Key Facts About Skin Cancer Everyone Should Know
Understanding skin cancer is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. This article covers common signs, diagnosis methods, and available treatments, emphasizing the importance of prompt medical attention to prevent serious health consequences.
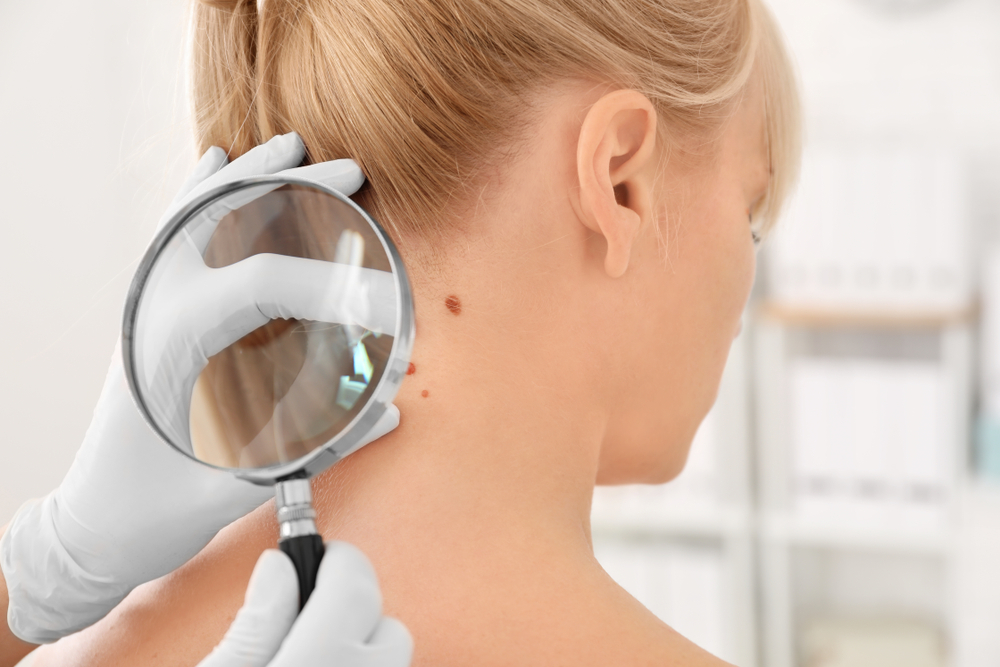
Are you aware of the essentials surrounding skin cancer? Here's what you need to know!
Skin cancer has emerged as a major health issue in recent years, earning the reputation of a modern epidemic among health professionals. It can develop on various parts of the body, primarily the skin, and although not always fatal, it can become severe if neglected, with the risk of spreading. Small skin spots or irregularities can be early indicators, making prompt diagnosis critical. Early detection and treatment are vital to preventing serious health complications.
If you're unsure when to seek medical advice, continue reading.
What is skin cancer?
It involves abnormal, rapid growth of skin cells.
Most commonly appears on sun-exposed areas.
Yet, skin cancer can also occur in areas not directly exposed to sunlight.
Typical sites where skin cancer occurs
Commonly found on the face—lips, scalp, neck—as well as arms and legs.
It can affect individuals regardless of skin color.
Melanoma, a serious type, tends to develop on less exposed regions like palms, soles, and genital areas.
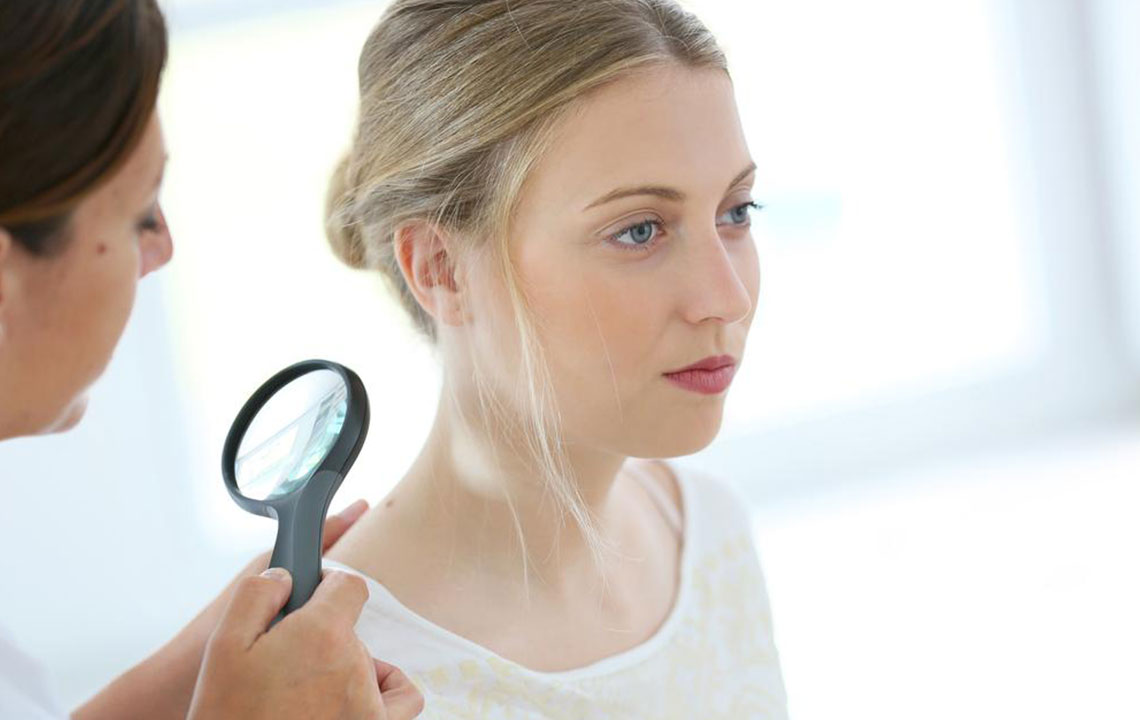
Identifying early signs and diagnosis
Early skin cancer may present as small brown lumps, sometimes with a scaly surface and a red center, especially on sun-exposed skin.
Melanomas often look like changing moles—in color, shape, or texture, or may bleed.
Visual guides and online resources can assist in recognizing these warning signs. If abnormalities are observed, see a healthcare professional promptly.
How skin cancer is diagnosed
Diagnosis often involves examining skin changes and performing skin biopsies.
A biopsy removes a small tissue sample for microscopic analysis to detect and classify the cancer.
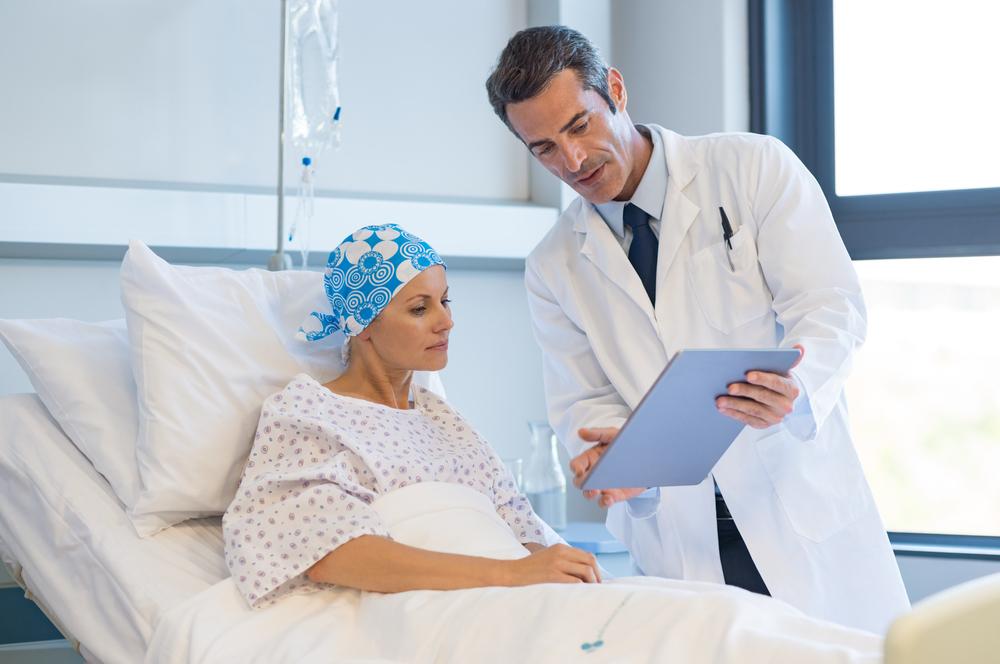
Typical treatments for skin cancer
Cryosurgery—freezing cancer cells—is effective for early-stage lesions.
Surgical removal of the affected area and some surrounding tissue.
Mohs surgery, which involves layer-by-layer removal and examination, is suited for complex cases.
Radiation therapy uses targeted high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells.
Topical or systemic chemotherapy may be used for superficial skin cancers.
This overview highlights the importance of early detection and treatment in managing skin cancer effectively.