Understanding the Main Causes of Bursitis
Bursitis is an inflammation of fluid-filled sacs around joints, caused mainly by trauma, overuse, or infections. This article explores various types, their causes, and risk factors, emphasizing the importance of early treatment to prevent mobility issues.
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs located around joints that serve as cushions between muscles, tendons, skin, and bones. They help facilitate smooth joint movements by minimizing friction. Bursitis occurs when these sacs become inflamed, leading to pain, swelling, and discomfort around the affected joints. If left untreated, bursitis can restrict movement and cause further health issues. It often results from injury or repeated trauma, which causes inflammation, redness, and tenderness. Different types of bursitis have unique causes mostly linked to overuse, injuries, or health conditions.
The most common cause is damage to the bursae due to trauma, repetitive activities, or infections. These factors contribute to symptoms such as pain, swelling, and redness.
Each bursitis type has specific origins:
Prepatellar bursitis: Usually caused by knee injuries, frequent kneeling, sports, or infections leading to swelling around the kneecap.
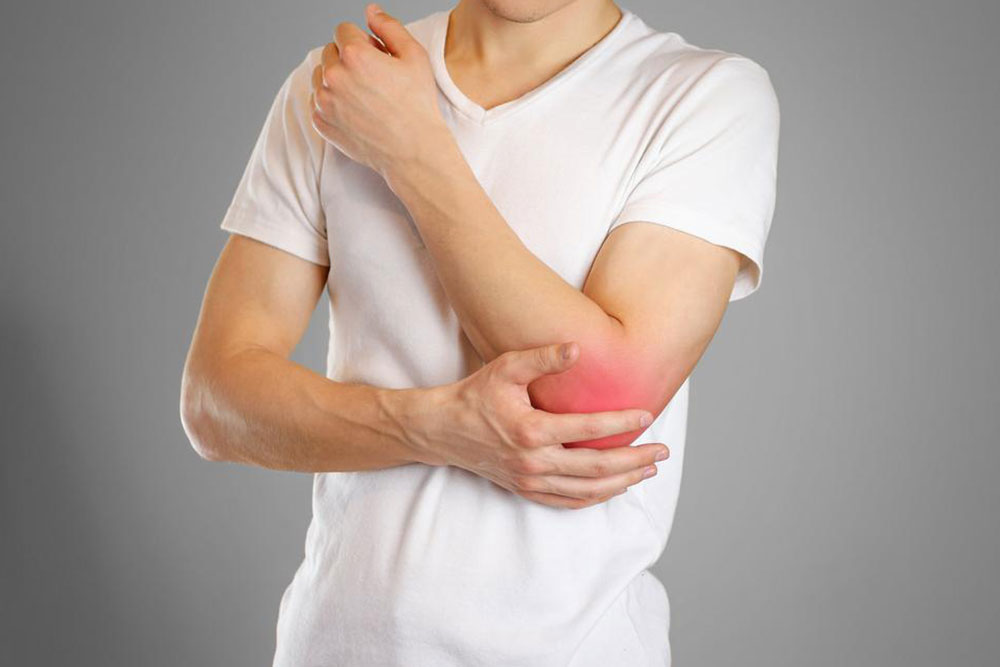
Olecranon bursitis: Results from continuous pressure on the elbow or direct impact.
Trochanteric bursitis: Often due to prolonged hip contact, injuries, poor posture, or arthritis.
Retrocalcaneal bursitis: Commonly triggered by running, jumping, or improper footwear, especially without warming up.
Additional factors: Conditions like arthritis, gout, or diabetes, as well as obesity and lack of activity, increase susceptibility. Occupations involving repetitive motion or physical labor also raise the risk of bursitis.