Rapid Relief Methods for Frozen Shoulder Pain
Discover effective and quick strategies to alleviate frozen shoulder pain and regain shoulder mobility. From targeted physical therapy exercises to minimally invasive procedures, learn how to manage and accelerate recovery. Lifestyle adjustments and medication options are also discussed for comprehensive care. Always seek professional medical advice for personalized treatment plans.

Rapid Relief Methods for Frozen Shoulder Pain
Frozen shoulder, medically known as adhesive capsulitis, causes stiffness and pain that restrict movement in the shoulder. It can develop due to injuries, repetitive strain, diabetes, or neurological events like stroke. More common among adults aged 40 to 70, especially women, it often resolves on its own within 12–15 months. However, targeted treatments can speed up recovery, focusing on pain management and restoring shoulder flexibility through physical therapy, medication, or minimally invasive procedures.
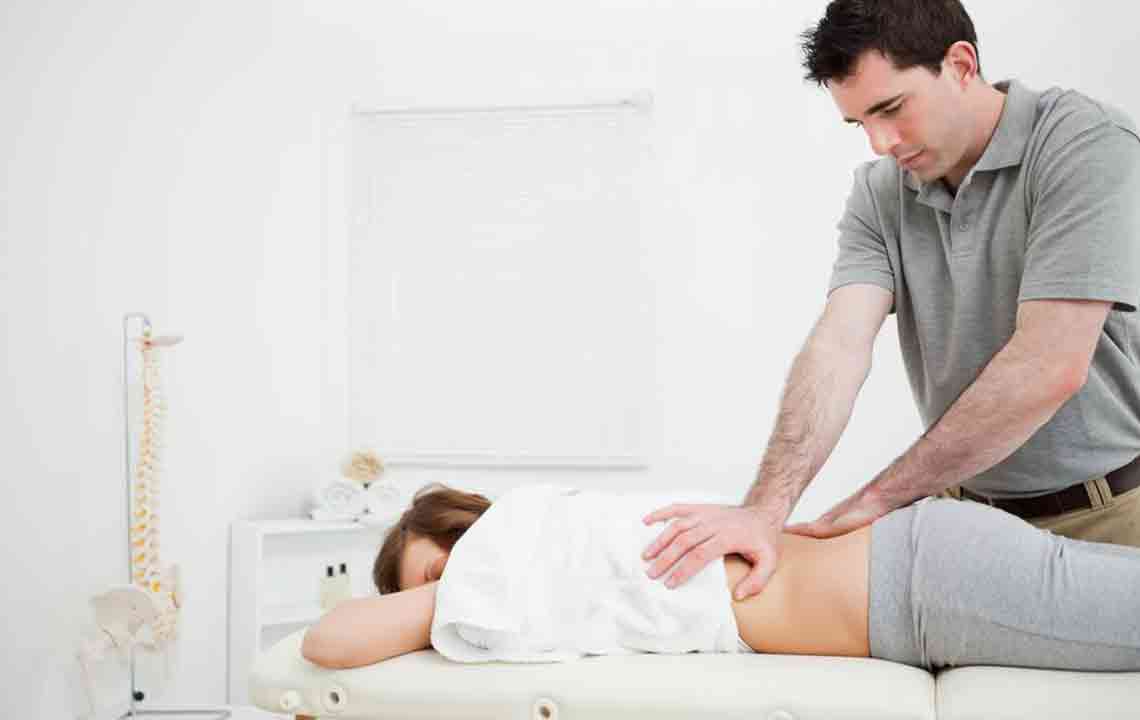
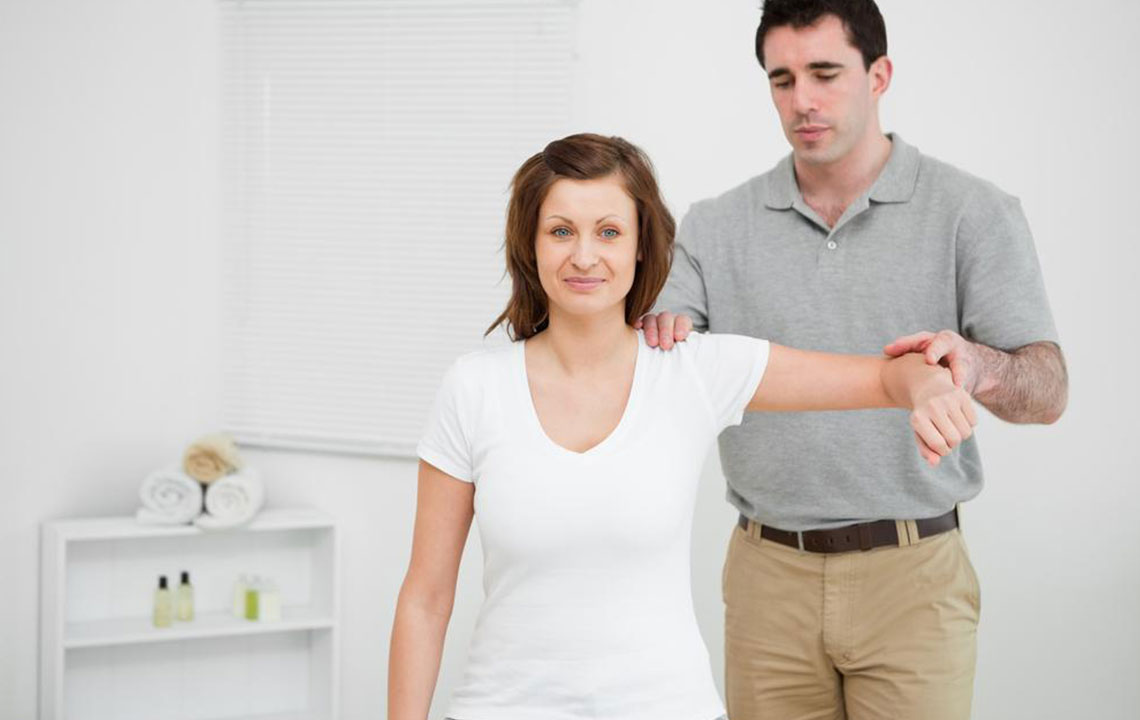
Physical Therapy: Includes stretching, strengthening routines, massage, and heat or cold therapies supervised by healthcare professionals.
Stretching Exercises: Use heat packs before stretching to warm muscles. Common moves include:
Pendulum Swings: Bend over a table, arm hanging freely, circle clockwise and counterclockwise 10 times, increasing size gradually as pain lessens.
Wall Finger Walks: Stand facing a wall, fingertips on the surface, walk fingers upward or sideways to stretch shoulder muscles. Repeat 10–20 times.
Cross-Body Stretch: Pull the affected arm across your chest with the opposite hand, hold for 15-30 seconds, then switch arms.
Strength Training: Once more flexible, add resistance exercises using elastic bands—stretch outward and inward 10 times per session.
Medications and Therapies: Use cold and heat packs alternately for pain relief, about 20 minutes each, following safety guidelines. NSAIDs like ibuprofen help reduce inflammation, while paracetamol alleviates discomfort.
Corticosteroid Shots: Injectable steroids, administered with imaging guidance, can temporarily decrease inflammation for ongoing pain. Use sparingly to avoid side effects.
Surgical Options: Arthroscopic capsular release involves minimally invasive removal of scar tissue around the joint, often reserved for severe cases. Surgery is rarely needed but beneficial for intense pain.
Hydrotherapy Techniques: Injecting a mix of steroids, saline, and anesthetic into the shoulder joint under local anesthesia offers quick, short-term pain relief lasting several months.
Lifestyle Changes: Can help prevent or worsen frozen shoulder:
Regular Movement: Daily shoulder stretches and rotations, especially if your activity is mostly sedentary.
Better Posture: Maintain upright posture with shoulders back when sitting, avoiding slouching.
Manage Related Conditions: Control diabetes, thyroid issues, and other health problems through proper diet and medication to lower the risk of shoulder stiffness.
Note: This article offers helpful information but does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized treatment options. We are not responsible for any discrepancies or unmentioned treatments.