rheumatoid factors, TSH, and sedimentation rate to exclude other conditions.
Management Strategies
Treatment involves medications such as pain relievers, antidepressants, and anti-seizure drugs. Mental health support through counseling, along with physical activities like yoga or physiotherapy, can significantly improve quality of life. Early detection, especially among women aged 18-40, is key for effective management.