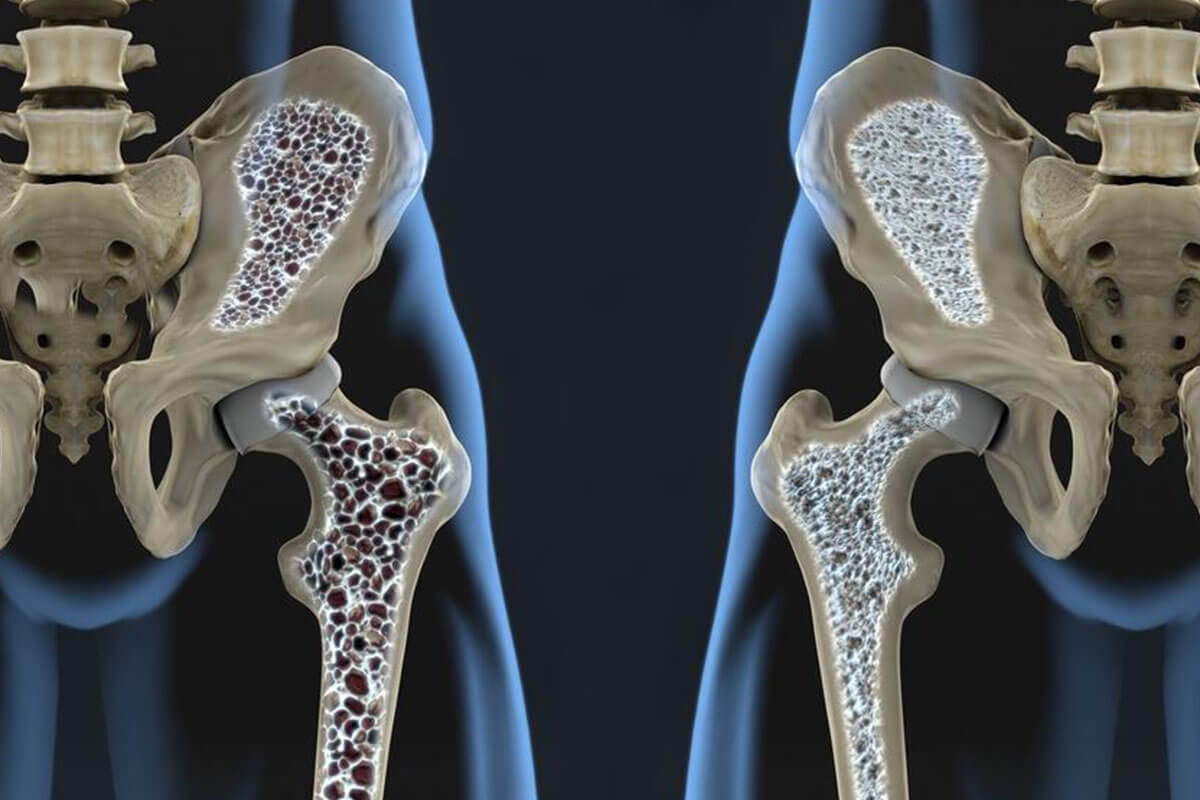
Common Health Conditions Increasing the Risk of Osteoporosis and Bone Weakness
Learn about five common health conditions that significantly increase the risk of osteoporosis and bone weakening. From thyroid issues to autoimmune diseases, understanding these factors can help in prevention and management of bone loss. Proper health monitoring and lifestyle choices are vital for maintaining strong bones as you age.

Common Health Conditions Increasing the Risk of Osteoporosis and Bone Weakness
Bone health declines with age, affecting many individuals worldwide. Around 33% of women and 20% of men over 50 face osteoporosis, a disease characterized by fragile bones that fracture easily. Certain medical conditions significantly raise the risk of developing osteoporosis:
Hyperthyroidism
An overactive thyroid speeds up bone turnover, leading to increased bone loss. Managing thyroid health is crucial to prevent deterioration.
Arthritis
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can weaken bones due to joint inflammation and treatments that inhibit bone-forming cells. Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce these risks.
Diabetes
Elevated blood sugar levels may hinder bone formation and healing, increasing osteoporosis risk and fracture susceptibility.
Asthma
Although asthma does not directly cause bone loss, the use of corticosteroids for management can contribute to osteoporosis. Breathing difficulties may also limit physical activity, affecting bone strength.
Celiac Disease
Gluten intolerance damages the intestinal lining, impairing calcium and vitamin D absorption, which are essential for bone health, thus promoting bone loss.
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment.