Persistent Cough: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies
A persistent cough lasting over weeks can impact health and daily life. Accurate diagnosis involves medical history, exams, and targeted tests to identify underlying causes like infections, allergies, or lung conditions. Early treatment is essential for relieving symptoms and preventing complications.

Persistent Cough: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies
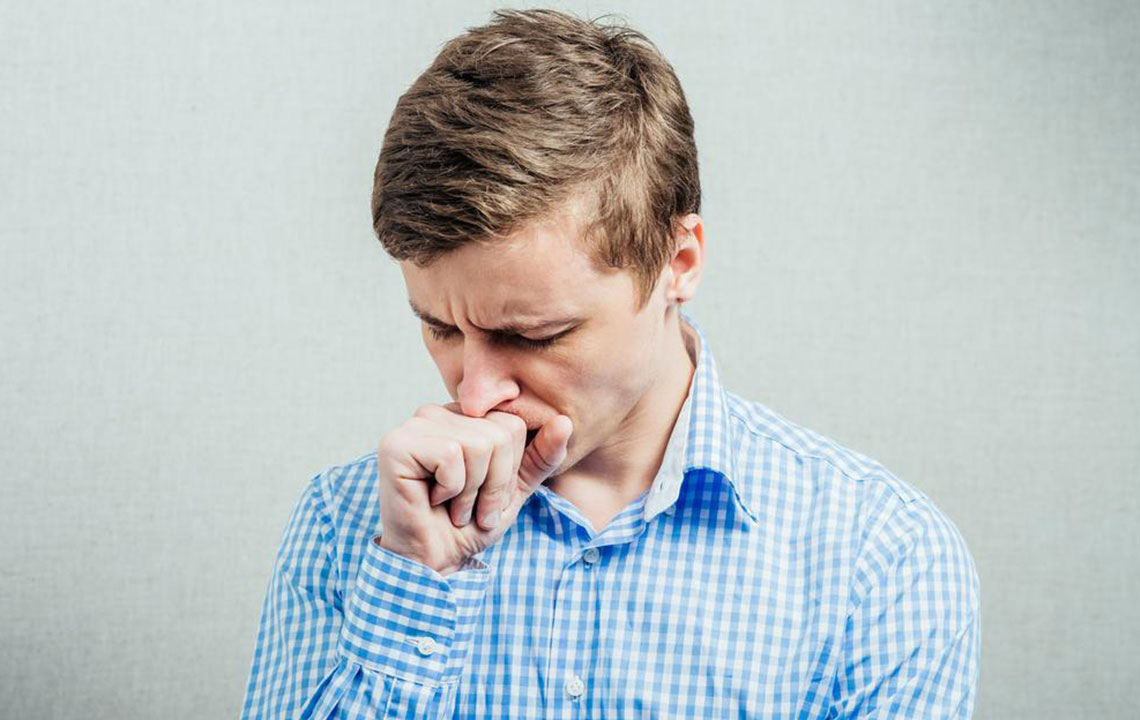
A cough that persists over several weeks can interfere with daily activities and health. When an adult’s cough lasts longer than eight weeks or a child's longer than four weeks, it is classified as chronic. Early medical consultation is important, especially if other symptoms appear. Noticing blood-stained or colored mucus warrants immediate attention. Chronic coughing may cause fatigue, sleep issues, and in serious cases, dizziness, headaches, or nausea. Often, underlying health conditions are responsible for prolonged coughs.
Effective treatment targets the root cause of the cough. Common accompanying symptoms include nasal congestion, postnasal drip, sore throat, wheezing, and breathing difficulties, often linked to allergies, infections, or asthma. Conditions like acid reflux and coughing up colored or blood-tinged mucus are also prevalent. If the cough disrupts sleep, daily life, or produces blood, seeking medical advice promptly is crucial. Some medications, such as certain blood pressure drugs, can also trigger long-term coughs.
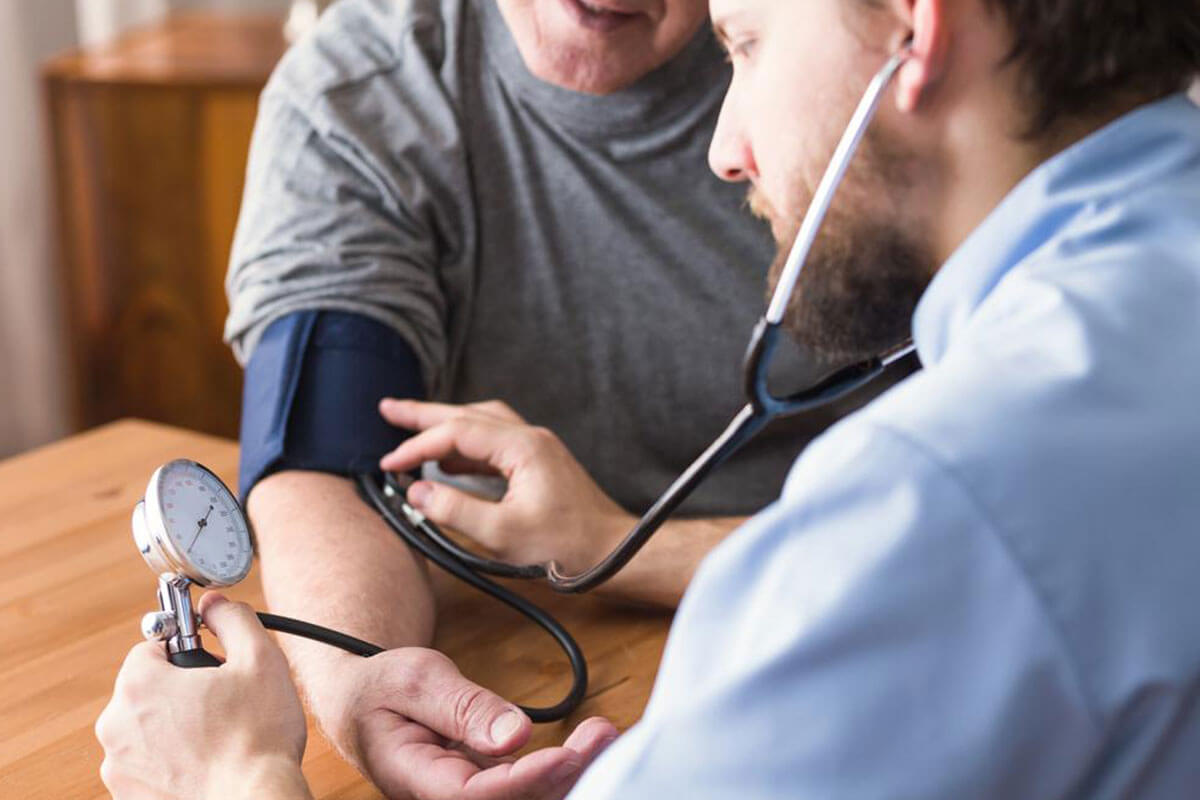
The diagnostic process involves reviewing medical history and conducting physical examinations. Further tests may be needed, including sinus x-rays to detect sinus or nasal issues, and chest x-rays for pneumonia, tuberculosis, or tumors. Pulmonary function tests and bronchial challenge assessments help diagnose asthma. When tests are inconclusive, procedures like endoscopy or biopsies may be performed. In children, chest imaging and spirometry are common diagnostic tools.