The Importance of A1C Testing in Diabetes Management
Discover the critical role of A1C testing in managing and diagnosing diabetes. Learn how it provides a long-term view of blood sugar control, guiding treatment adjustments and helping prevent complications, making it a vital tool for patients and healthcare providers alike.
How A1C Testing Enhances Diabetes Care
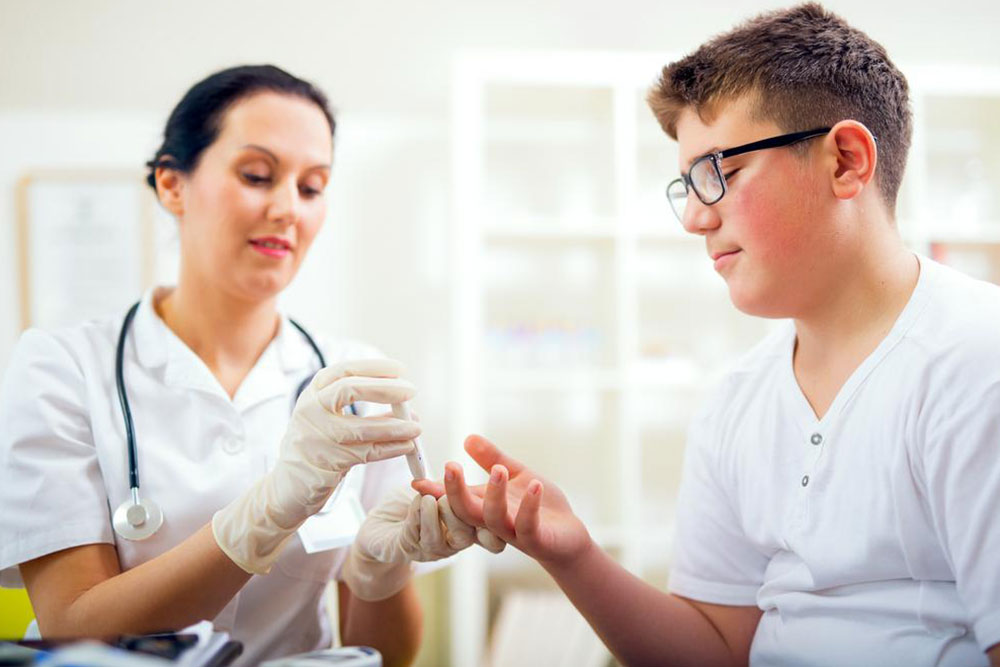
A1C testing is essential for evaluating long-term blood sugar control, providing valuable data for diagnosing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Unlike tests that measure current glucose levels, the A1C reflects average blood sugar over the previous few weeks, with lower levels indicating improved control.
Diagnostic Reliability
A1C tests are highly accurate for detecting diabetes, with recent innovations minimizing result discrepancies to around 0.5%. Though occasional anomalies can occur, A1C remains a trusted diagnostic measure.
The A1C test is simple, does not require fasting, and can be done anytime, making routine screening for diabetes and prediabetes straightforward and accessible. Early detection aids in better management.
Regular testing helps prevent complications like vision loss, nerve damage, kidney problems, and severe hypoglycemia by allowing timely medical adjustments.
Controlling Diabetes
If recent glucose levels are controlled but previous months showed poor management, A1C can identify this pattern.
Elevated A1C prompts healthcare providers to modify treatment strategies to lower blood sugar and reduce complication risks.
Results guide treatment adjustments—patients might transition from medication to lifestyle changes, emphasizing diet and physical activity.
Although regular A1C testing may involve costs, it plays a critical role in improving long-term health by preventing diabetes-related complications.