Ultimate Guide to Identifying and Treating Swollen Ankles
This comprehensive guide explains causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and remedies for swollen ankles. It highlights when to seek medical attention and offers practical tips for relief, suitable for all ages. Understanding this condition helps manage it effectively and prevent complications through timely intervention and lifestyle adjustments.

Ultimate Guide to Identifying and Treating Swollen Ankles
Key Facts About Swollen Ankles
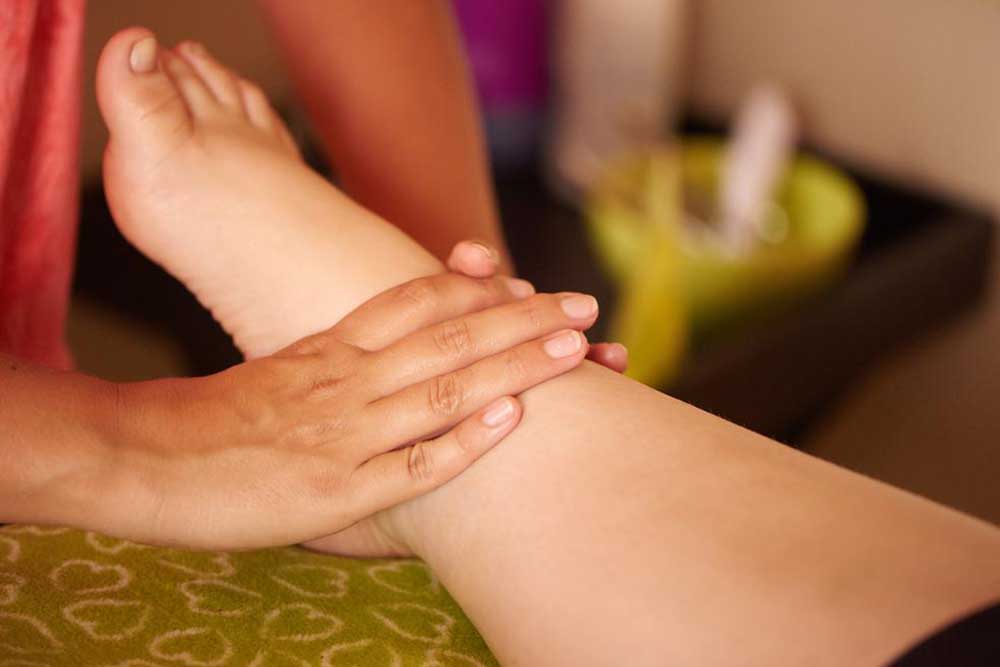
If you notice your ankle swelling, discomfort, or increased size, it can interfere with your daily routines. Swelling or pain can make walking difficult and footwear uncomfortable. Medically termed peripheral edema, this condition affects people of all ages and often appears after prolonged inactivity or strenuous activity. Understanding its causes and knowing when to seek medical care are essential steps toward effective treatment and relief.
This article provides comprehensive information on swollen ankles, covering typical causes, medical insights, symptoms requiring urgent attention, diagnostic procedures, and DIY remedies.
Common Triggers of Ankle Swelling
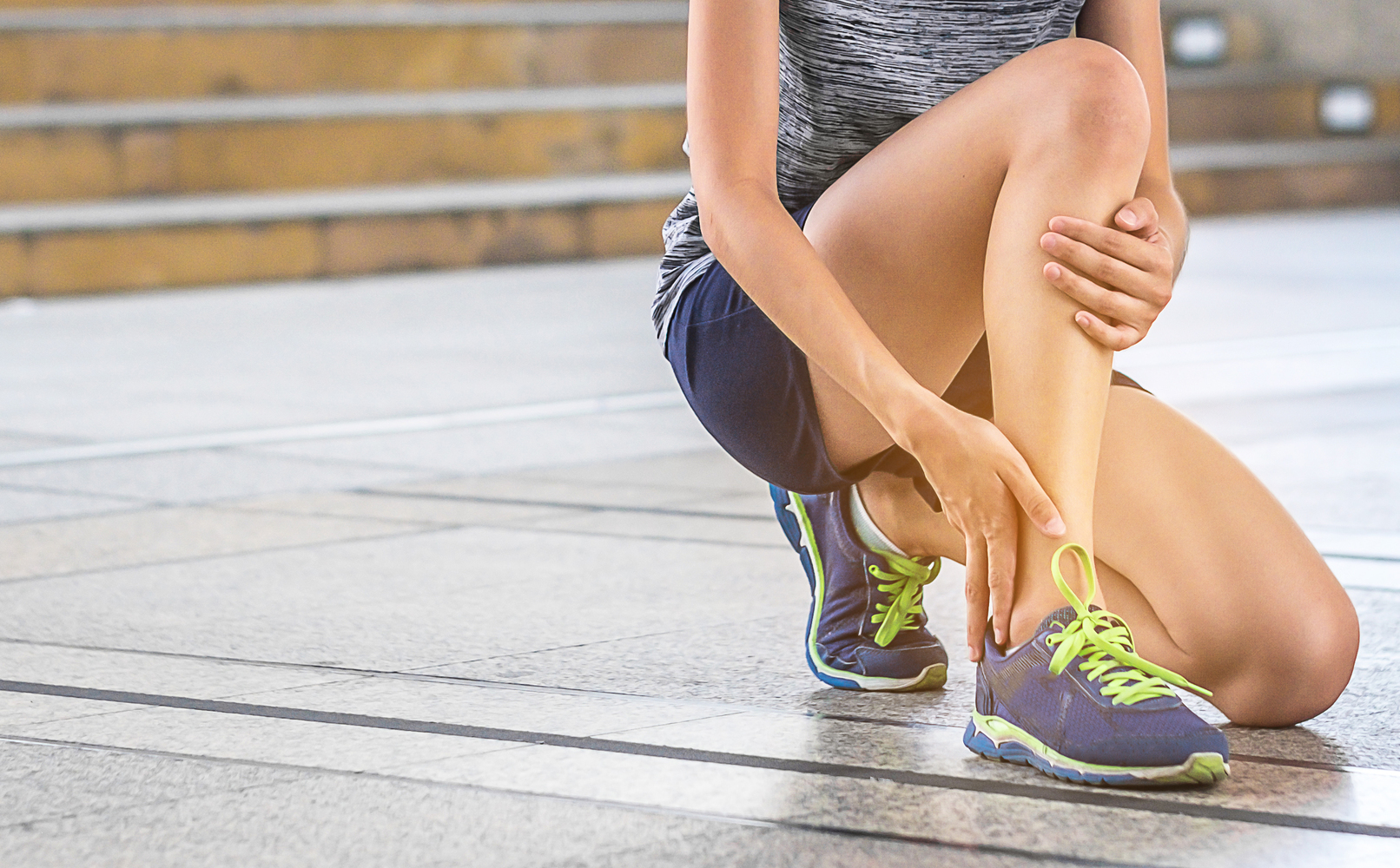
Trauma from accidents or sports activities can cause swelling.
Pressure from tight shoes, socks, or clothing around the ankle.
Prolonged standing or sitting leading to fluid buildup.
High salt intake can cause fluid retention and swelling.
Insect bites from mosquitoes or fleas may result in localized swelling.
Burn injuries from heat exposure or sunburn can cause ankle swelling.
Medical Causes of Swollen Ankles
Excess weight can impair circulation and lead to fluid accumulation.
Certain medications, including steroids, antidepressants, diabetes drugs, contraceptives, and anti-inflammatory agents, may induce swelling.
Pregnancy and hormonal changes are also contributing factors.
Serious health conditions like heart failure, blood clots, kidney, or liver diseases can cause edema.
Infections such as cellulitis or joint disorders like gout and arthritis can lead to swelling.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Persistent swelling after rest or elevation demands medical assessment.
Swelling during ongoing treatments for heart, liver, or kidney issues, or pregnancy, should be evaluated.
Unusual warmth, redness, or increasing swelling warrants professional attention.
Severe or worsening symptoms require urgent care.
Diagnostic Methods
Examinations and imaging tests like X-rays, ultrasounds, MRI, or CT scans help identify underlying causes.
Blood analysis assists in evaluating organ function and detecting infections or blood clots.
Electrocardiograms assess heart health and function.
Treatment Options
Injury-related swelling may need surgical intervention, physical therapy, or medications such as pain relievers.
Addressing underlying health conditions is critical for other causes of swelling.
Home Strategies for Relief
Rest the affected ankle to facilitate recovery.
Use ice packs to reduce inflammation and soothe pain.
Elevate the ankle during sleep to assist fluid drainage.
Reduce salt consumption to less than 2,300 mg daily to avoid fluid retention.