Critical Role of Hemoglobin A1C Testing in Blood Sugar Management
This article discusses the significance of Hemoglobin A1C testing in managing blood sugar levels. It explains how the test reflects long-term glucose control, its importance for diabetics and non-diabetics, and benefits of regular monitoring. Clear insights help individuals maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent diabetes. Regular testing and understanding A1C can support overall health and proactive disease management.
Why Hemoglobin A1C Testing Matters
Hemoglobin, a key protein in red blood cells, plays a crucial role in transporting oxygen throughout the body. It also contributes to the blood's distinctive red color and ensures red blood cell integrity through its iron content. When glucose levels are high, glucose molecules bind to hemoglobin, creating glycated hemoglobin, or A1C. This process, known as glycation, provides a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the previous 3-4 months.
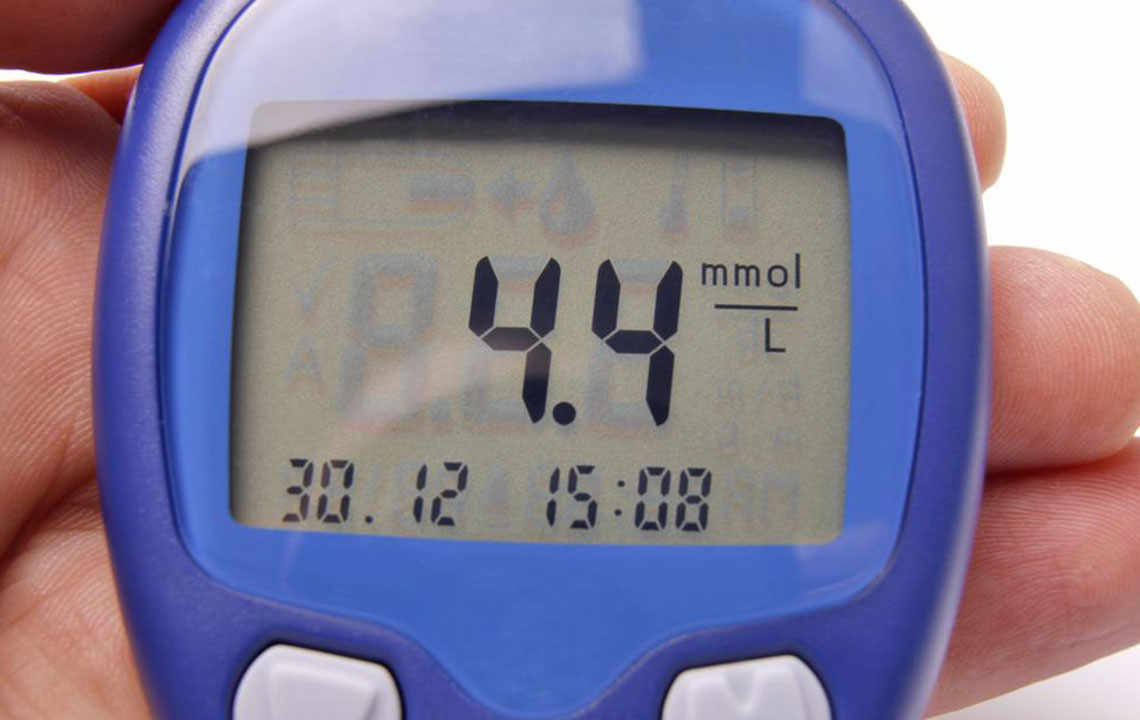
Measuring A1C is essential for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes. A higher A1C indicates poorer blood sugar control, while maintaining levels near or below 5% suggests good management. Even individuals without diabetes should consider regular testing, especially if they consume high-sugar diets or are overweight, to prevent or delay diabetes onset.
Consistent A1C monitoring enables proactive health decisions and effective glucose management, supporting long-term health goals.
Note:
This content aims to provide general health information. While based on scientific research, it does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare providers for personalized guidance and treatment options.