Causes Behind Excessive Sweating and When to Seek Help
Excessive sweating can stem from various causes including infections, genetics, hormonal changes, menopause, and stress. Recognizing these factors helps in seeking appropriate treatment. Consult a healthcare professional if persistent sweating affects your quality of life.

Causes Behind Excessive Sweating and When to Seek Help
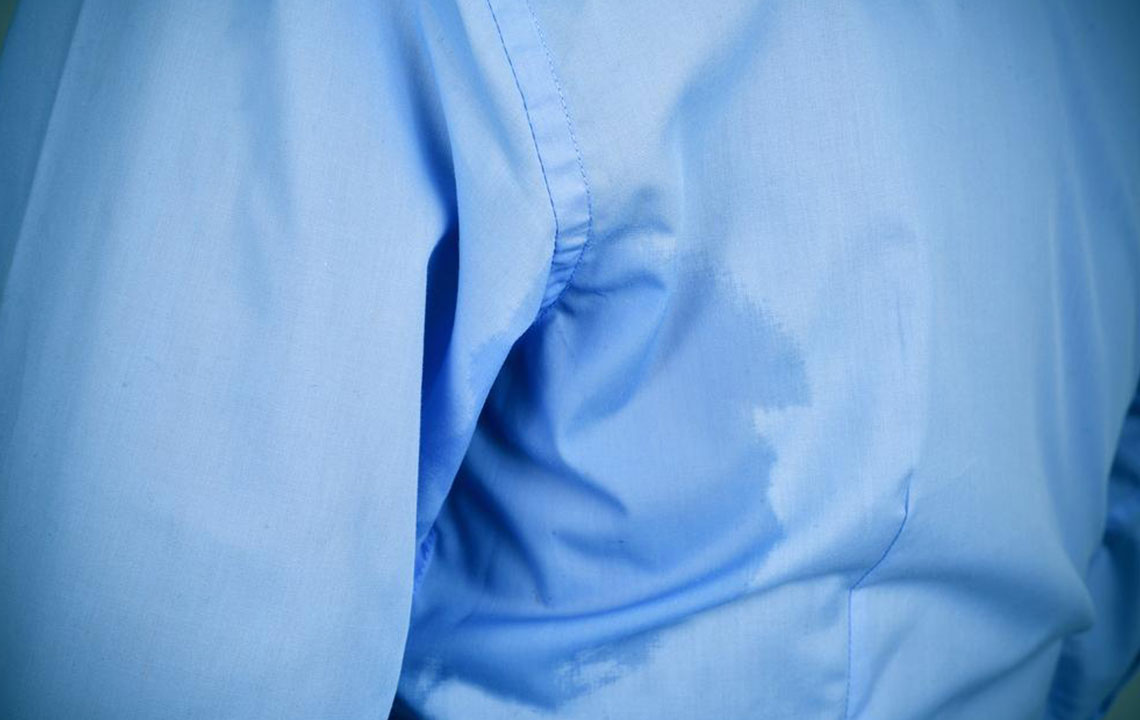
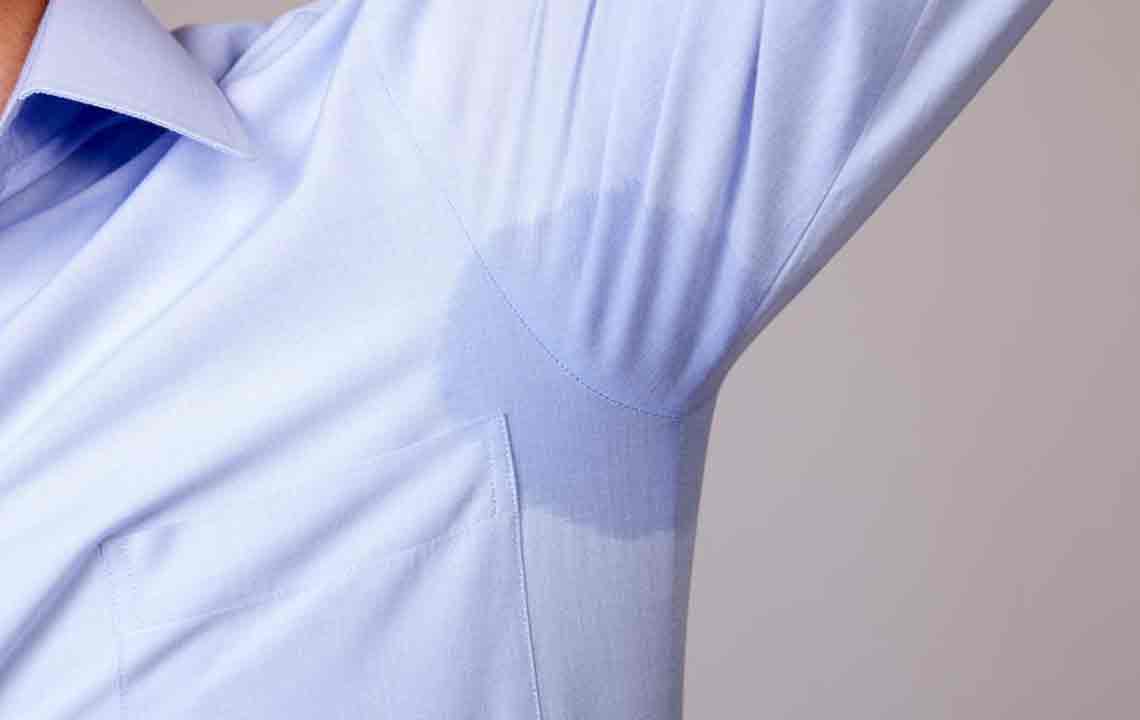
Sweating is a vital body process that helps regulate heat by releasing moisture from sweat glands. It typically occurs when the body overheats, aiding in cooling down, and assists in removing waste products. While normal sweating is healthy, excessive sweating can stem from various health issues, genetics, hormonal shifts, or emotional stress. It may also emit strong odors, often masked with deodorant or antiperspirant products.
Understanding the underlying reasons for abnormal sweating is essential for effective management and treatment.
Common causes of abnormal sweating include:
Fever or infections: Diseases like viral infections, tuberculosis, or typhoid often cause the body to sweat excessively as it tries to dissipate heat caused by illness.
Genetic predisposition: Some individuals inherit a higher density of sweat glands, resulting in increased perspiration regardless of environmental temperatures.
Additional factors influencing excessive sweating include:
Hormonal imbalances: Conditions such as hyperthyroidism can raise thyroid hormone levels, speeding up metabolic processes and leading to more sweating. Diabetes, especially with low insulin levels, can also contribute.
Menopause: Hot flashes and night sweats are common during menopause due to lower estrogen levels.
Emotional stress: Anxiety and high stress can cause the body temperature to rise, triggering excess sweating.
If persistent sweating and body odor are issues, consulting a healthcare provider is important for proper diagnosis and treatment.