Essential Guide to Understanding Blood Pressure Levels
Learn how to interpret blood pressure readings accurately with this comprehensive guide. Discover healthy ranges, risk signs, and lifestyle tips to maintain optimal BP levels. Regular monitoring and medical advice are key for preventing hypertension-related health issues and ensuring overall wellness.
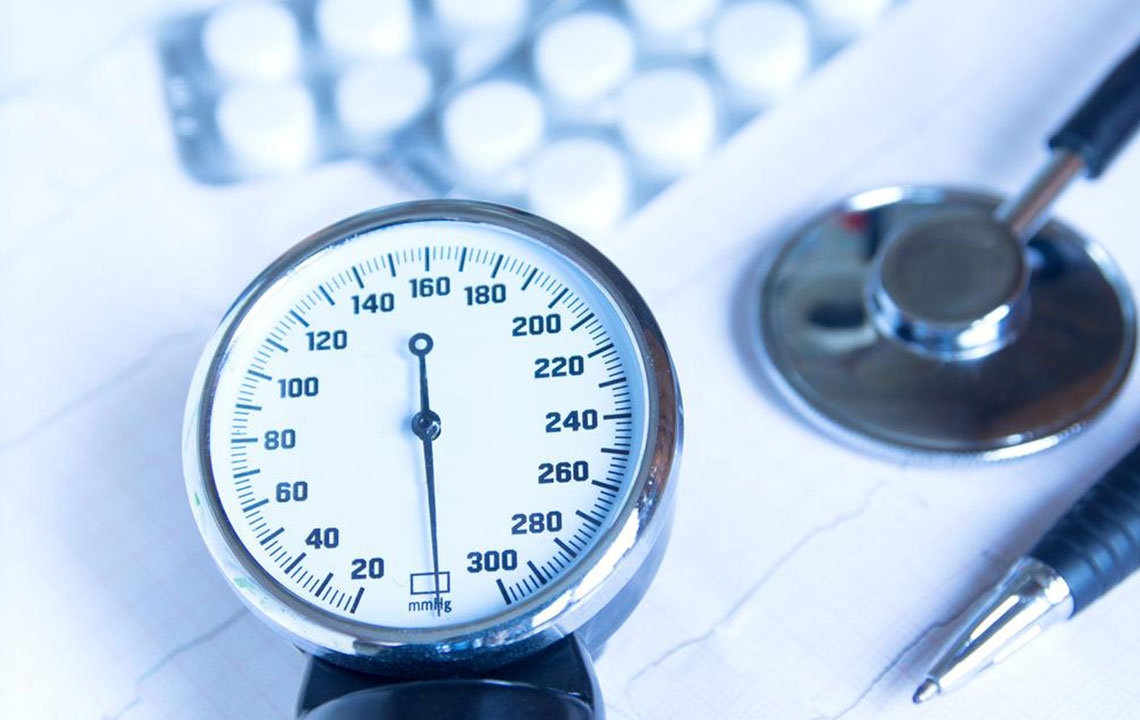

Decoding Your Blood Pressure Readings
The circulatory system relies on the heart to pump blood, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the body. The pressure exerted during this process is known as blood pressure (BP). Elevated BP, or hypertension, poses significant health risks. Blood pressure consists of two measurements: systolic (heartbeats) and diastolic (heart relaxation). Accurate readings are crucial because high BP often lacks symptoms but can lead to serious long-term health issues. Regular monitoring helps prevent damage to the heart, kidneys, eyes, and brain. Maintaining normal BP is essential for optimal health.
Healthcare professionals advise checking blood pressure weekly, especially for those with higher risk. Understanding blood pressure categories helps differentiate between healthy and concerning levels. Systolic measures the maximum pressure during heartbeats, while diastolic reflects the minimum. Keeping BP below 120/80 mmHg is ideal. Elevated levels suggest prehypertension or stages 1 and 2 hypertension, requiring lifestyle changes and possibly medication. Severe spikes, such as readings of 180/110 mmHg or higher, demand immediate medical attention to prevent hypertensive emergencies.
Understanding your blood pressure results enables better health decisions. Achieving and maintaining normal levels can help avoid complications. Lifestyle adjustments like regular exercise, a diet low in sodium, weight control, and limiting alcohol intake are effective strategies. Medications prescribed by healthcare providers can also manage BP effectively. Consistent monitoring and following medical advice are vital to prevent health issues related to high blood pressure.
Disclaimer:
This article offers health information based on research but should not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, always consult your healthcare provider. The website may not include all available schemes or offers; thus, professional guidance is essential for personal health care decisions.