Gout Attacks Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Long-Term Impact
Learn about gout flare-ups, their causes, symptoms, and how repeated attacks can lead to joint damage. Early treatment is essential to prevent long-term complications and manage symptoms effectively.
Gout Attacks Explained: Causes, Symptoms, and Long-Term Impact
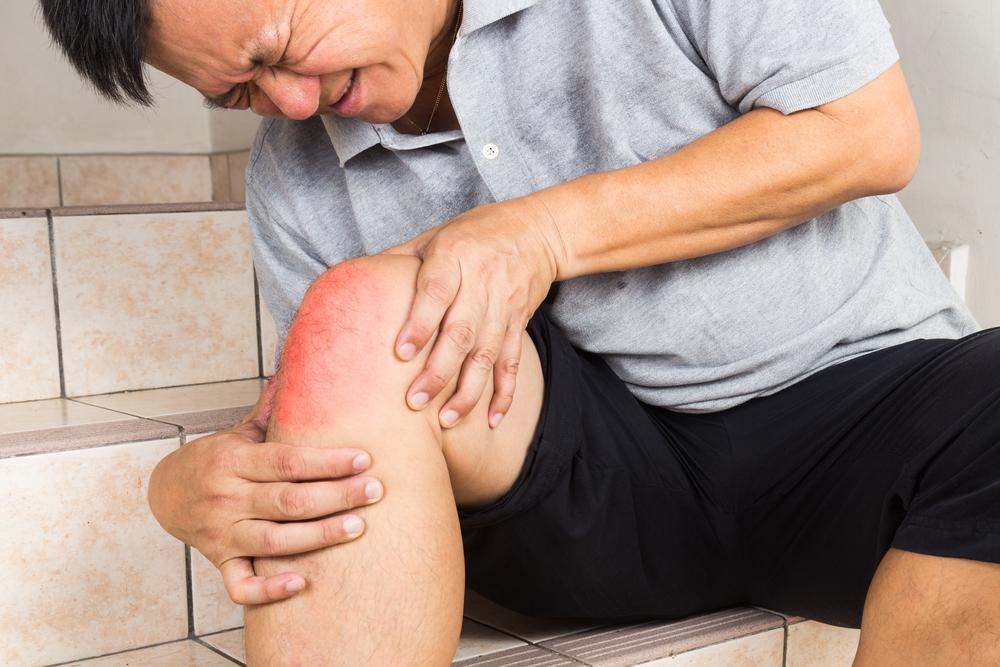
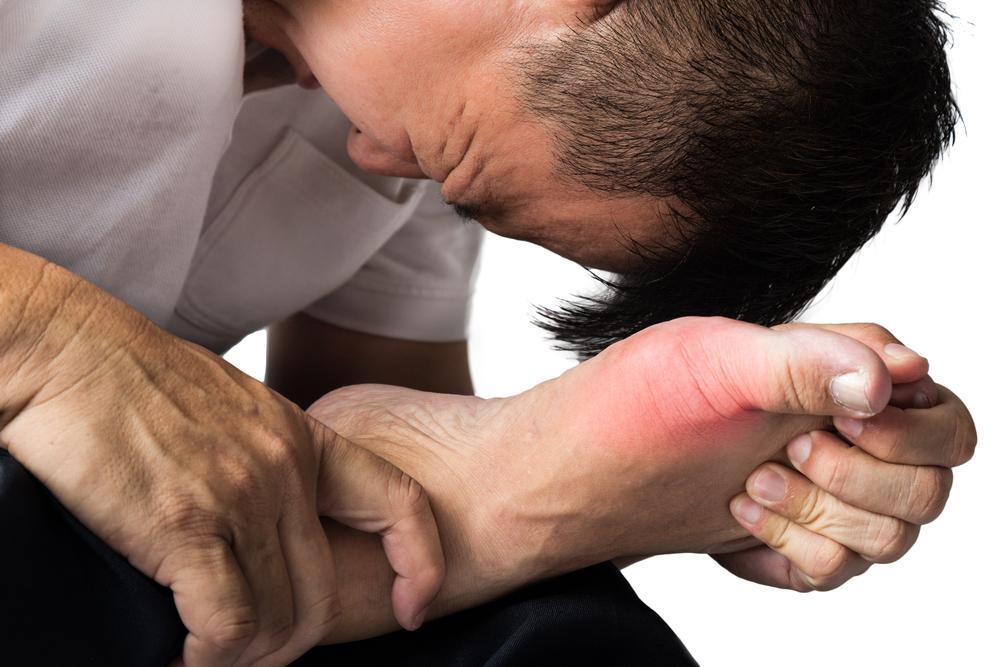
Gout, also known as hyperuricemia, occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in joints and tissues, causing inflammation and intense pain in a condition called gout attack. Elevated uric acid levels in the blood are the primary culprit, though the exact causes remain unclear. Genetics may play a role. During a flare, the big toe is often affected, leading to redness, swelling, stiffness, and burning sensations.
Gout episodes tend to recur. Without treatment, repeated attacks can damage joints and tissues. Symptoms are often mistaken for sprains or tendinitis. Most attacks happen at night, starting mildly and worsening over hours. Mild flare-ups may resolve in hours, but severe attacks can last weeks, requiring prompt medical attention to prevent worsening of joint damage.