A Guide to Knee Arthroplasty: Causes, Variations, and Preparation Tips
This article provides a comprehensive overview of knee replacement surgery, including causes, different types, and preparation tips. It highlights when surgery is necessary, how procedures are performed, and the importance of consulting medical professionals for personalized care. Ideal for patients exploring treatment options for severe knee pain and joint issues, the piece illustrates the benefits of modern surgical techniques and available online resources for educational support.
As time progresses, our joints, especially the knees, experience degradation that can hinder everyday activities. Persistent pain and mobility issues due to joint deterioration greatly affect overall well-being. Modern medical innovations now enable effective treatment options for advanced knee conditions.
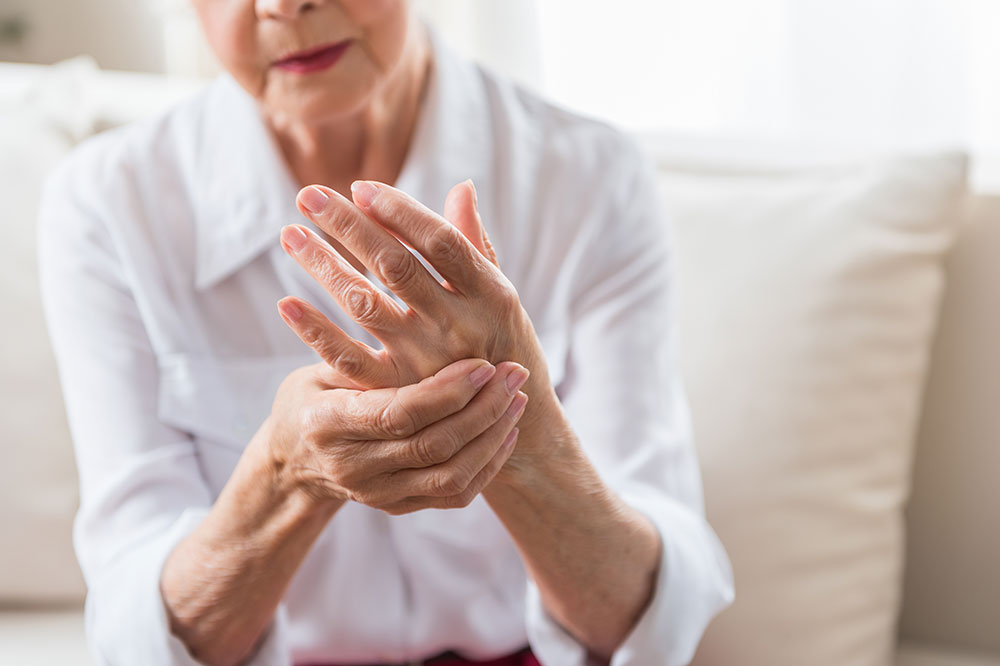
Knee discomfort, predominantly caused by osteoarthritis, can limit movement and cause ongoing pain. When conservative treatments no longer provide relief, knee arthroplasty becomes a practical solution.
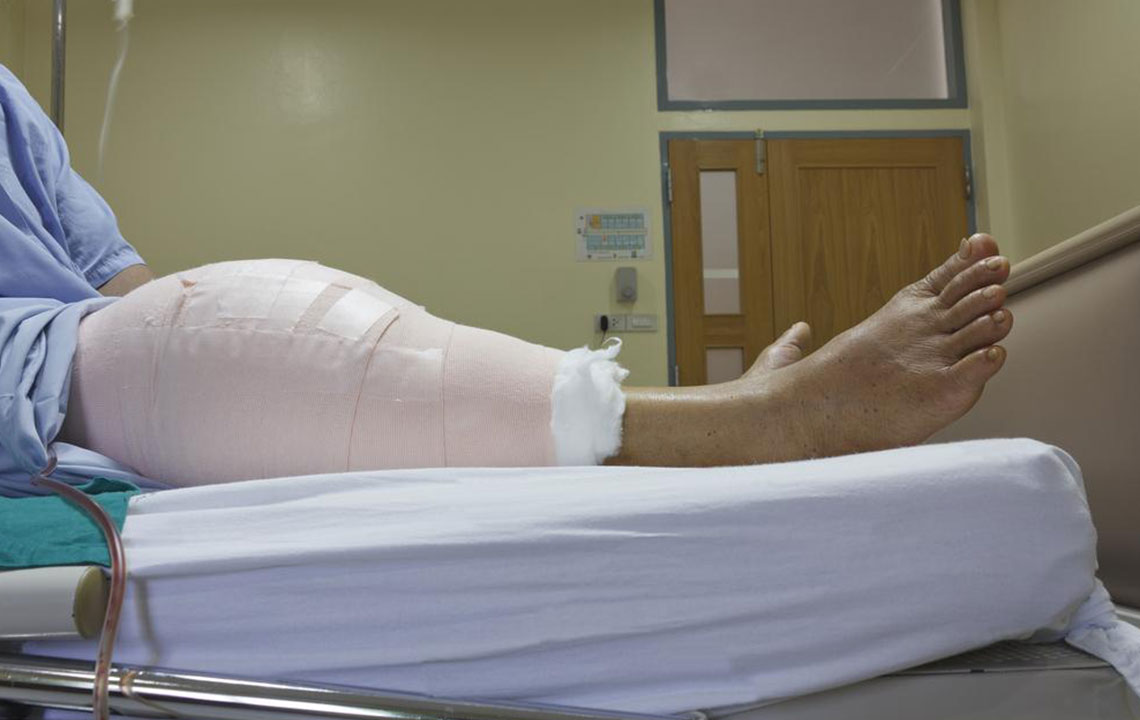
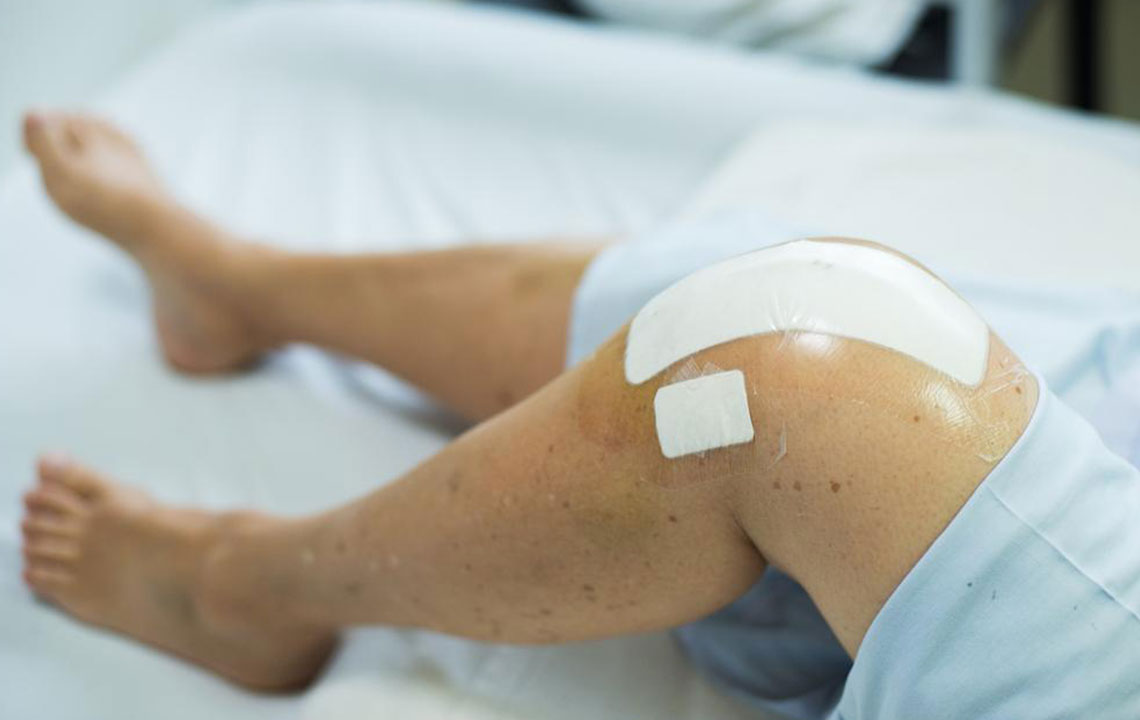
This procedure involves replacing damaged parts of the knee joint to reduce pain and improve mobility. Numerous online platforms feature comprehensive videos explaining the surgical process for patients considering the operation.
Patients typically opt for surgery when conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, traumatic joint injuries, deformities, or inadequate blood flow cause significant pain and restrict movement.
Knee replacement can be classified into four primary types based on severity:
Complete knee replacement: Replaces the entire joint.
Partial knee replacement: Focuses on the affected section of the joint.
Kneecap replacement: Replaces the undersurface of the kneecap.
Revision surgery: Addresses previous implants or complex cases.
Preparatory steps for surgery include viewing trusted educational videos from sources like Arthritis-Health, WebMD, Surgical Videos, and Healthline. These resources provide helpful insights on pre- and post-operative care.
Note: The information provided here serves as general guidance and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek personalized recommendations from qualified healthcare providers.