Top 5 Early Warning Signs of Diabetes You Should Know
Recognizing early signs of diabetes is vital for prompt treatment and prevention. Key symptoms include frequent urination, constant thirst, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and genital itching. Understanding causes and maintaining healthy habits can significantly reduce risk. Always seek professional medical advice for diagnosis and management. This article highlights the importance of awareness and lifestyle choices in battling diabetes effectively.
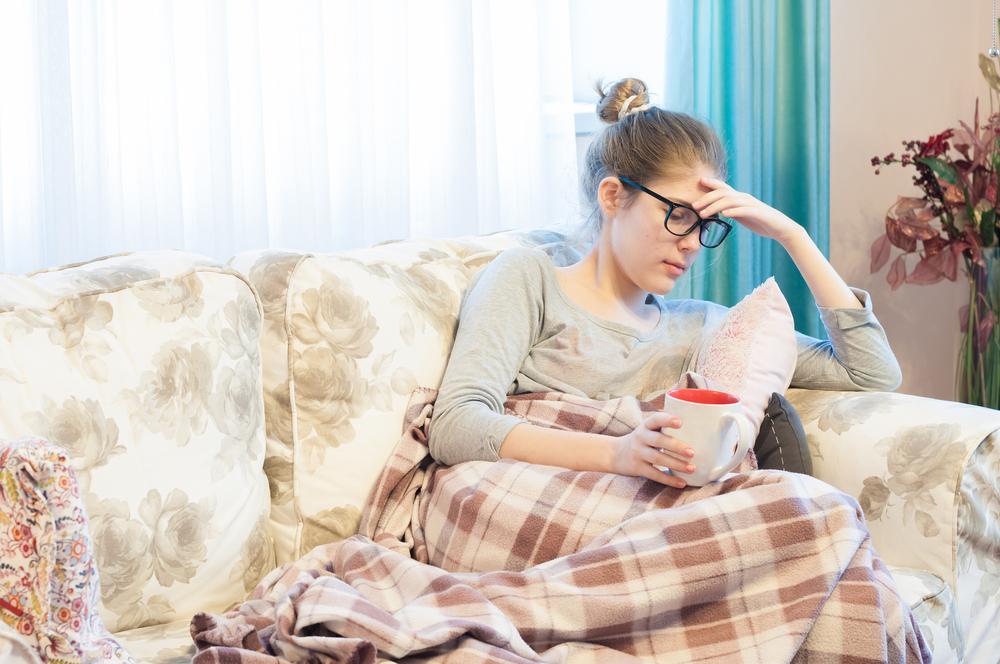

Diabetes is a widespread health issue impacting people of all ages and backgrounds, including well-known personalities like Justin Bieber and Al Pacino. Recognizing early indicators is essential for timely intervention and better health outcomes.
Understanding Diabetes:
Diabetes involves elevated blood sugar levels beyond normal limits. For fasting measurements, normal individuals typically have levels between 3.9 and 5.5 mmol/L, while those with diabetes often present levels from 4.4 to 7.2 mmol/L.
Post-meal blood sugar surges are normal; non-diabetics usually show levels of 6.5 to 7.8 mmol/L, whereas diabetics may reach about 10.0 mmol/L.
Five Major Symptoms to Monitor:
- Increased urination, especially during nighttime
- Constant thirst
- General fatigue and low energy
- Sudden unintentional weight loss
- Itching or yeast infections in the genital area
Causes and Types of Diabetes:
The disease primarily results from issues with insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar. When insulin production or function falters, sugar builds up in the bloodstream, leading to diabetes.
Without proper insulin activity, cells cannot absorb glucose for energy, causing various health problems. Types of diabetes include:
Prediabetes: An initial state with elevated blood sugar levels, preventing progression through lifestyle modifications.
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition destroying insulin-producing cells, requiring insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, characterized by insulin resistance; managing it involves diet and weight control.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy, often managed with insulin and diet adjustments.
Adopting healthy habits, such as balanced eating, regular physical activity, and reducing sugar intake, can greatly decrease your risk of developing diabetes.
Disclaimer: This article provides general health information. For personalized diagnosis and treatment, consult healthcare professionals. Our content is intended for educational purposes only.