Comprehensive Guide to Types of Pain and Effective Relief Methods
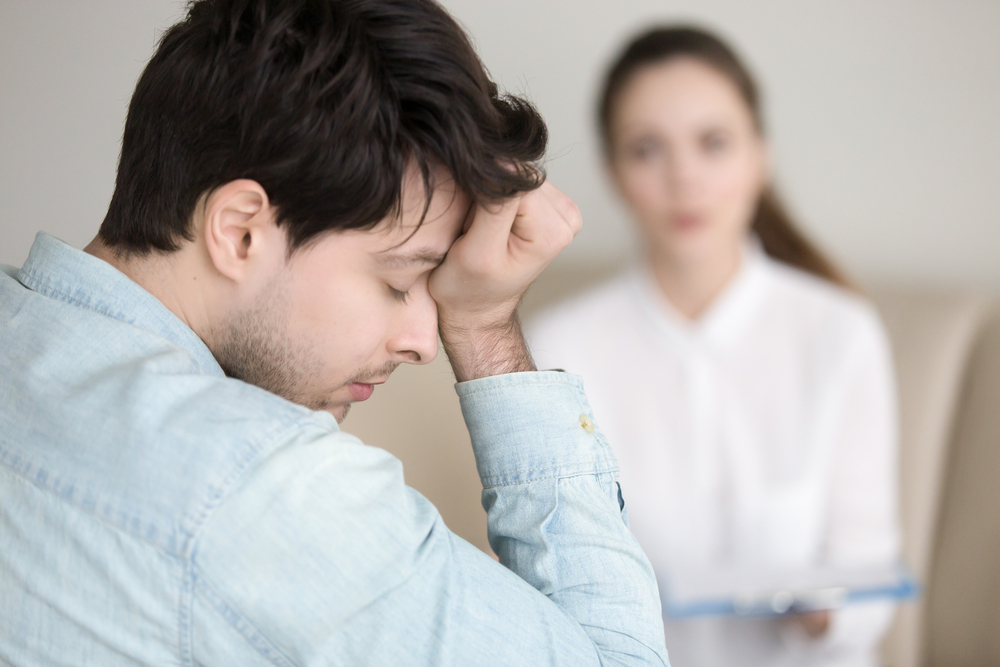
This comprehensive guide explains the different types of pain, their causes, and effective management methods. It emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, including medication options, therapies, and procedures. Proper pain relief begins with understanding pain characteristics and consulting healthcare providers to ensure safe and effective care tailored to individual needs.

Comprehensive Guide to Types of Pain and Effective Relief Methods
Effective pain management depends on identifying its underlying cause. For example, nerve irritation from herniated discs may respond well to epidural corticosteroid injections, while urgent issues like appendicitis often require surgery. Understanding the origin of pain is vital for proper treatment. Common causes include cancer, tendinitis, plantar fasciitis, sciatic nerve problems, muscle injuries, nerve trauma, infections, and headaches. Precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plans are essential for successful relief.
How Pain Is Managed
Understanding the history, intensity, duration, and triggers of pain is crucial for effective treatment. Sharing comprehensive details with healthcare providers ensures accurate diagnosis and targeted management.
Types of Pain
Nociceptive pain: Caused by tissue damage, it can be acute or chronic, affecting superficial layers or internal organs.
Neuropathic pain: Due to nerve damage or dysfunction, it can occur without apparent injury, as seen in shingles or diabetic nerve issues.
Strategies for Alleviating Pain
Psychological therapy and counseling
Physical and chiropractic treatments
Pharmacological approaches
Minimally invasive procedures
Medications for Pain Relief
Adjuvant agents: Including antidepressants and muscle relaxants that enhance systemic health and reduce inflammation.
Powerful opioids: Such as morphine, for moderate to severe pain in adults.
Combination therapies: Using opioids with counseling or other methods to decrease dependency.
Weaker opioids: Suitable for milder pain cases.
Non-opioid options: Over-the-counter remedies like NSAIDs, aspirin, and acetaminophen.
Since pain profiles can evolve with disease advancement or treatment, adapting management strategies is essential. Consult healthcare professionals before initiating any medication to avoid complications or worsening health conditions.