Complete Overview of Bladder Cancer Awareness and Prevention
This comprehensive overview highlights the key aspects of bladder cancer, including symptoms, risk factors, types, and prognosis. Early detection and medical consultation are emphasized for effective management. The guide aims to increase awareness and encourage proactive health measures for those at risk.
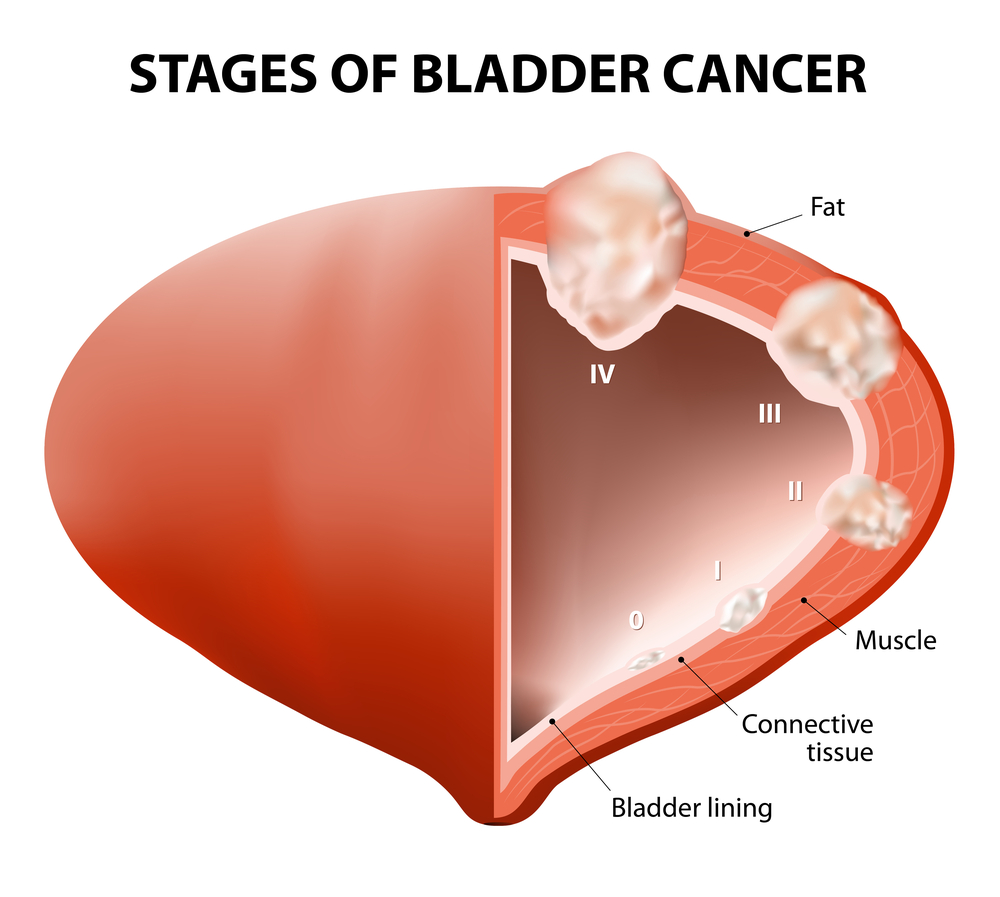
Essential Information on Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is one of the most common malignancies affecting individuals across all age groups. It originates from the lining cells called urothelial cells within the bladder. Detecting the disease early significantly improves treatment success and patient outcomes. Seeking expert medical advice and using trusted health resources are crucial to understanding risks and symptoms associated with bladder cancer.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Initial signs include blood in urine, pain during urination, increased frequency, and lower back or pelvic pain.
Sometimes, blood may be hidden in urine; any visible blood warrants prompt medical attention.
Factors Increasing the Risk of Bladder Cancer
Abnormal cell growth in the bladder can result from multiple risk factors.
Major risks involve smoking, exposure to harmful chemicals, radiation, persistent bladder irritation, and infections.
Types of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancers are categorized into three main types:
Urothelial carcinoma – The predominant type, arising from transitional cells lining the bladder interior.
Squamous cell carcinoma – Often diagnosed at advanced stages and tends to be aggressive.
Adenocarcinoma – A less common form from glandular cells, sometimes linked to parasitic infections or other organ cancers.
Details on Bladder Cancer Subtypes
Urothelial carcinoma – Develops from the transitional epithelial cells that line the bladder, ureters, and urethra, facilitating bladder expansion and contraction.
Squamous cell carcinoma – Results from chronic irritation, with urothelial cells transforming into squamous cells, often mimicking urinary infections.
Adenocarcinoma – Affects mucus-producing glands within the bladder and may originate from other organs like the prostate or colon.
Causes of Bladder Irritation
Persistent catheter use or infections can stimulate irritation leading to squamous cell carcinoma.
This cancer subtype is less common in regions with low parasitic infections.
Prognosis and Survival Chances
Early detection generally results in a better prognosis, particularly in urothelial carcinoma cases.
Patient survival depends on cancer type and stage; early diagnosis significantly enhances treatment success.
Important Reminder:
Our blog offers well-researched, insightful health information. However, it should not replace professional medical advice. For personalized diagnosis and treatment options, always consult healthcare providers. We are not responsible for any inaccuracies or omissions and do not cover all available treatments or schemes.


