Essential Strategies for Relieving Heartburn and Acid Reflux
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies for managing heartburn and acid reflux, emphasizing lifestyle changes, symptom recognition, and when to seek medical help. Tips include dietary modifications, weight management, and proper hydration to alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.

Essential Strategies for Relieving Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Heartburn, or acid reflux, happens when stomach acid irritates the esophagus. Chronic cases, known as GERD, impact many individuals. Over 60 million Americans encounter heartburn regularly, with 15 million experiencing daily symptoms. Typical signs include a burning chest sensation, sour taste, swallowing difficulties, or breathing issues. While occasional discomfort is common, persistent symptoms may indicate serious health conditions requiring medical care.
Minor cases of heartburn often improve with lifestyle modifications and over-the-counter remedies. However, ongoing or worsening symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Recognizing symptoms like chest pain, sore throat, regurgitation, bloating, or persistent cough is essential for timely treatment.
Common symptoms include:
A burning feeling in the chest, especially after eating
Intense chest pain when bending or lying down
Throat irritation or bitter taste in the mouth
Frequent stomach cramps
Dry mouth and gum discomfort
Tooth erosion and bleeding
Changes in voice, persistent cough, or wheezing
Nausea after meals with increased saliva
Bloating, gas, and acid reflux into the throat
This often results in a bitter or salty taste. Repeated acid exposure can damage tissues, cause esophageal narrowing, and impair swallowing. Early management is key to preventing complications.
Factors that trigger heartburn
Diet, lifestyle, and health conditions can influence its occurrence. Recognizing these helps in preventing symptoms.
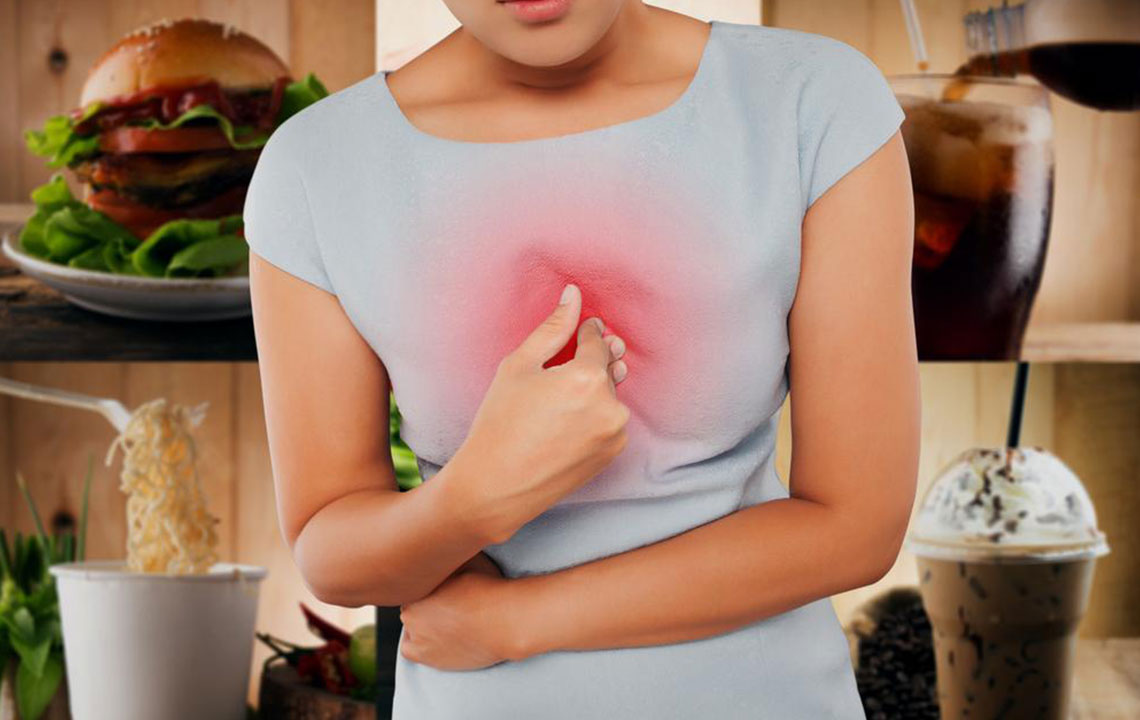
Dietary triggers include:
Overeating and large portions
Foods high in salt and sugar, processed snacks
Spicy dishes, onions, garlic, chocolate, citrus, and tomato-based foods
Alcohol, caffeine, and carbonated drinks
Eating before bedtime
Frequent use of certain medications
Lifestyle factors that influence heartburn:
Being overweight or obese
Smoking habits
Tight clothing or belts
Stress and anxiety
Physical inactivity
Medical conditions associated with heartburn include:
Prenancy
Hiatal hernia
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Use of anti-inflammatory drugs
Managing persistent symptoms early by avoiding triggers, improving sleep posture, and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce discomfort. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and staying well-hydrated are also beneficial.Note:
This platform provides health information but does not replace professional medical advice. If symptoms are severe or ongoing, consult a healthcare provider. Staying informed helps detect and treat heartburn effectively. Seek personalized medical guidance for persistent issues.