Effective Approaches to Control and Prevent Asthma Attacks
Discover comprehensive strategies to effectively manage and prevent asthma attacks. This article covers types of asthma, early warning signs, trigger factors, and essential treatment options like inhalers, nebulizers, and medications. Learn how tailored approaches and professional guidance can help individuals lead healthier, active lives despite asthma challenges.

Understanding and Preventing Asthma Exacerbations
Asthma presents primarily as allergic and non-allergic types. Allergic asthma results when environmental allergens trigger symptoms, while non-allergic asthma can be caused by stress, infections, weather conditions, or emotional factors. Genetics influence individual susceptibility. Though there's no cure, proper management and preventive techniques can lessen the frequency and intensity of episodes. Early identification of symptoms—such as ongoing cough, wheezing, tightness in the chest, and breathing issues—is essential for timely treatment. Focused strategies allow individuals to maintain active lifestyles despite asthma.
Triggers for asthma often involve inherited factors or environmental exposures. Warning signs, like coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing, may appear before an attack. Prompt medical consultation is recommended when symptoms occur. While no permanent cure exists, various treatments—such as inhalers, nebulizers, steroids, anti-inflammatory medications, bronchodilators, immunomodulators, and corticosteroids—help control symptoms and improve quality of life. Consulting healthcare professionals ensures customized management plans tailored to each individual.
Key methods to manage asthma include:
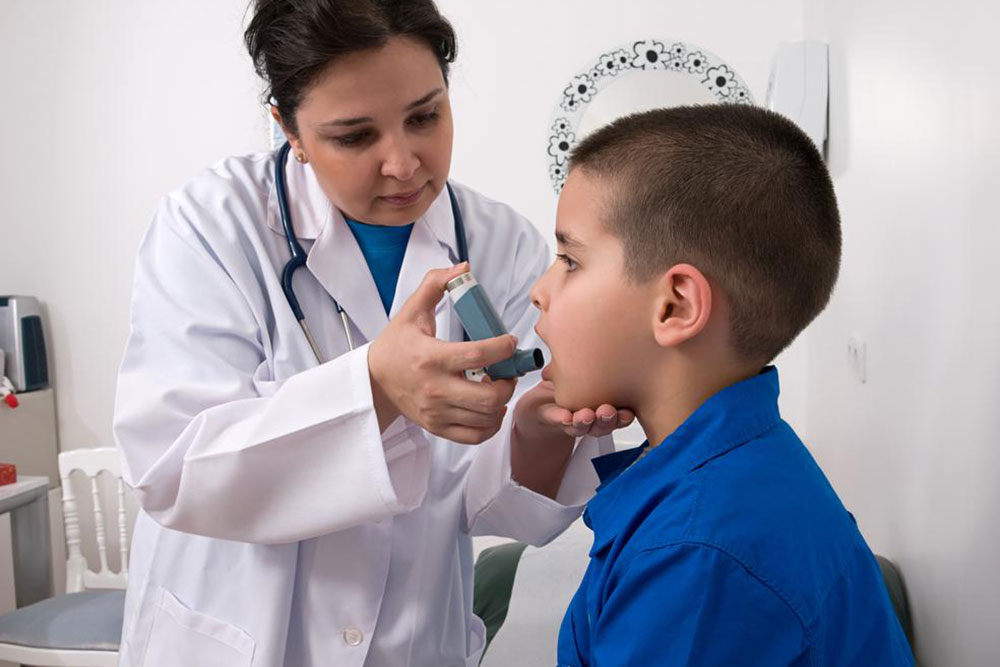
Inhalers
Inhalers deliver medication rapidly directly to the lungs. Available as metered-dose inhalers (MDI) or dry powder inhalers (DPI), they may contain single or multiple medications for enhanced relief.
Nebulizers
Nebulizers convert liquid medicine into vapors, facilitating easier inhalation, especially in children and seniors. They come with masks or mouthpieces for comfortable use.
Anti-inflammatory Agents
Inhaled steroids and anti-inflammatory drugs reduce airway swelling and mucus, helping prevent attacks and lowering sensitivity to triggers.
Bronchodilators
Rescue inhalers or bronchodilators relax airway muscles to improve breathing during an attack. They provide quick relief but should be used under medical supervision for regular use.
Immunomodulators
Injectable immunomodulators help regulate immune responses and reduce allergic inflammation in severe cases.
Oral Corticosteroids
When inhaled options are insufficient, oral steroids in pill or liquid form assist with long-term control, especially in serious cases.
Beta-agonists
Often combined with inhaled steroids, beta-agonists relax airway muscles to ease breathing. Short and long-acting variants are used for immediate or sustained relief.
Important Reminder:
Our blog offers a wide range of health insights and practical tips. While we base content on rigorous research, individuals should consult healthcare professionals for personal advice. This article is not a substitute for medical guidance. For optimal asthma management, seek tailored medical care rather than relying solely on general information.