Key Factors and Risks Associated with Fibromyalgia Development
Fibromyalgia is a widespread chronic condition causing pain and fatigue, mainly affecting women aged 20-50. Key risk factors include hormonal imbalances, genetics, and sleep issues. Early recognition and professional care are vital for managing symptoms effectively.

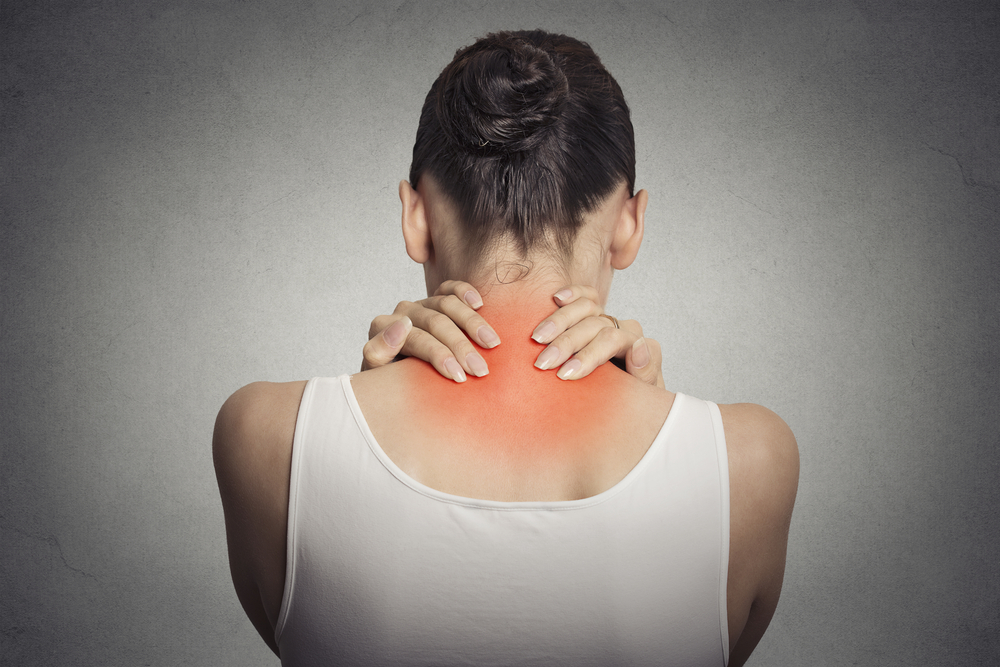
Fibromyalgia is a long-term disorder marked by widespread pain, ongoing fatigue, and other related symptoms. Individuals with fibromyalgia often exhibit heightened pain sensitivity compared to those without the condition. It is a prevalent disorder, affecting approximately 10 million people in the United States, as reported by the National Fibromyalgia Association.
The precise causes of fibromyalgia are not fully understood, but multiple contributing factors are recognized. These include irregular pain signaling, hormonal issues, genetic predispositions, specific trigger events, and problems with sleep. Women, especially between ages 20 and 50, and those with a family history or associated rheumatic diseases, face higher risks. While not life-threatening, awareness and proper management are essential to reduce symptom impact.
Knowing these risk factors can facilitate early diagnosis and tailored treatment. Seeking medical advice is crucial for effective symptom control and quality of life improvement.