Comprehensive Overview of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment Strategies
This article provides an in-depth look at non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), highlighting its subtypes, symptoms, and treatment options. Emphasizing early detection and specialized therapies, it aims to inform patients and caregivers about effective management strategies for better prognosis.
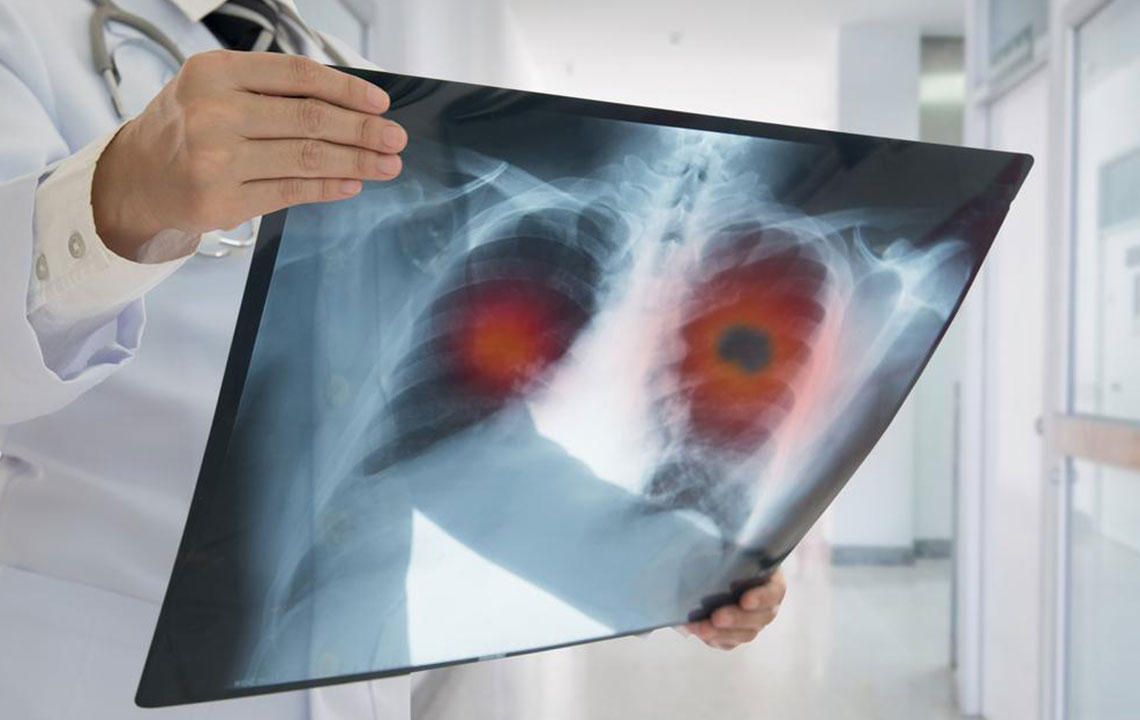
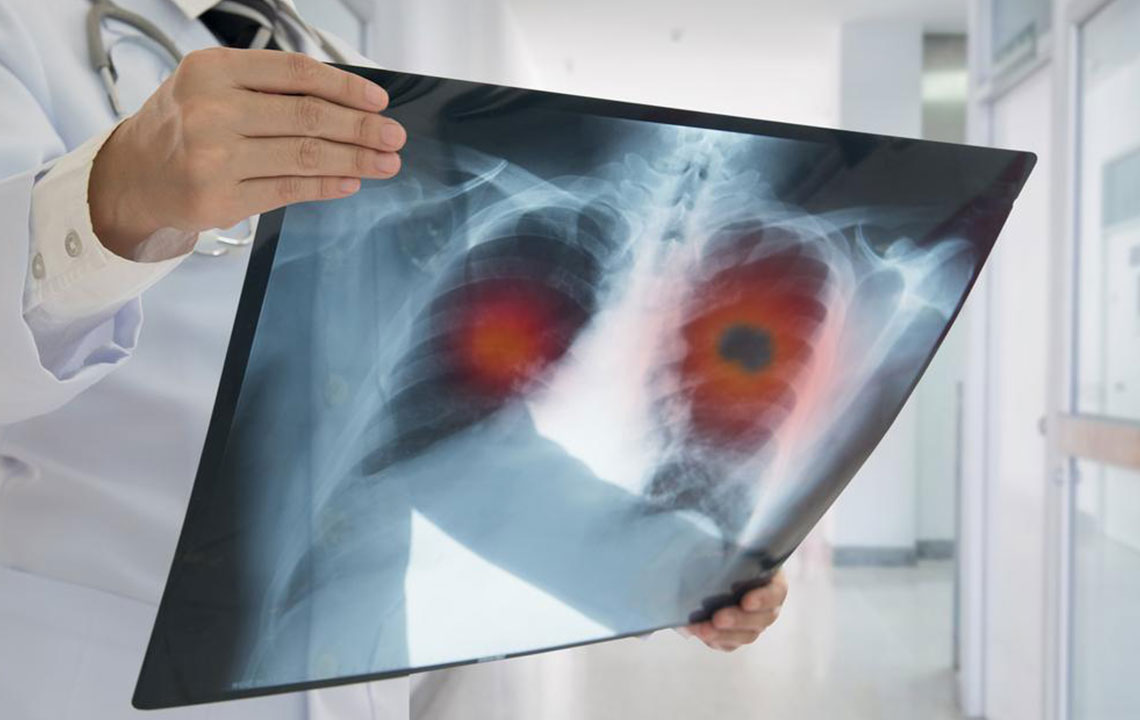
Lung cancer arises from abnormal cell growth within lung tissues, forming tumors that can metastasize. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the most prevalent form, encompasses subtypes including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma, frequently seen in smokers but also in non-smokers, makes up the majority of cases. Squamous cell carcinoma tends to develop in central lung regions and is linked to smoking habits. Large cell carcinoma is characterized by rapid growth and can appear anywhere in the lung. Early detection plays a vital role, with treatments like targeted therapy offering improved prognosis. Recognizing symptoms such as persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, neurological problems, and fatigue is essential for early diagnosis. Support services and medical consultation can significantly enhance treatment outcomes for patients and their families.