Eczema Overview: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies
Eczema is a common skin condition causing inflammation, with symptoms like dryness and itching. It predominantly affects children, often improving with age, but can persist. Causes involve immune response and skin barrier issues. Management includes topical treatments and skin care practices to reduce flare-ups. Consulting healthcare providers ensures personalized care. This overview highlights important symptoms, causes, and treatment options for effective eczema management.

Eczema Overview: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies
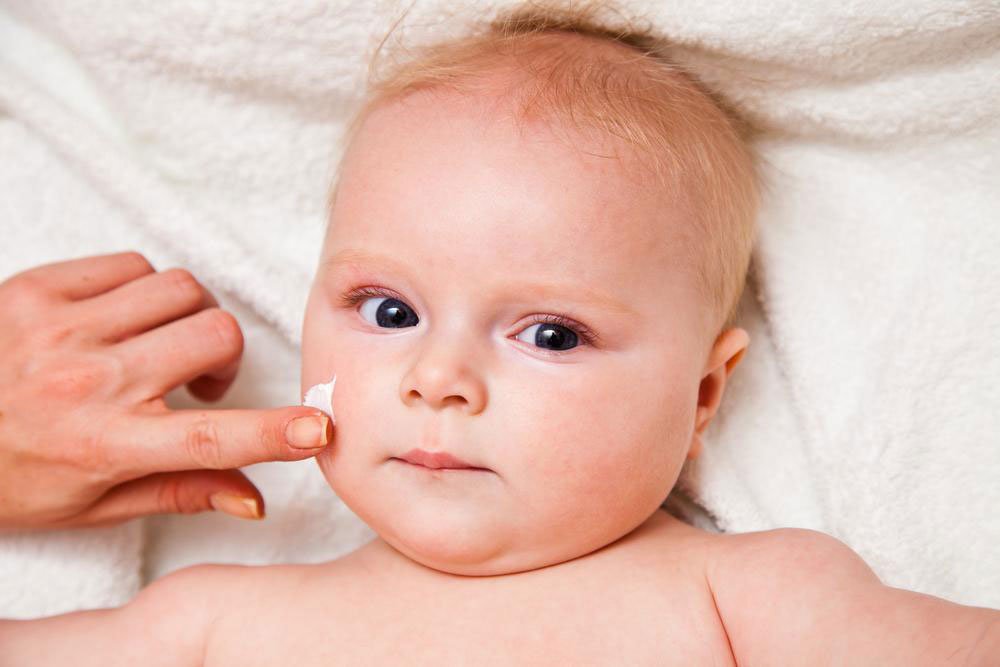
Eczema is a widespread skin disorder marked by inflammation and irritation. In the U.S., approximately 10-20% of infants and 3% of adults develop this condition. Most children outgrow eczema by age ten, though some continue to experience flare-ups. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type, often associated with hereditary allergies like asthma and hay fever.
Causes of Eczema
While the precise cause remains unknown, it’s believed to involve an overactive immune response to certain triggers. Factors include a weakened skin barrier that loses moisture easily, genetic factors, stress, exposure to irritants, and infections.
Signs and Symptoms
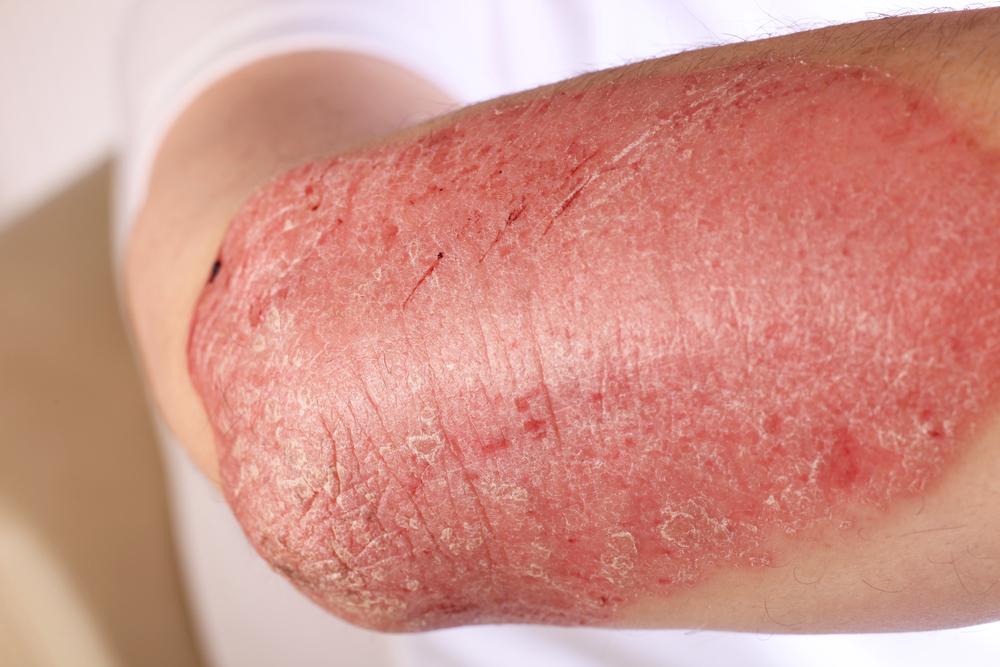
Typical signs include itchy, red, dry, and rough skin. Rashes commonly appear on the face, hands, feet, or behind the knees. Lighter skin may show redness initially, while darker skin might experience pigmentation changes, resulting in lighter or darker patches.
Management Strategies
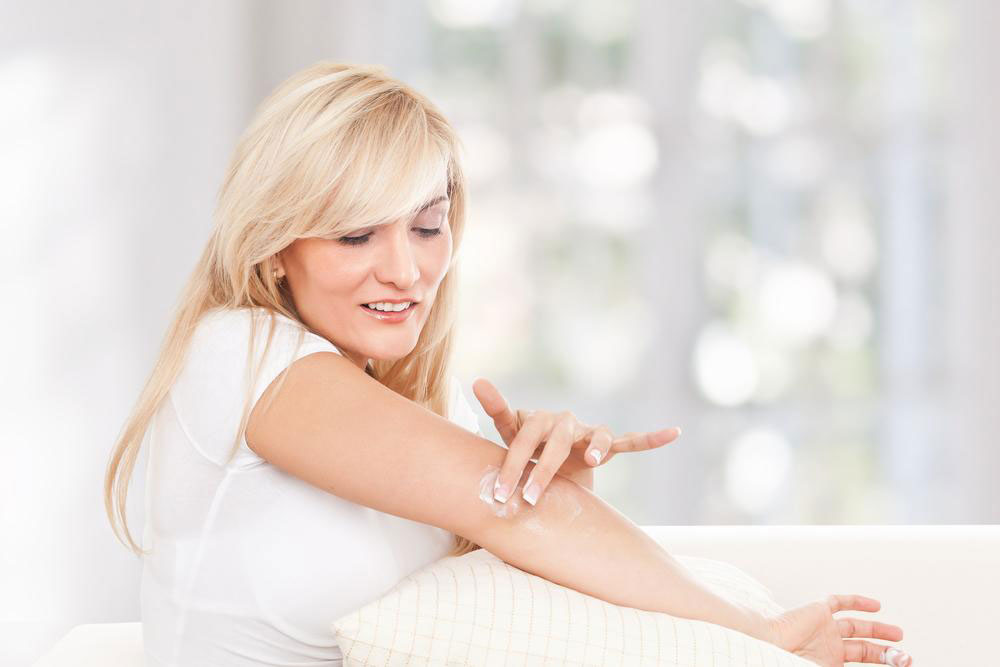
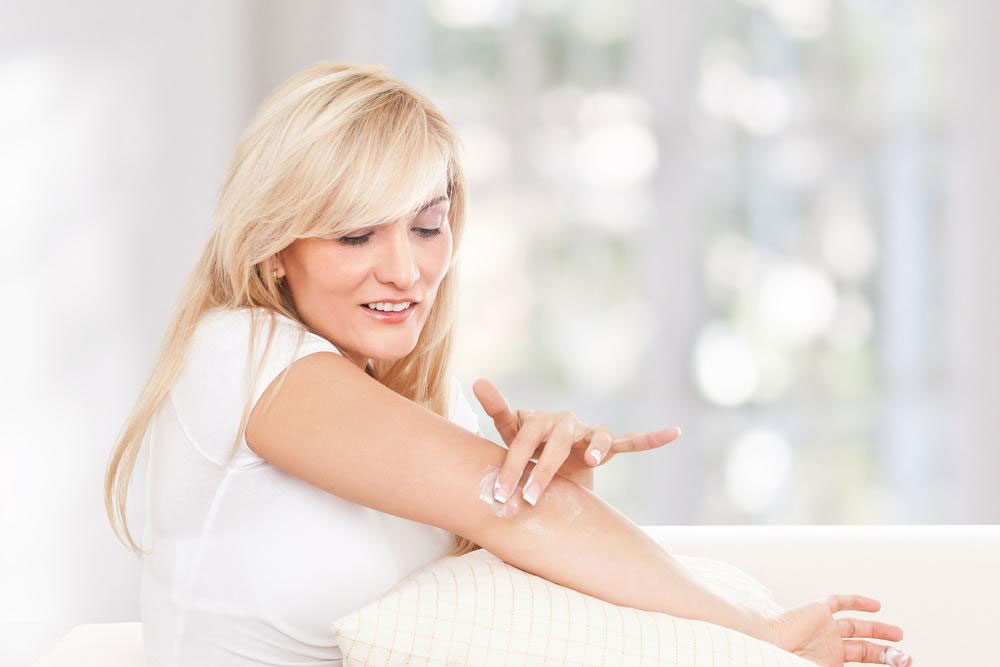
There’s no cure for eczema, but symptoms can be managed with proper treatment and skincare. Consulting a healthcare provider is recommended for a tailored plan. Treatments include anti-itch creams, corticosteroids, moisturizers, and antibiotics for secondary infections from scratching. Keeping skin healthy through regular bathing, moisturizing, avoiding irritants, and wearing loose clothing can help prevent flare-ups.