Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia: Essential Information
Learn to recognize the symptoms of hypoglycemia to prevent health emergencies. This article covers common signs like hunger, tremors, dizziness, and confusion, emphasizing the importance of early intervention for diabetics. Understanding these indicators enables quick response and effective management of low blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of serious complications.
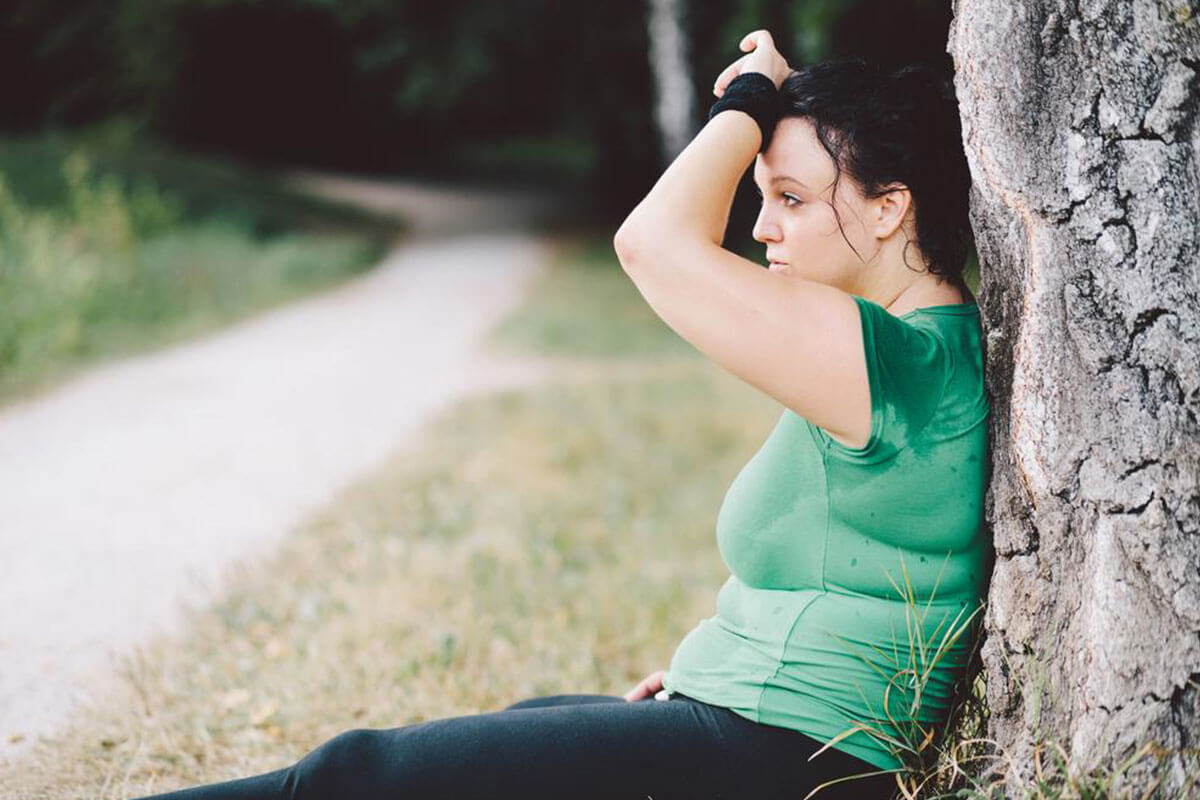

Understanding the Indicators of Low Blood Sugar
Are sudden and unexplained bodily changes affecting you? These could be signs of hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar.
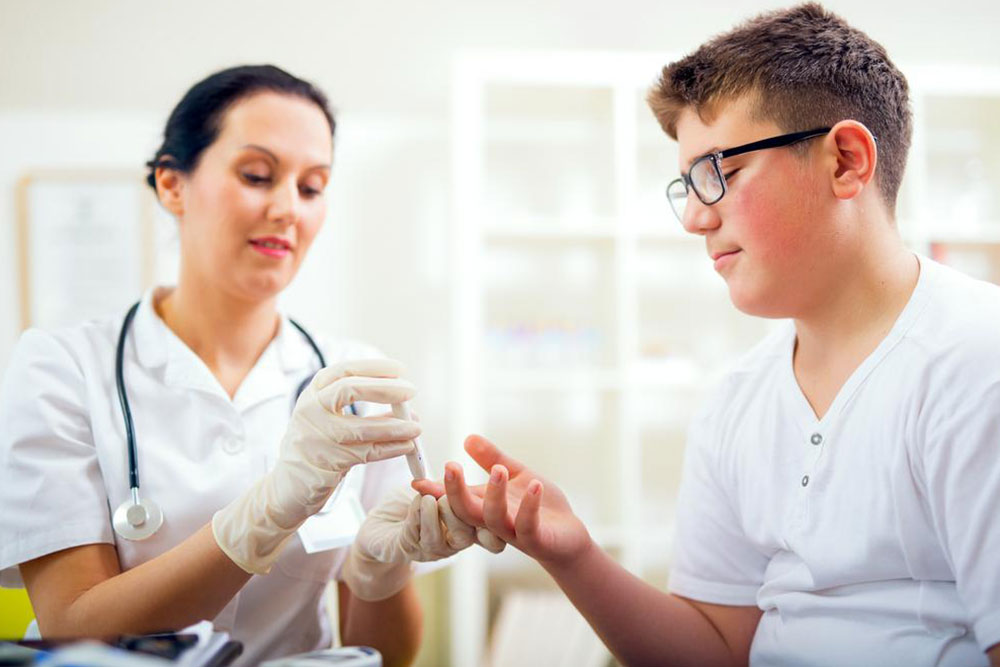
Hypoglycemia happens when blood glucose drops below approximately 70 mg/dl. Since glucose supplies energy to both the brain and muscles, its deficiency can impair their normal function. Frequently seen in diabetics, especially those using insulin, mild hypoglycemia can often be alleviated with a quick sugary snack. However, if left untreated, it can cause confusion, fainting, seizures, or even coma.
Common among type 2 diabetics and insulin users, hypoglycemia presents recognizable symptoms requiring immediate attention. Early identification can prevent serious health risks. Key signs include:
Ongoing hunger: Feeling hungry despite recent meals suggests the need for more glucose. Quick sources include fruit, raisins, or hard candies.
Trembling and shakiness: Low glucose levels impact nerve function, causing involuntary movements like shivering.
Anxiety or nervousness: An adrenaline surge triggered by low sugar causes agitation.
Nighttime awakening: Nocturnal hypoglycemia can lead to nightmares, sweating, or confusion upon waking.
Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded can cause falls; lying down immediately is recommended.
Excessive sweating: Sudden sweating despite weather indicates low blood sugar.
Mood swings and confusion: Emotional volatility and difficulty focusing also suggest hypoglycemia.
Regular blood sugar checks and prompt action upon symptoms are vital for safe management. Early recognition and swift response are crucial in preventing complications.