Effective Use of Ozempic for Managing Type 2 Diabetes
This comprehensive guide explores how Ozempic is used to manage type 2 diabetes effectively. It covers proper administration, storage, safety tips, and precautions to help patients optimize their treatment and maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
Type 2 diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a metabolic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels. Maintaining proper blood sugar is essential for energy and health, but excessive levels can lead to complications. The disorder often results from inadequate insulin production or the body's resistance to insulin. Long-term uncontrolled diabetes can cause serious health problems. Besides lifestyle adjustments such as healthy eating, physical activity, and weight control, medication may be necessary. Ozempic®, an injectable drug, is often prescribed when other treatments fall short.
Ozempic® contains a GLP-1 receptor agonist that aids blood sugar regulation by prompting insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon. Suitable for type 2 diabetes patients, it is not recommended for type 1 diabetes. The medication comes in a prefilled injection pen that requires correct handling and storage. Follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and avoid adjusting doses independently.
Using Ozempic Safely
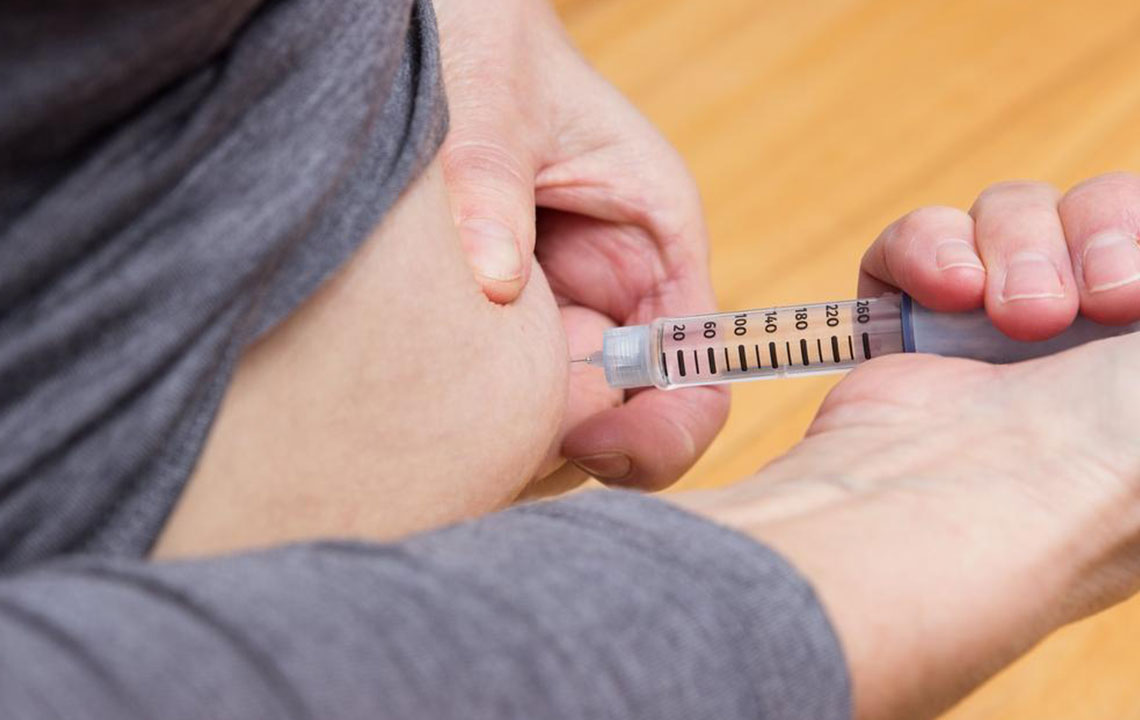
Administer the injection exactly as prescribed, with dosage adjustments based on response and blood sugar levels.
Adhere to instructions, and consult your doctor if unsure about injection technique.
Inject under the skin, ensuring proper site rotation and technique.
Do not alter the dosage or extend treatment beyond prescribed duration.
If the medication appears cloudy or discolored, dispose of it safely.
Storage Tips
Keep unopened Ozempic® refrigerated at 36ºF to 46ºF. Avoid freezing.
After opening, the pen can be kept at room temperature for up to 56 days, away from heat and light.
Cover the pen with its cap after use, and dispose of needles properly. Use a new needle each time for safety.
Safety Precautions
Report symptoms such as hoarseness, neck lumps, or swallowing difficulties, which may indicate thyroid concerns.
If signs of pancreatitis occur, discontinue use and seek medical help immediately.
Pregnant women or those planning pregnancy should inform their healthcare provider due to potential risks.
Common initial side effects include nausea, diarrhea, or constipation, which often improve with time.