Early Warning Signs and Management of Diabetes
This article outlines early warning signs of diabetes, including excessive thirst, hunger, frequent urination, weight loss, and fatigue. It emphasizes the importance of early detection through symptom awareness and promotes lifestyle choices like balanced diet and regular exercise to manage the condition effectively.
Recognizing the First Symptoms of Diabetes
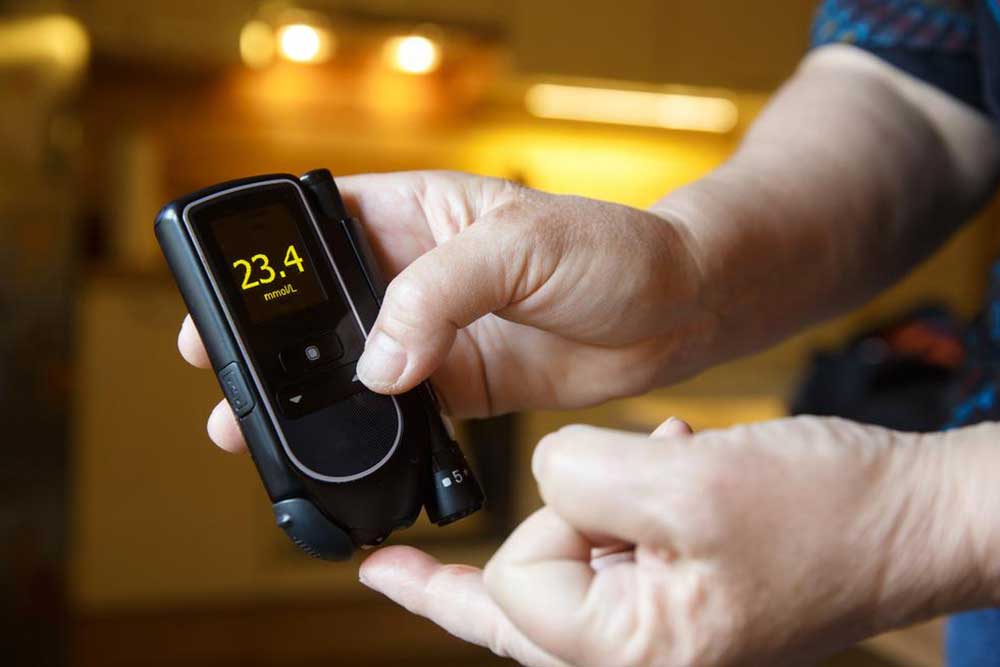
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that may be inherited or triggered by unhealthy lifestyle habits. It arises when blood sugar levels rise due to insufficient insulin production, a hormone crucial for glucose metabolism. Normally, carbohydrates are converted into glucose and absorbed into the bloodstream for energy. In diabetics, impaired insulin secretion leads to excess sugar in blood and urine. There are two main types: Type 1, often affecting children and involving destruction of pancreatic cells, and Type 2, more common in adults over 40, which can often be managed through lifestyle modifications or require medication.
The insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas may be damaged or destroyed in diabetics, resulting in high blood glucose. Blood sugar levels exceeding 400 mg per deciliter are often accompanied by sugar in urine. Recognizing early symptoms is vital for timely intervention.
Key early signs include:
Intense Thirst (Polydipsia)
Consistent dry mouth and throat despite fluid intake could indicate diabetes.
Constant Hunger (Polyphagia)
Feeling hungry frequently despite eating suggests ineffective glucose utilization.
Increased Urination (Polyuria)
Urinating more than three liters daily is common due to kidney filtration of excess sugar.
Unexpected Weight Loss
Rapid weight decline signals energy shortage caused by insulin issues.
Persistent Fatigue
Ongoing tiredness and low energy are typical symptoms when diabetes is uncontrolled.
For diet, diabetics should focus on high-fiber foods, salads, and avoid refined flour, fried dishes, and high-carb foods like rice and potatoes. Consumption of alcohol and artificially sweetened drinks should be limited. Incorporating regular physical activity, such as morning walks, can help control blood sugar, though lifelong management is necessary. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits is crucial for effective control.