Top 3 Natural Foods to Lower Blood Sugar Levels
Discover three natural foods—broccoli, berries, and oats—that can help lower blood sugar levels. This article explains how these nutrient-dense options support glucose regulation, reduce oxidative stress, and improve insulin sensitivity. Learn practical ways to incorporate them into your diet and understand the importance of balanced eating for better health and diabetes prevention.
Top 3 Natural Foods to Lower Blood Sugar Levels
Elevated blood sugar is a hallmark of diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions globally. The International Diabetes Federation 2021 report estimates that around 537 million adults live with diabetes, with many unaware of their condition. Managing blood glucose relies on healthy lifestyle choices, balanced nutrition, and effective remedies. In this article, we highlight three powerful foods that can naturally help reduce blood sugar levels and discuss the critical role of diet in glucose regulation.
Three nutrient-rich foods supporting blood sugar balance and how to enjoy them
Broccoli
Consuming cruciferous vegetables like broccoli is associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.

Broccoli is rich in sulforaphane, a bioactive compound that may lower blood sugar and possess anti-diabetic effects. It helps reduce oxidative damage and enhances insulin sensitivity. For optimal benefits, eat broccoli raw, steamed, or lightly boiled. Use it in salads, soups, stir-fries, or as a side dish paired with lean proteins to maximize its health effects.
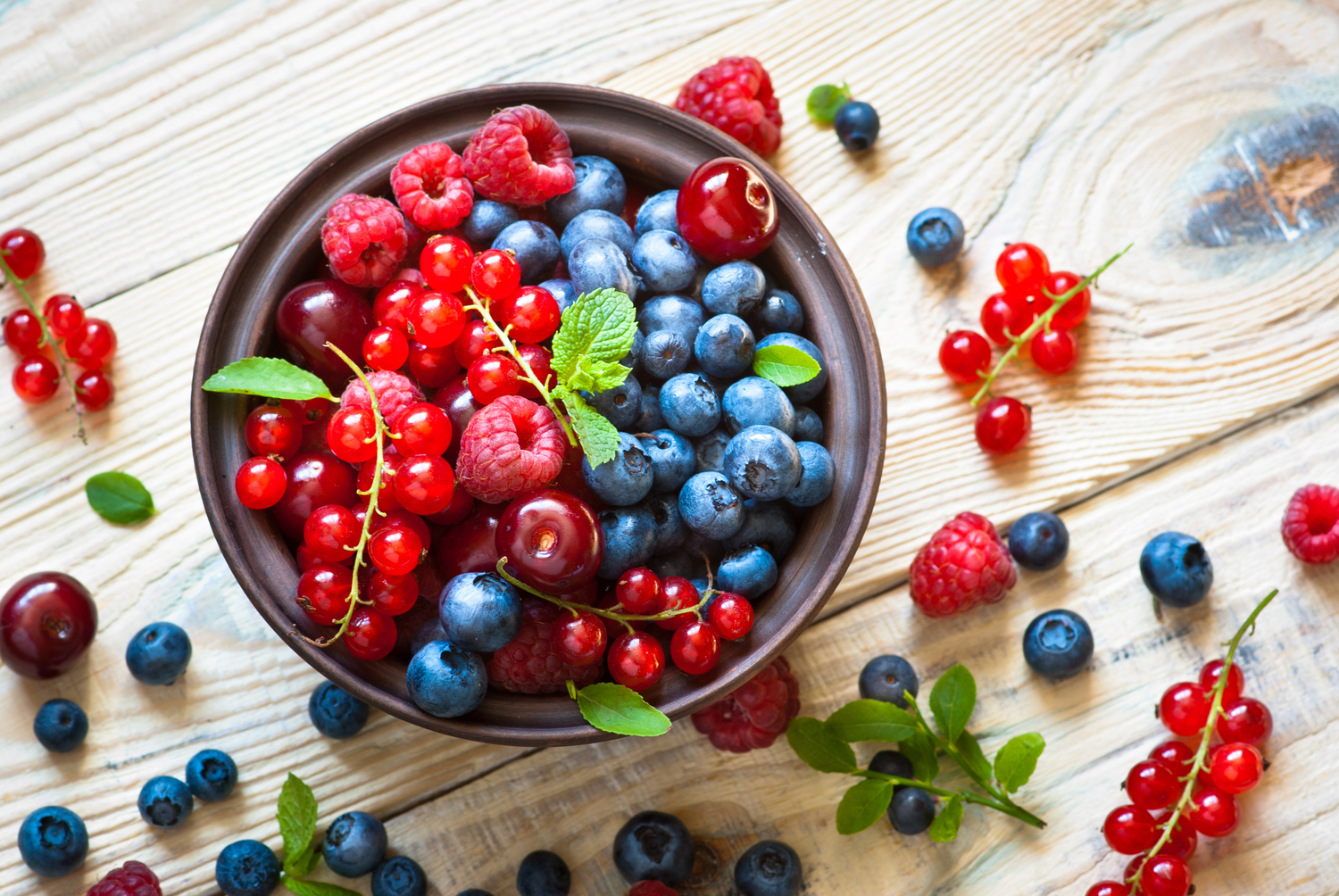
Berries
Fruits like strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, cranberries, and mulberries are loaded with antioxidants, making them excellent for blood sugar regulation. They help prevent post-meal glucose spikes and support weight management. Enjoy berries fresh, blended into smoothies, or as part of healthy desserts to get their advantages. Research indicates that consuming two cups of raspberries after meals can help lower postprandial blood glucose, particularly in prediabetic individuals.
Oats and Oat Bran
Oats contain beta-glucan fiber, which aids in stabilizing blood sugar by boosting insulin response. They promote feelings of fullness, reducing unhealthy snacking and preventing blood sugar spikes after meals. Prepare oats traditionally or soak overnight in milk for convenience. Adding berries enhances flavor and nutritional value. Oat bran, similar to oats, helps maintain stable blood glucose levels—drinking oat bran mixed with water before consuming processed bread can help prevent surges. Oats also improve cholesterol, supporting overall metabolic health.
Integrating these foods into your daily diet can greatly support blood sugar management. Continue reading to learn about foods that can raise glucose levels and the influence of diet on your overall health.
Dietary impacts on blood sugar levels
Oxidative stress and insulin resistance are key contributors to elevated blood glucose. Nutrients influence the body's response differently. Consuming refined carbs, white bread, sweets, and high-GI foods generates glucose spikes, stimulating insulin release. Over time, aging and other factors impair insulin function, leading to resistance and potential diabetes. Diets rich in unsaturated fats, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains can prevent spikes, promote fat loss, and reduce health risks. Limiting red meats and processed foods is recommended for better control. Seek personalized advice from healthcare professionals and incorporate regular physical activity to improve health outcomes.