Effective Strategies for Managing Thrombocytopenia
This article discusses comprehensive methods to manage thrombocytopenia, a condition marked by low platelet levels in the blood. It covers causes such as infections, medications, autoimmune diseases, and lifestyle factors. Treatment options include addressing underlying causes, platelet transfusions, splenectomy, and medication. Lifestyle modifications, like avoiding injury and maintaining a nutritious diet, are also emphasized. Proper management is crucial for preventing severe bleeding and improving overall well-being.

Approaches to Treating Low Blood Platelet Counts
Thrombocytopenia, characterized by abnormally low platelet numbers, is a condition where platelet levels fall below the normal range. Blood platelets are essential for clot formation and tissue healing, with standard levels between 150,000 and 450,000 per microliter of blood. When counts drop below 150,000, bleeding risk increases, and extremely low counts (<5,000) may lead to severe bleeding requiring immediate care. Treatment varies based on cause and severity.
The lifespan of platelets averages 8-9 days, with production occurring in the bone marrow. Disruptions in production or over-destruction cause thrombocytopenia. Causes include:
Enlarged spleen: Excess activity in the spleen sequesters platelets, lowering circulating levels.
Infections: Viral illnesses such as hepatitis, HIV, or bacterial infections like malaria can induce temporary or persistent platelet decline.
Medications: Certain drugs, including antibiotics and pain relievers, may suppress platelet production.
Alcohol: Heavy alcohol consumption inhibits platelet synthesis, resulting in mild to moderate thrombocytopenia.
Pregnancy: Gestational thrombocytopenia affects some pregnant women but typically resolves after childbirth.
Underlying health issues: Conditions such as leukemia or lymphoma impair bone marrow function, and chemotherapy can also reduce platelet levels.
Autoimmune conditions: Diseases like immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) involve immune system attack on platelets, decreasing their count.
Handling Low Platelet Counts
The treatment plan depends on symptoms and severity. Mild cases without symptoms may require no intervention, while severe thrombocytopenia needs targeted treatment.
Medical interventions include:
Addressing root causes: For example, stopping medications like blood thinners if they are responsible.
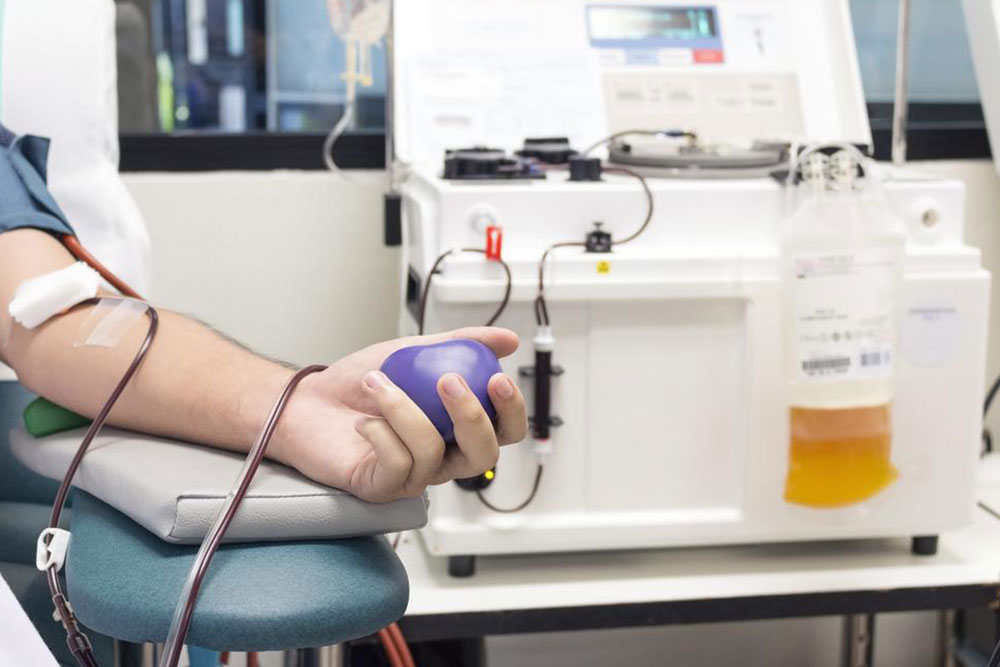
Platelet transfusions: Used in cases of heavy bleeding or extremely low levels.
Surgical options: Removing the spleen (splenectomy) can help restore platelet counts, often resulting in improvement.
Medications: Drugs that enhance platelet production are prescribed for autoimmune-related cases.
Healthy Lifestyle Tips
Avoid activities that increase injury risk
Limit alcohol intake
Use caution with over-the-counter medications
Consume foods rich in vitamin B12 and maintain a balanced diet
Avoid exposure to toxic chemicals
Combining proper medical treatment with healthy habits and lifestyle changes can effectively manage low platelet counts and promote better health.