Signs, Causes, and Early Detection of Melanoma
This article discusses melanoma, a serious skin cancer, highlighting its causes, early signs, and importance of timely detection. It emphasizes risk factors like UV exposure, genetics, and tanning bed use, and explains warning symptoms such as irregular moles and persistent sores. Early recognition and professional medical advice are crucial for effective treatment.
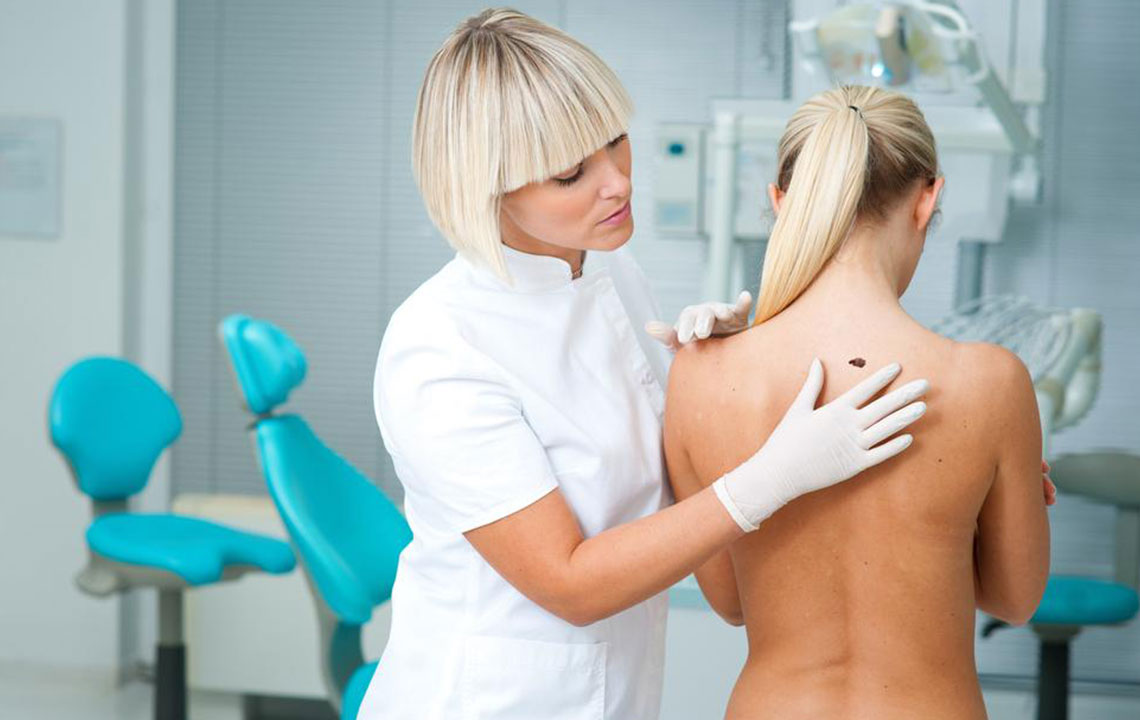
Signs, Causes, and Early Detection of Melanoma
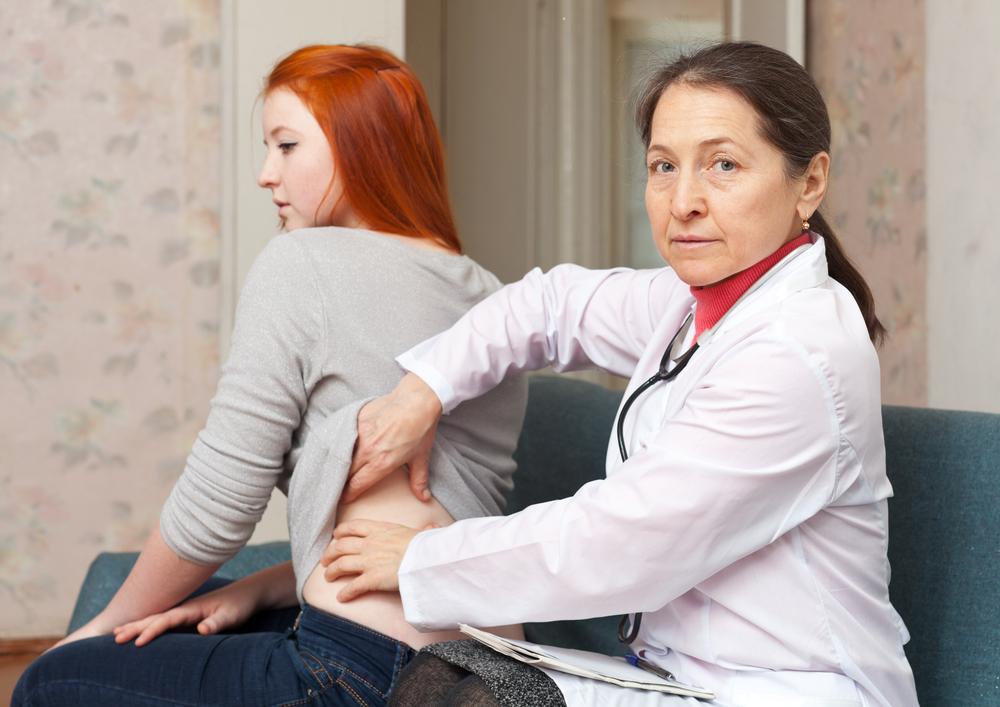
Melanoma is an aggressive skin cancer marked by atypical pigment growth originating from moles or directly on the skin. It can develop anywhere on the body, including the eyes. The cancer results from DNA damage in skin cells, leading to uncontrolled multiplication. Recognizing risk factors and early warning signs is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Major risk factors include exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight, genetic predisposition, and use of tanning beds. UV radiation harms skin and DNA, increasing melanoma chances. A family history heightens vulnerability, though preventative measures can mitigate risks. Tanning bed usage notably raises melanoma risk, particularly among youth.
Early indicators include irregular moles with asymmetric borders, inconsistent coloring, or progressive shape changes. These may grow, bleed, or spread pigment. Non-healing sores or scaly skin patches also signal potential issues. Prompt medical evaluation is essential if these symptoms appear.
Note: This content is intended for informational purposes only. Always consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment options. Relying solely on online resources is not advisable for health decisions.