Comprehending Thrombocytopenia: Causes, Management, and Dietary Support
This article explores the causes of low platelet levels, treatment options such as medication adjustments and transfusions, and the role of diet in supporting immune health. It emphasizes personalized healthcare and dietary strategies to manage thrombocytopenia effectively.
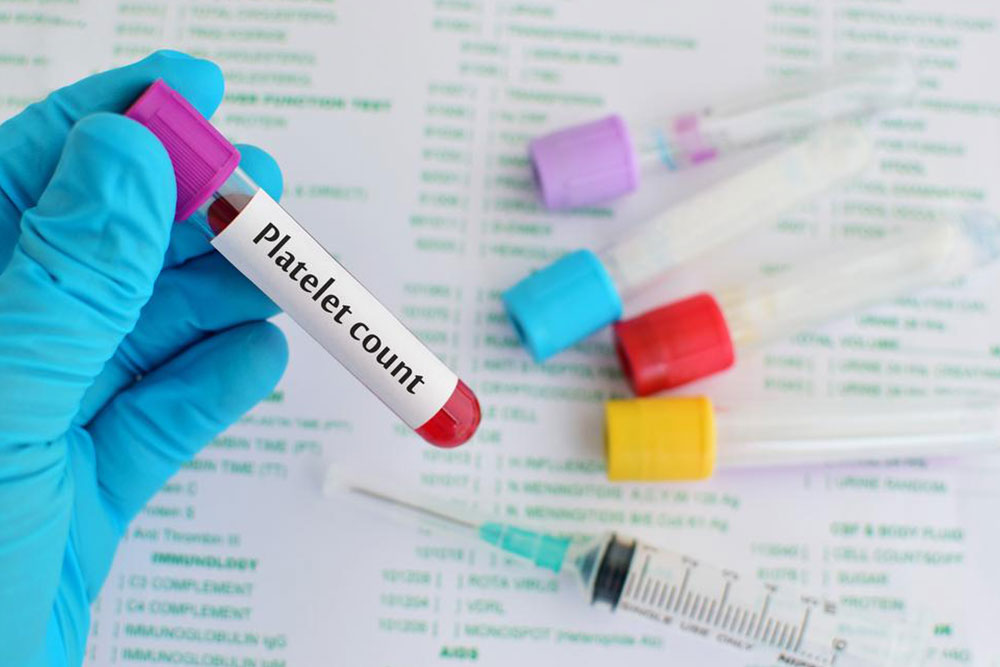
Thrombocytopenia, characterized by low platelet counts, varies in severity and necessitates personalized treatment strategies based on its root cause. The main aim is to avert significant bleeding and related health issues.
Light cases often require no specific treatment. Nevertheless, even with normal platelet levels, serious injuries can result in substantial bleeding, especially following accidents.
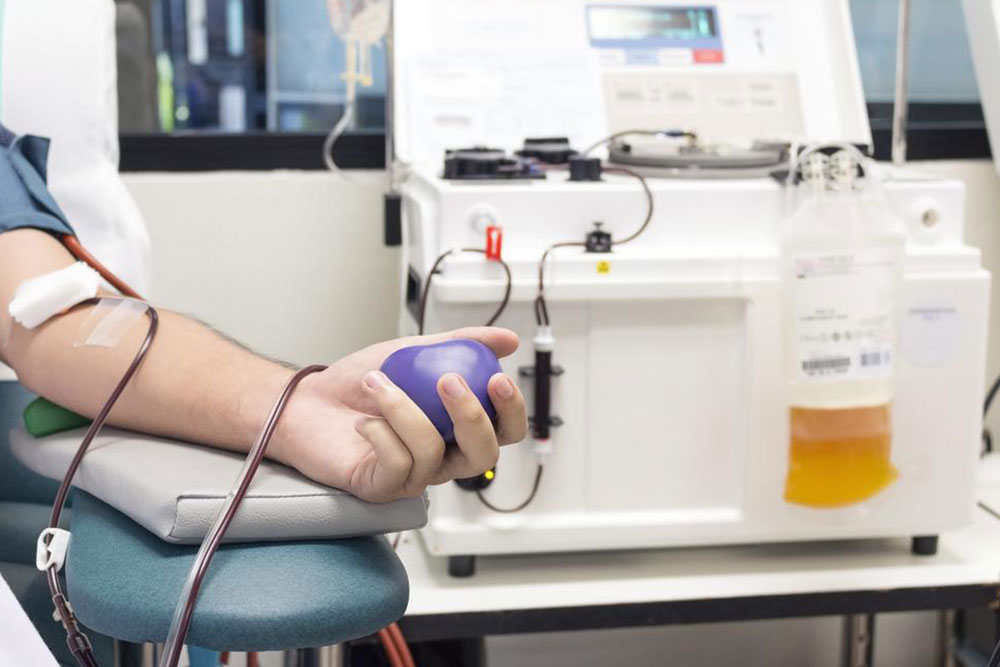
Understanding and targeting the cause—such as medication effects or underlying health conditions—can help resolve thrombocytopenia. Changing blood-thinning drugs like anticoagulants might be beneficial. Treatment approaches include immune-modulating therapies in autoimmune cases, blood or platelet transfusions in severe situations, and surgical procedures like splenectomy when necessary, especially in immune thrombocytopenia.
Alongside standard therapies, adopting dietary habits such as eating antioxidant-rich fruits like berries, tomatoes, and plums, or incorporating omega-3 sources like fish and flaxseed, can bolster immune function and enhance platelet production.
Always consult healthcare professionals for tailored diagnoses and treatment plans. This overview is educational and not a substitute for medical advice.