Effective Methods for Alleviating Plantar Fasciitis Pain
Discover effective strategies to relieve plantar fasciitis pain, including lifestyle changes, supportive footwear, stretching, and medical treatments. Learn how to identify symptoms early and implement proper care for faster recovery.
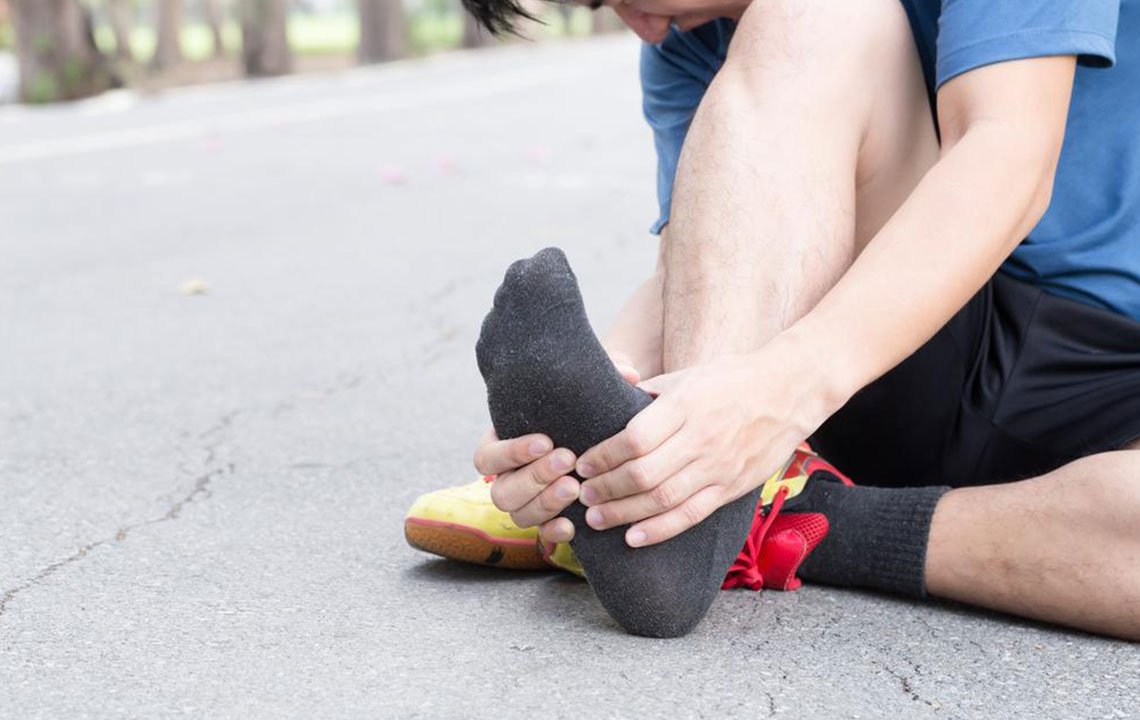

Proven Techniques to Relieve Plantar Fasciitis Discomfort
Plantar fasciitis happens when the connective tissue under the foot thickens, causing pain and discomfort.
This condition can stem from recent injuries or repetitive minor stress over time.
Understanding Causes and Initial Management
Identifying and addressing the root causes is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further harm. Several factors may contribute to developing this condition.
Reducing aggravating influences is vital. Although women are more frequently affected, men are also susceptible. Key risk factors include:
Being overweight
Sudden increase in physical activity intensity or starting new exercises
Standing for long durations on hard surfaces
Autoimmune illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
Wearing high heels or switching suddenly to flat shoes
Worn-out footwear lacking good arch support
Having flat feet or high arches
Discrepancies in leg length or abnormal walking patterns
Tight Achilles tendons or heel cords
Recognizing Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms
The main indicator is heel pain, especially upon waking or after physical activity.
Typical signs include:
Pain in the bottom of the heel
Discomfort that improves with walking but is most intense in the morning
Pain caused by pressure or certain foot positions
Seeking Medical Help
If heel pain persists or worsens, or if redness or bruising appears, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Diagnosis Process
Doctors examine painful areas and may order X-rays to rule out stress fractures. They press on the foot to locate painful spots. Typical pain characteristics include pain when waking, relief after walking, and localized tenderness.
Objectives of Treatment
Reduce inflammation and heel pain
Improve foot strength and flexibility, correcting structural issues
Promote healing of small tears in the fascia
Restore normal daily functions
Available Treatment Strategies
Several approaches can effectively ease symptoms and aid recovery.
Early-Stage Care
Rest your feet: Limit activities that increase heel pain, such as running or walking on hard surfaces.
Use ice packs: Apply to affected areas to reduce swelling and discomfort.
Wear cushioned heel inserts: Soft padding provides additional comfort.
Stretch regularly: Perform daily stretching to lengthen the Achilles tendon.
Opt for supportive footwear: Choose shoes with good shock absorption and arch support.
Avoid walking barefoot: Walking without support can worsen pain.
Night splints: Wear overnight to prevent fascia shortening.
Ultrasound therapy: Helps decrease inflammation and promotes healing.
Steroid injections: Offer relief but should be used cautiously.
Surgical options: Like plantar fascia release if other treatments fail.