Complete Overview of Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores lung cancer's causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It emphasizes early diagnosis and the importance of understanding risk factors like smoking, environmental exposures, and genetics. The article provides insights into symptoms and available therapies, catering to patients and caregivers seeking essential information about lung cancer management.
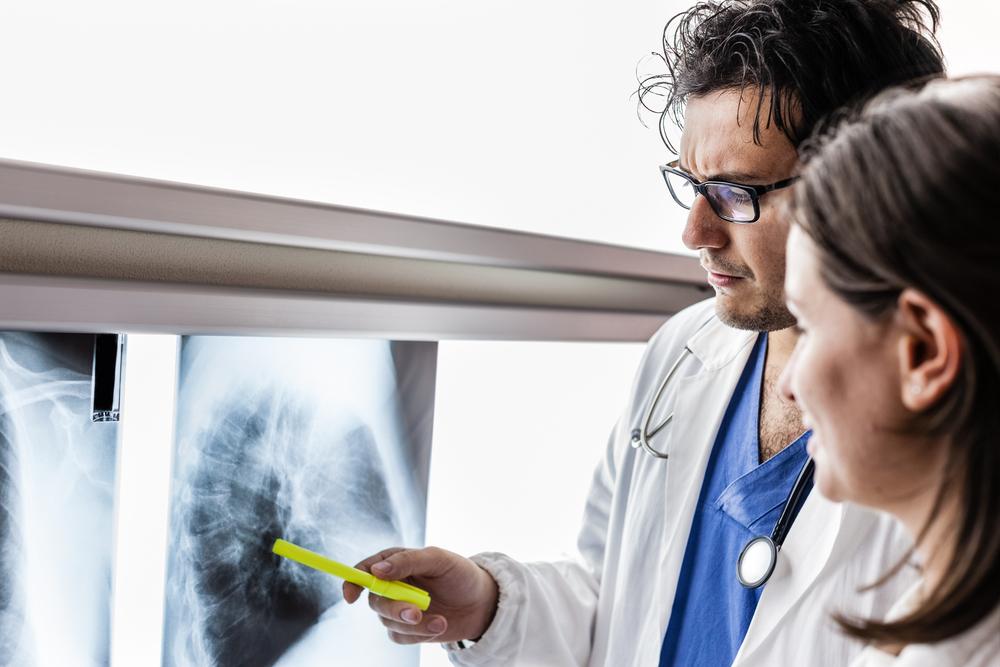
Understanding Lung Cancer: Essential Facts and Information
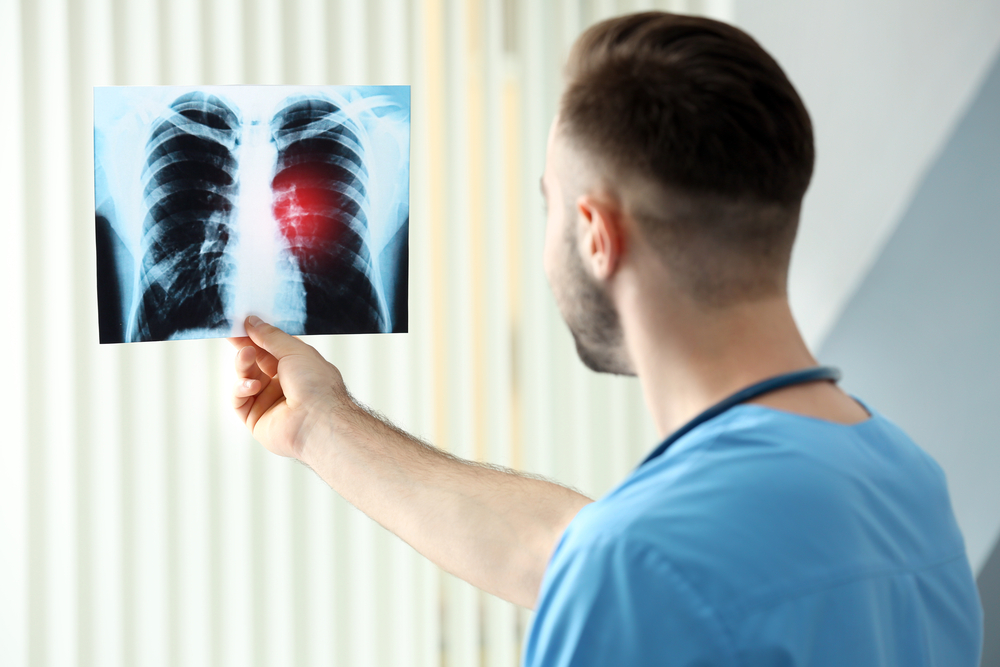
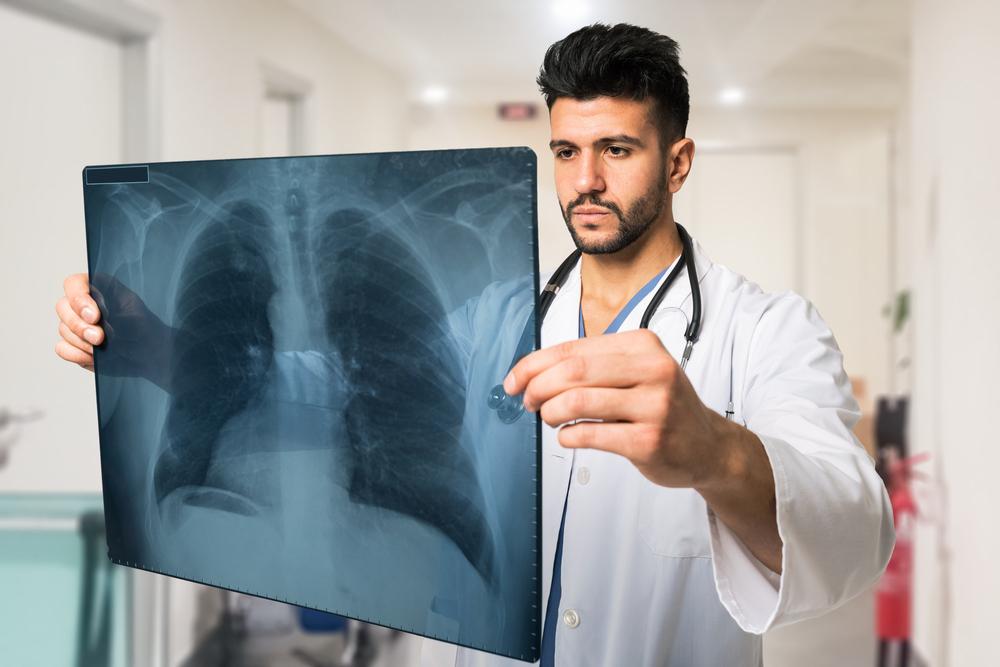
Lung cancer develops when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably within the lungs, potentially spreading to other areas and causing serious health issues. It mainly originates from the lining cells of the larger bronchi and smaller bronchioles. The condition predominantly affects seniors, with over 70% of cases diagnosed in people over 60 years old.
The disease can metastasize, impacting other organs beyond the lungs. As one of the leading causes of death worldwide, early detection and treatment—such as chemotherapy, radiation, and radiosurgery—are vital for better survival rates.
Various factors influence lung cancer risk, with smoking being the most significant. However, non-smokers are also vulnerable, especially due to environmental exposures like air pollution. The cancer can spread from the lungs through metastasis to other parts of the body.
Primary Causes of Lung Cancer
Tobacco Consumption: Cigarette smoking accounts for roughly 90% of cases, with long-term use markedly increasing risk.
Asbestos Contact: Occupational exposure to asbestos fibers can cause lung tumors, as fibers can remain lodged in lung tissue for extended periods.
Secondhand Smoke Exposure: Non-smokers inhaling cigar or pipe smoke face about a 25% higher risk, especially with ongoing exposure.
Radon Inhalation: Breathing in radon gas from soil sources over time can elevate the likelihood of developing lung cancer.
Inherited Factors: Family history and genetic predispositions can also influence individual risk.
Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Early stages often lack noticeable symptoms, but as the disease advances, symptoms such as a persistent cough, sometimes with blood, shortness of breath, and hoarseness emerge. Additional signs include weight loss, fatigue, neurological symptoms like memory issues, and unexpected bone fractures.
Treatment Options
Approach depends on the patient's age, overall health, and cancer stage. Treatments include surgical removal of tumors, radiation therapy, radiosurgery, chemotherapy, and targeted treatments. Surgery is preferred if the cancer is localized; otherwise, radiation and medication are used to target cancer cells effectively.