Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rosacea and Its Types
This comprehensive guide explores rosacea, detailing its different types and effective management strategies. Understanding triggers and treatment options can significantly improve quality of life for those affected by this chronic skin condition. Learn about symptoms, causes, and safe skincare practices in this informative overview.

Comprehensive Guide to Managing Rosacea and Its Types
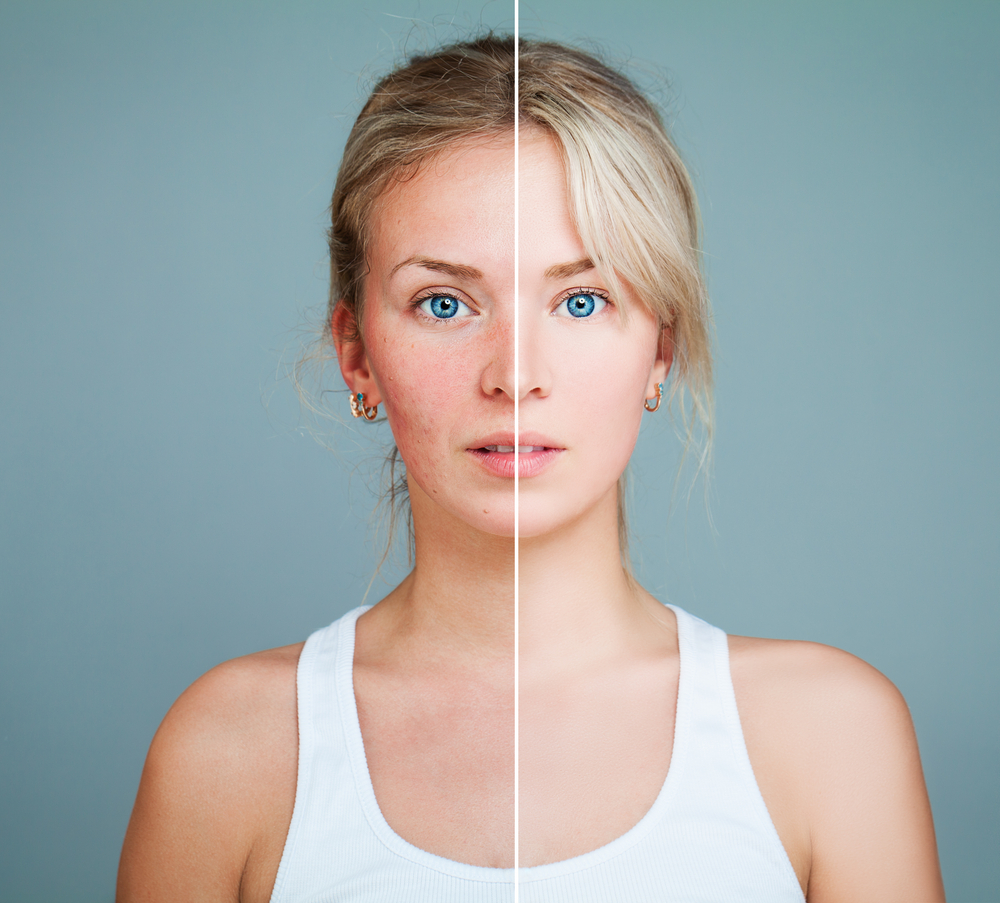
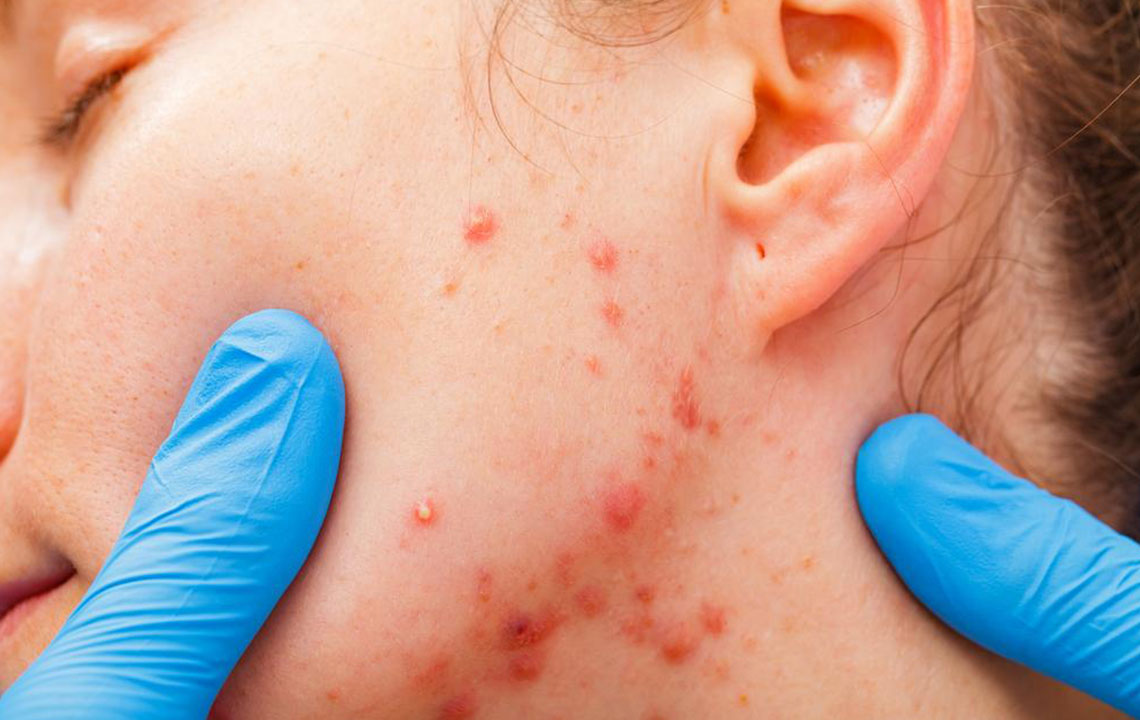
Rosacea is a persistent skin condition impacting over 16 million people, especially middle-aged women. Although not a life-threatening disease, it can lead to discomfort and self-esteem issues. Commonly appearing on the nose, cheeks, and forehead, it manifests as intermittent redness, bumps filled with pus, and visible blood vessels during flare-ups.
Types and Causes
The American Academy of Dermatology outlines four primary rosacea types:
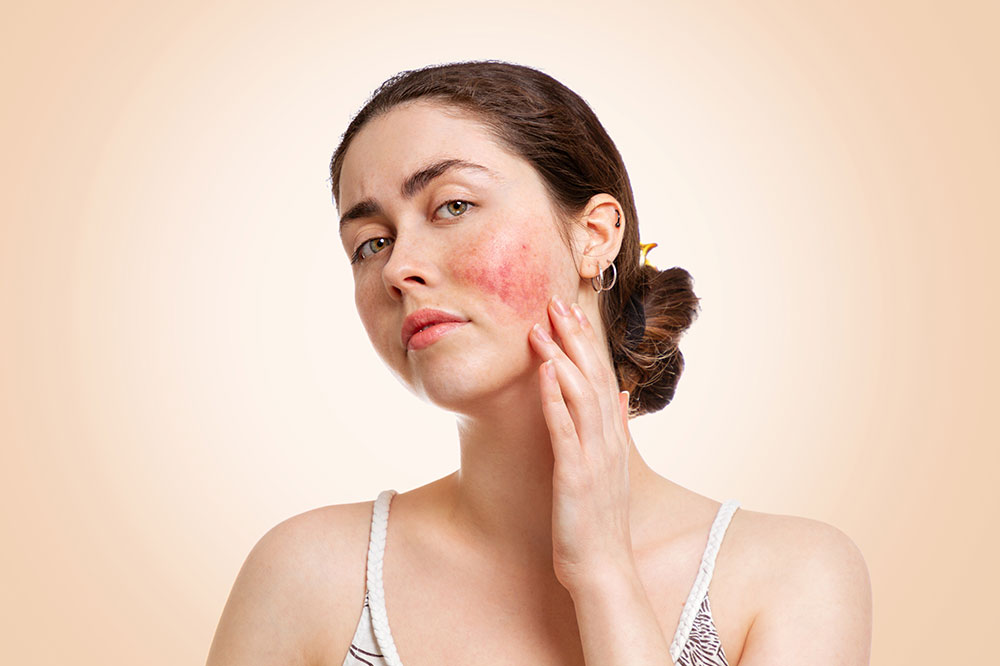
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR): Features facial redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels in the central face.
It can also cause skin sensitivity, swelling, dryness, and rough patches.
Papulopustular rosacea: Presents with redness, swelling, acne-like bumps, oily or sensitive skin, and prominent veins.
Phymatous rosacea: A rare form mainly affecting men, causing thickened, bumpy skin, enlarged pores, and visible blood vessels, commonly on the nose, chin, or forehead.
Ocular rosacea: Affects the eyes, leading to redness, dryness, burning, itching, visual disturbances, and blood vessels on the eyelids.
The exact cause remains uncertain but is thought to involve abnormalities in facial blood vessels, genetics, and skin sensitivity. Triggers include extreme weather, physical exertion, emotional stress, spicy foods, alcohol, and hot beverages.
Treatment Strategies
While rosacea has no permanent cure, symptoms can be managed using lifestyle adjustments and medications. Topical creams help reduce redness and inflammation and are used daily alongside oral antibiotics for quicker relief. Laser treatments target visible blood vessels, decreasing redness. It’s essential to use gentle, water-based skincare products and avoid irritants such as alcohol, menthol, and harsh exfoliants. Identifying and avoiding triggers like sunlight, stress, spicy foods, and alcohol is beneficial. Regular monitoring of diet and skincare routines can help control flare-ups. Consulting healthcare specialists ensures personalized management plans.