Causes and Diagnosis of Persistent Itching: What You Need to Know
Persistent itching can be caused by skin conditions, infections, internal health issues, or psychological factors. Proper diagnosis involves medical evaluation and lab tests. If you experience ongoing itching, consulting a healthcare professional is vital to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. This article explores common causes, symptoms, and diagnostic methods to help manage itchy skin effectively.
Causes and Diagnosis of Persistent Itching: What You Need to Know
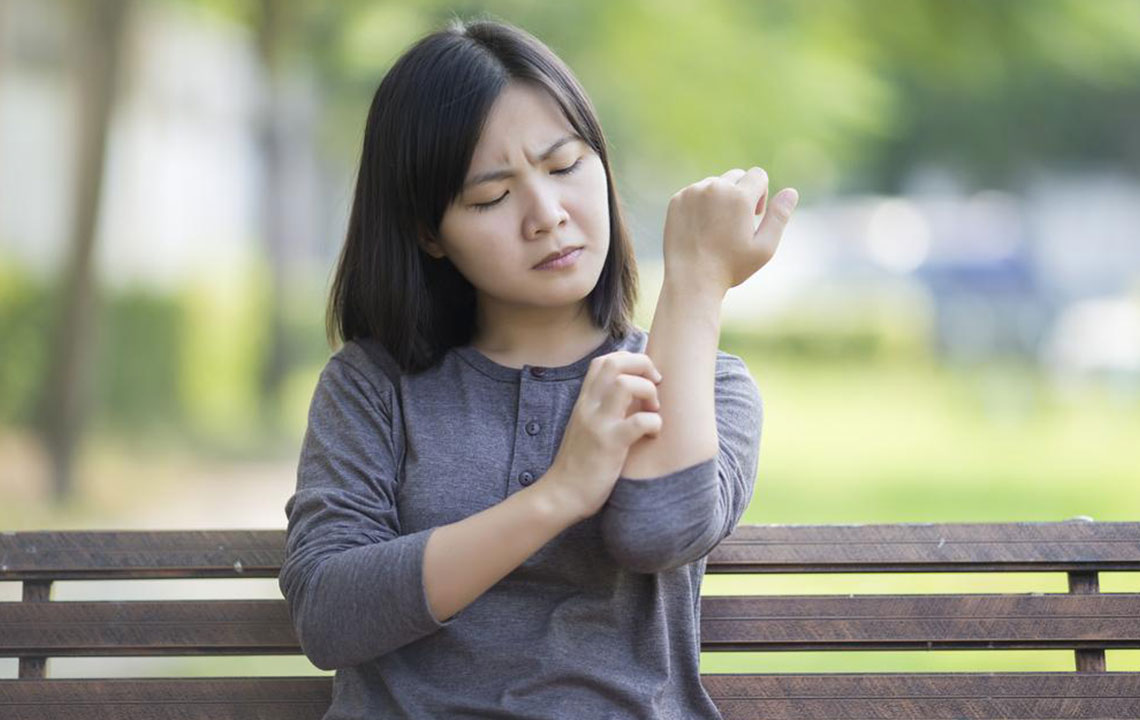
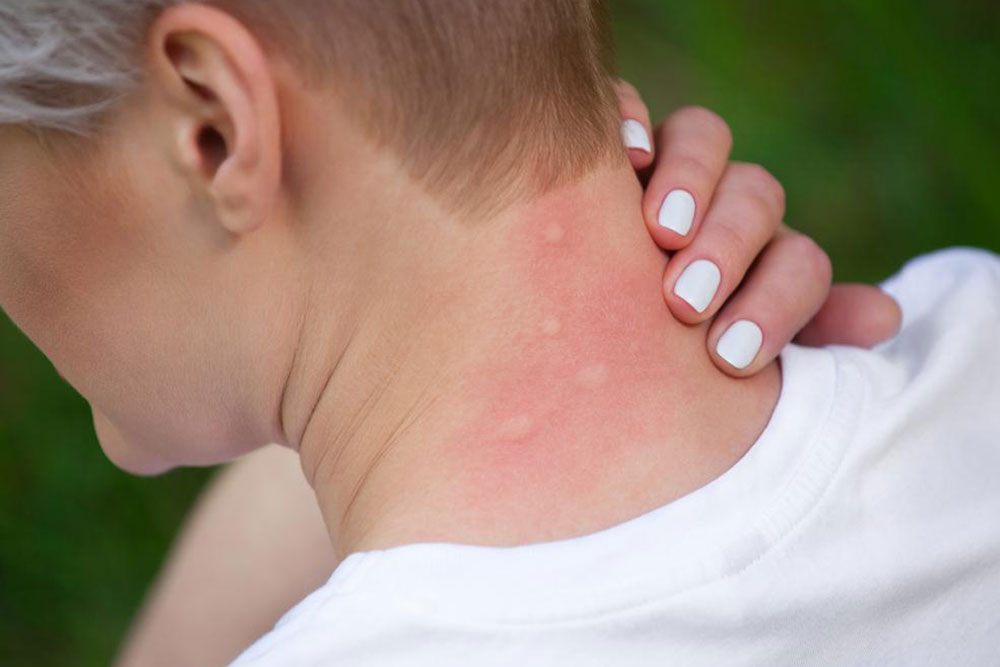
Chronic itching can be incredibly uncomfortable, often accompanied by redness and skin rashes. Scratching can aggravate the problem, creating a cycle of worsening symptoms. Medically called Pruritus, itchy skin can arise from minor allergies or more serious health issues like kidney dysfunction. If you experience prolonged itching, seeking medical advice is essential. While usually harmless, persistent itchiness may signal an underlying condition that needs prompt attention. Here are common causes and methods doctors use to diagnose itchy skin.
Skin conditions
Dermatitis leads to redness, swelling, and warmth.
Eczema causes persistent itching and rashes.
Dermatographism appears as raised, itchy lines on the skin.
Infections causing itching
Conditions such as chickenpox, lice, fungal infections, mites, scabies, pinworms, and exposure to irritants can trigger itching. Contact with irritants may also cause skin inflammation.
Health problems inside the body
Diseases like liver issues, anemia, diabetes, hypothyroidism, HIV, leukemia, lymphoma, kidney failure, and pregnancy may result in itchy skin.
Itching is common during pregnancy, affecting around 10% of women.
Psychological factors
Mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, psychosis, and trichotillomania can lead to compulsive scratching.
Diagnosis of itchy skin
Identifying the cause typically involves a doctor evaluating symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. Standard diagnostic procedures include:
Blood tests: Detect infections and internal health issues.
Thyroid tests: Check for thyroid imbalances that may cause itching.
Skin allergy testing: Identify allergies or infections responsible for skin irritation.


