Guidelines for Normal Blood Pressure Across Different Age Groups
This article explains normal blood pressure ranges across different ages, emphasizing the importance of maintaining healthy arteries and monitoring blood pressure to prevent cardiovascular problems. It provides guidelines for understanding typical readings and the impact of age on blood pressure levels.
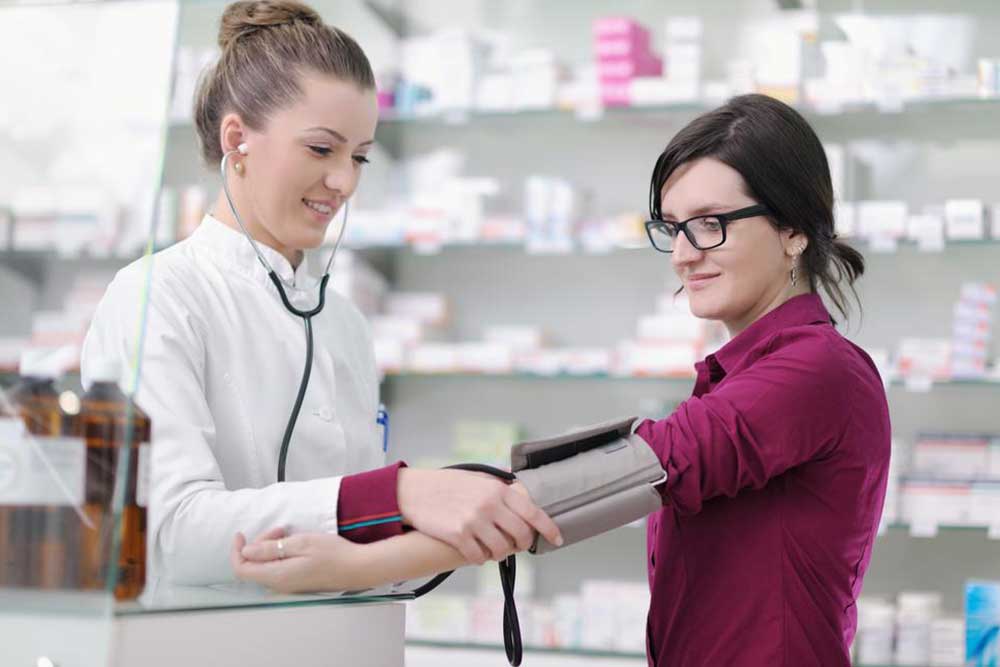

The circulatory system distributes blood throughout the body, with blood pressure indicating the force exerted by blood flow. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is vital for ensuring organ health and overall well-being.
Blood transports oxygen, nutrients, antibodies, and hormones, supporting body functions. The heart’s pumping action generates blood pressure, propelling blood through arteries and veins.
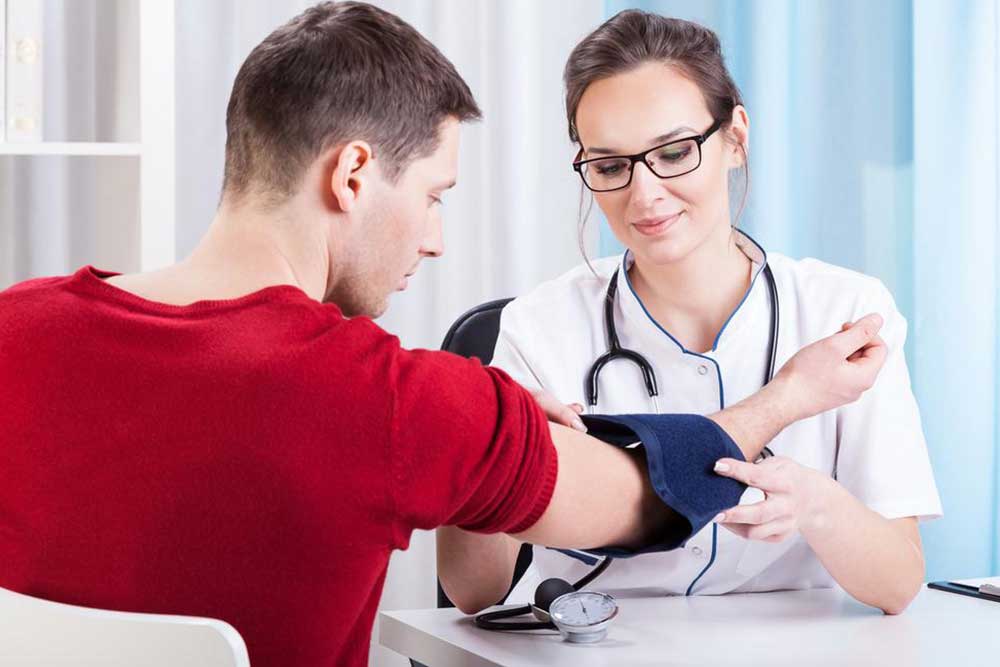
Blood is expelled from the heart with each beat, creating pressure that peaks during ventricular contraction and decreases as blood travels into smaller vessels. Elastic arterial walls help sustain steady blood flow. Blood pressure is measured in mmHg using a sphygmomanometer.
Normal Blood Pressure by Age
Medical professionals utilize charts to compare readings against standard healthy ranges. For adults, a typical healthy blood pressure is about 120/80 mmHg, though levels up to 130/80 mmHg are considered elevated by the American Heart Association.
Blood pressure generally ranges from 70/40 to 90/60 mmHg, with optimal readings between 90/60 and 120/80 mmHg. Readings from 120/80 to 140/90 mmHg suggest prehypertension, while values exceeding 140/90 mmHg indicate hypertension. Age influences these levels; persistent abnormal readings call for lifestyle adjustments to lower cardiovascular risks.
Healthy, flexible arteries are essential; narrowed or stiff vessels can impair blood pressure regulation, leading to health issues if not addressed. Regular monitoring and healthy habits help maintain balanced blood pressure and prevent disease.