Identifying Common Stomach Problems and Their Symptoms
This article explores common gastric issues such as gallstones, GERD, IBS, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease, highlighting their symptoms and treatments. Recognizing these signs is crucial for effective management and health maintenance. Always seek professional medical advice for diagnosis and care.
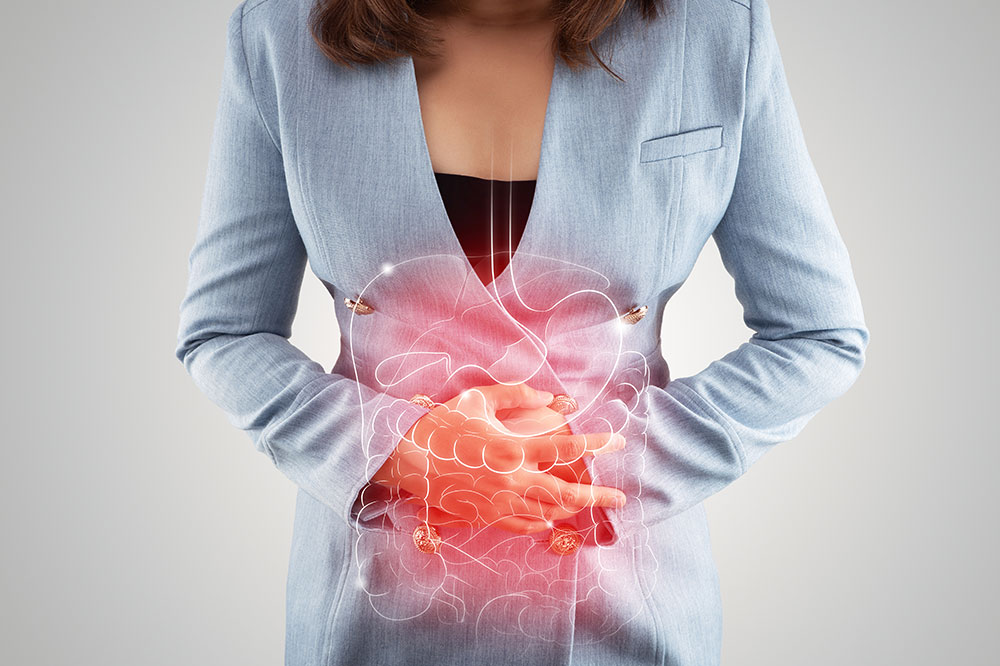

The stomach, located between the esophagus and small intestine, plays a key role in digestion. Disruptions can stem from lifestyle choices, diet, or health issues, often presenting with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, appetite changes, belching, or stomach pain. Recognizing these signs helps identify underlying gastric conditions. Popular issues include:
Gallstones: Hardened deposits forming within the gallbladder due to concentrated bile, excess cholesterol, or waste buildup. Stones can block bile flow, causing severe pain that may require medication or surgery.
The gallbladder's main function is storing and releasing bile for digestion. Blockages lead to significant discomfort.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease): Characterized by stomach acid reflux into the esophagus, leading to heartburn. Symptoms like chronic heartburn, bad breath, and difficulty swallowing suggest GERD. Lifestyle modifications and medications can help manage mild cases.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Causes recurrent abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, or diarrhea. Though its exact origin is unknown, dietary changes, probiotics, and fiber intake can alleviate symptoms.
Ulcerative Colitis: An autoimmune disorder affecting the colon, leading to inflammation, ulcers, urgent bowel movements, and blood in stool. Treatment includes diet adjustments and medications.
Crohn’s Disease: An inflammatory disorder impacting the small intestine and colon with symptoms like diarrhea, cramps, weight loss, and fever. Management involves medication and sometimes surgery.
Important: The details provided are educational and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.