Neurofibromatosis Explained: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
Discover comprehensive insights into neurofibromatosis, including its types, symptoms, and available management strategies. Learn how different variants affect individuals and the current treatment options to improve quality of life. This informative guide aims to educate about this hereditary nervous system disorder, emphasizing personalized care and medical monitoring for affected patients.

Neurofibromatosis Explained: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
Neurofibromatosis is a hereditary condition affecting the nervous system, characterized by the growth of benign tumors called neurofibromas along nerves in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. Although most tumors are non-cancerous, some can become malignant over time. This disorder results from genetic mutations and presents in several forms, each with distinctive features and management strategies. This article reviews the different types of neurofibromatosis and available treatment options for patients.
Types and Associated Symptoms
The condition primarily includes three variants, each showing unique symptoms and progression patterns.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
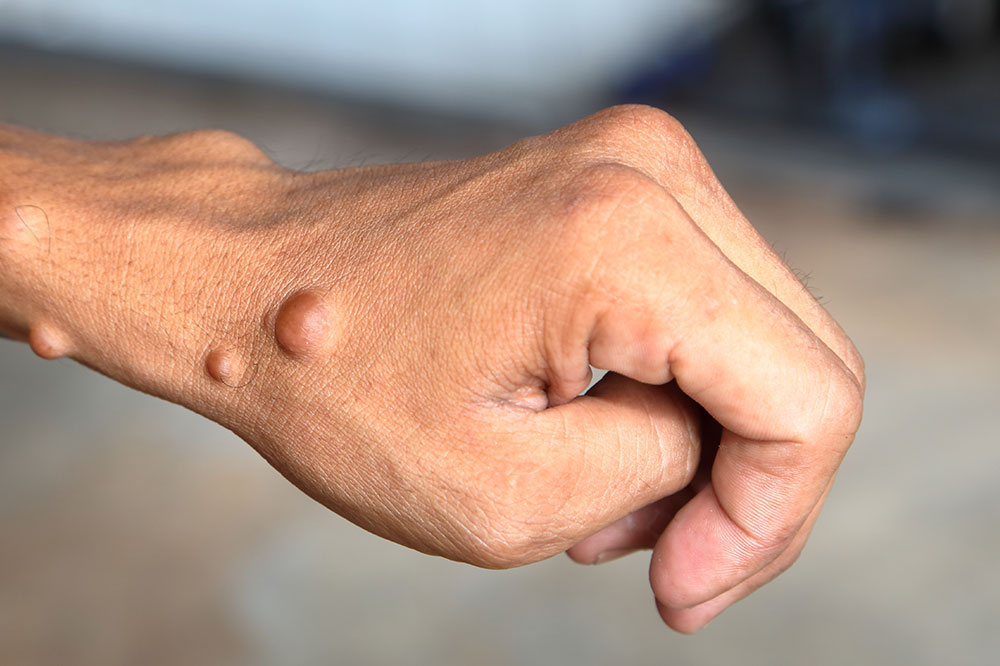
NF1 is the most common type, often diagnosed in early childhood or infancy. Symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Typical signs include:
Coffee-colored skin patches called café au lait spots
Freckles appearing in areas like the armpits or groin
Soft, painless bumps under or on the skin
Brown spots on the iris known as Lisch nodules
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2)
This less common but more serious form usually develops during adolescence. It is characterized by tumors called acoustic neuromas that grow on nerves connecting the inner ear and brain. Symptoms may include:
Progressive hearing loss
Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
Balance disturbances
Numbness and weakness in limbs
Schwannomatosis
This rare subtype typically appears between ages 25 and 30, with tumors on cranial, spinal, and peripheral nerves. Common symptoms include:
Persistent, severe pain in the body
Weakness or numbness in limbs
Muscle wasting
Treatment Options
While there is currently no cure for neurofibromatosis, various approaches can help manage symptoms. These include:
Surgical Removal
Operations focus on excising tumors or reducing their size to alleviate symptoms. In NF2 cases, surgery may restore hearing or relieve nerve pressure.
Precision Radiation Therapy
Stereotactic radiosurgery provides targeted radiation to neuromas, minimizing damage to adjacent tissues.
Most skin manifestations, like café au lait spots, usually require no intervention but are monitored for any changes. Treatment plans are individualized based on patient needs.
Important Reminder:
This content is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment options. Use this information responsibly and seek expert guidance for health-related concerns.