Comprehensive Overview of Bone Density Testing and Its Importance
This guide covers essential information about bone density testing, highlighting its role in preventing osteoporosis and fractures. It explains the testing process, recommended candidates, and how results inform treatment. Regular screenings are vital for maintaining healthy bones and preventing severe fractures, especially for at-risk populations. Consult your healthcare provider to personalize your screening schedule and safeguard your bone health effectively.
Comprehensive Overview of Bone Density Testing and Its Importance
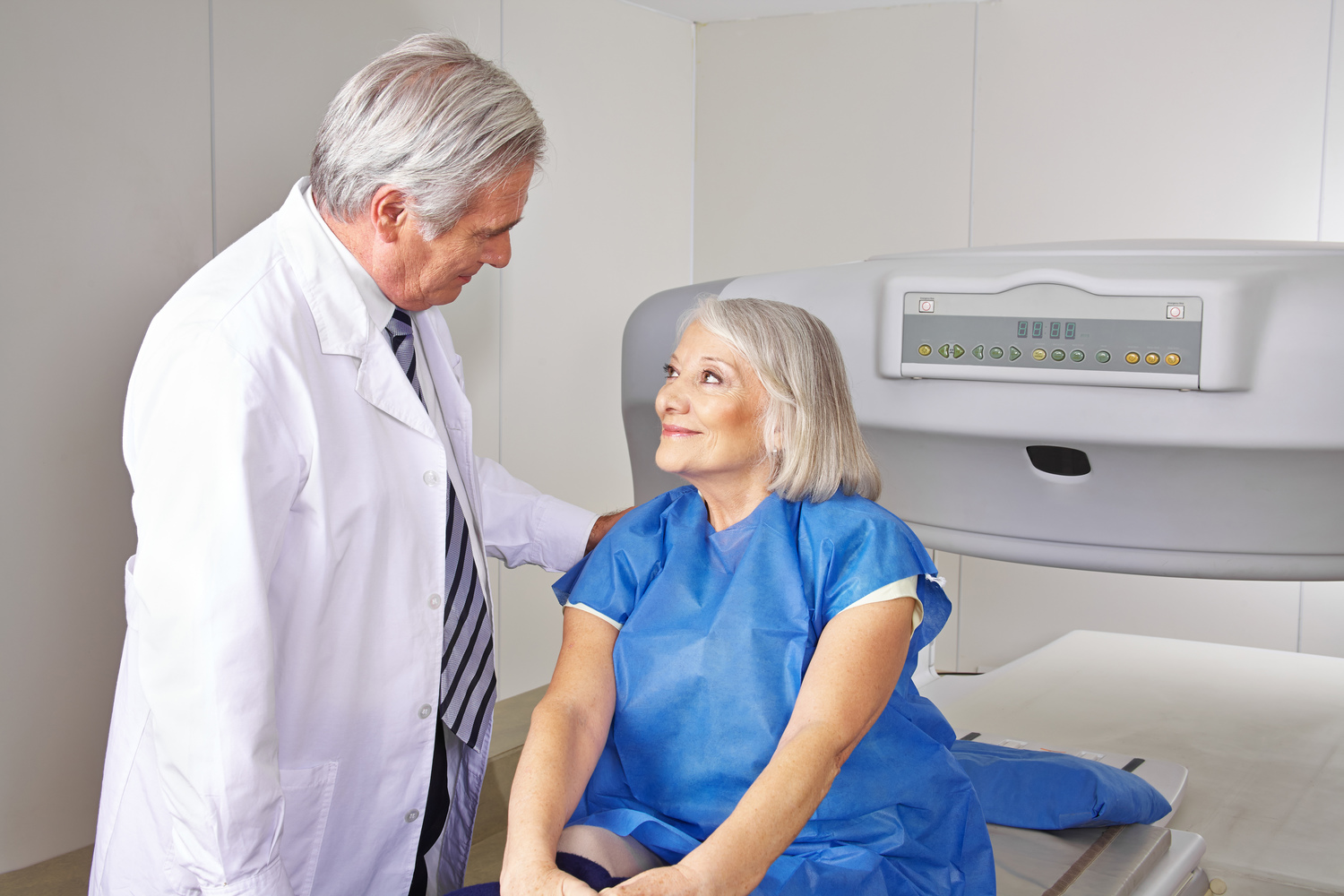
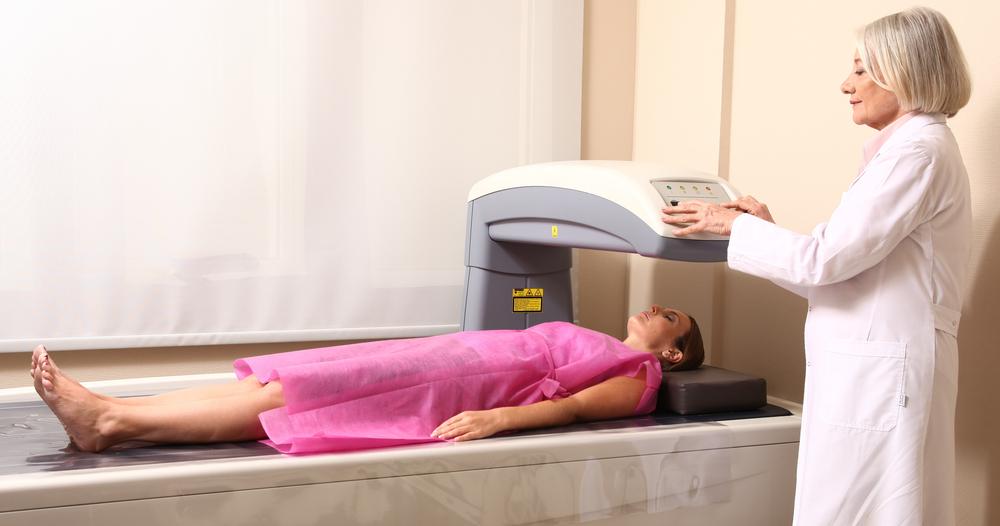
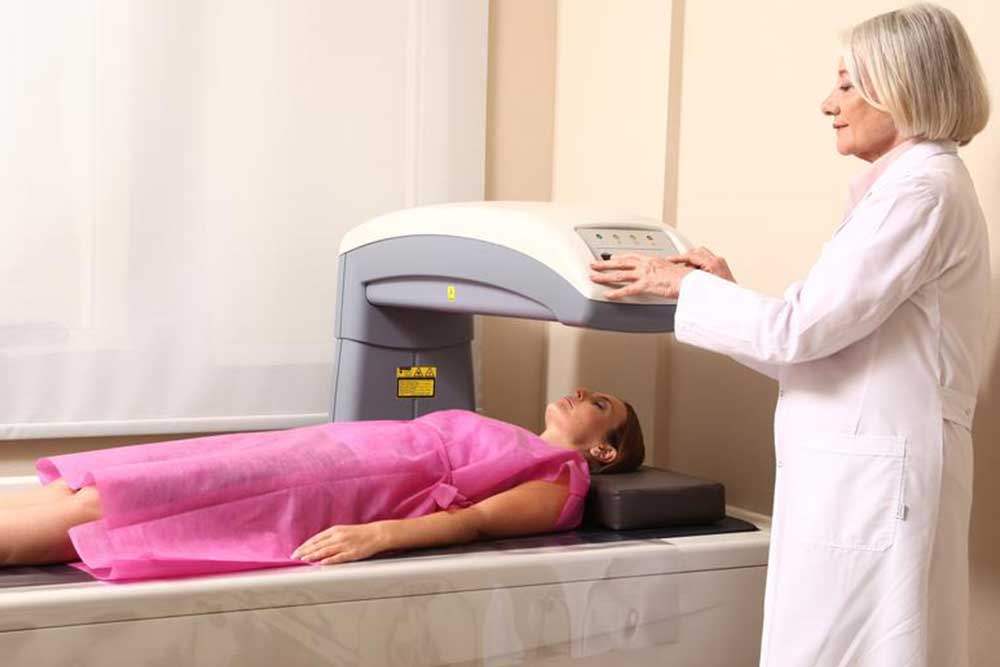
Bone density testing measures mineral content within bones, providing key insight into bone strength and identifying conditions like osteoporosis. The most common method, Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA), uses low-radiation scans of areas such as the hips, spine, or wrists. Recommendations vary: women over 65 and at-risk women should undergo screening; men are advised to start at age 70. Preparation involves avoiding calcium supplements and metal objects. Results are reported with T-scores and Z-scores, where lower scores indicate weaker bones. Testing intervals depend on individual risk factors, generally ranging from 2 to 15 years. This non-invasive exam helps detect bone loss early, enabling timely intervention to prevent fractures and strengthen bone health.
Bone density assessments are essential tools in diagnosing osteoporosis and assessing fracture risk. These painless, quick tests help healthcare providers develop effective treatment plans to promote bone health. Regular screenings can significantly reduce fracture chances, enhancing quality of life. Consult your medical professional for personalized guidance on when and how often to have this important test based on your health profile and risk factors.
Bone mineral density
Osteoporosis screening
Fracture risk evaluation
DEXA imaging
Bone health management