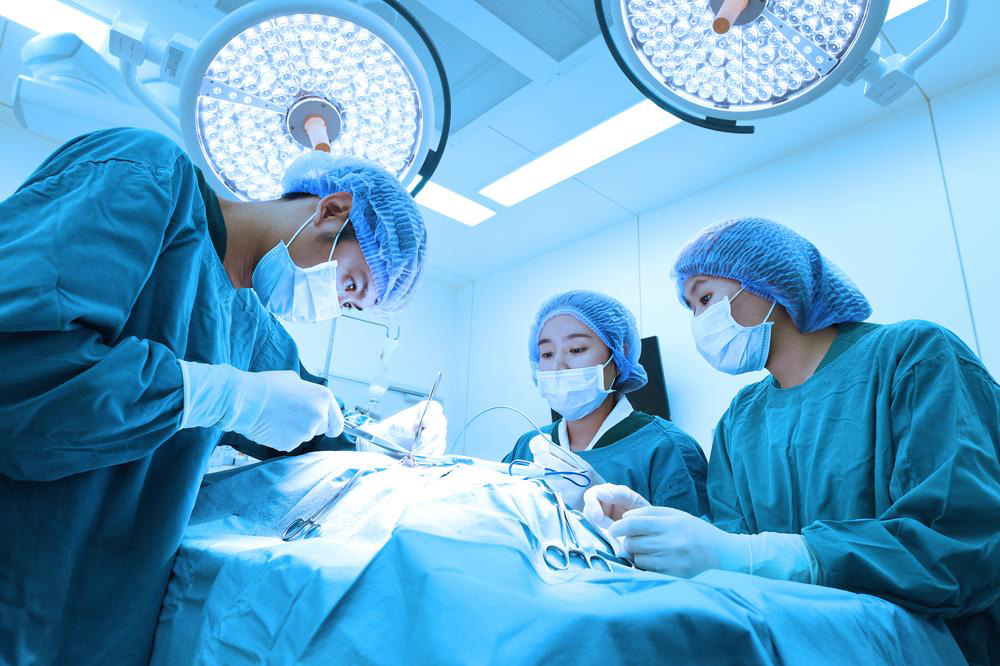
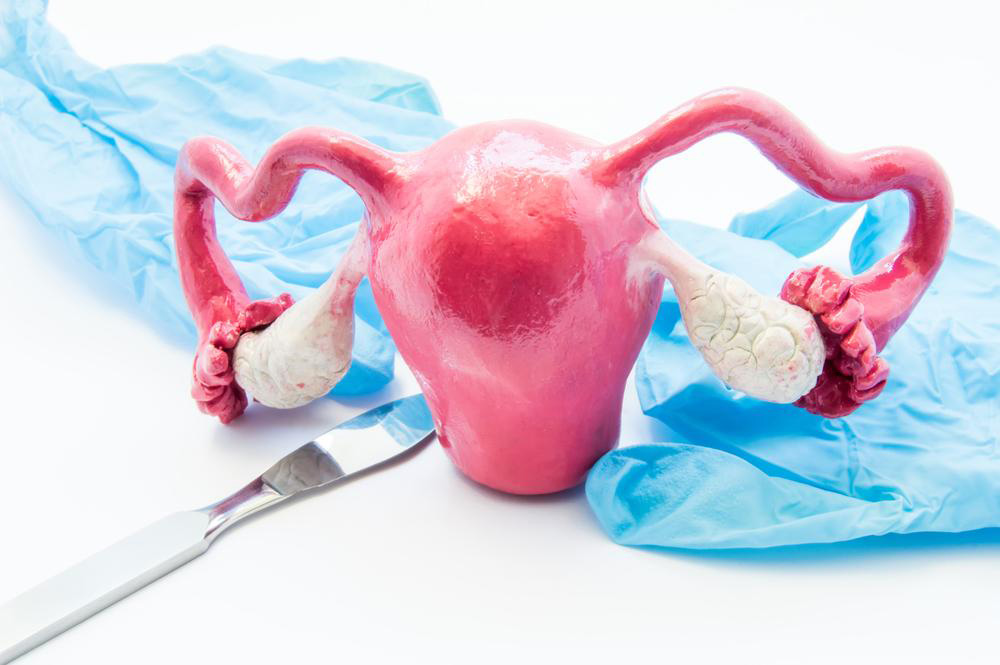
A Complete Overview of Fallopian Tube Reversal Techniques
This comprehensive guide explores various fallopian tube reversal techniques, including mini-laparotomy, laparoscopy, and robotic surgery. It explains the procedures, recovery times, and benefits, helping women choose the best option for restoring fertility. Learn about the surgical steps and success factors involved in these advanced procedures aimed at re-establishing natural conception.
Understanding Various Fallopian Tube Reversal Methods
While tubal ligation serves as a permanent contraception method, it can often be reversed through different surgical approaches. These procedures are known by names such as tubotubal anastomosis, microsurgical tubal rejoining, tubal reimplantation, and neofimbrioplasty, depending on the technique employed. Most skilled surgeons specializing in tubal reversal perform these surgeries. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable method for your situation.
There are three primary surgical options available for restoring fallopian tube function:
Mini-laparotomy
Ideal for those prioritizing affordability, mini-laparotomy involves small 2-4 centimeter incisions above the pubic area, easily concealed beneath clothing. Recovery usually lasts around two weeks, with many women resuming routine activities within a week. This approach remains popular due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Laparoscopic Surgery
This minimally invasive method uses three tiny incisions to insert surgical instruments and a mini camera. It minimizes scarring and shortens recovery time. Surgeons can accurately identify and reconnect the fallopian tubes using laparoscopy, leading to precise restoration of tube function.
Robotic-Assisted Reversal
Robotic tubal reversal is the most advanced and least invasive technique. Controlled by the surgeon via a console, robotic instruments with high-definition imaging enable highly precise procedures with minimal tissue disruption. Recovery typically takes about a week, though it is generally more costly. This method ensures meticulous suturing and alignment, increasing the chances of successful fertility restoration.
In all these procedures, the surgeon carefully removes damaged or blocked sections of the tubes and reconnects healthy segments using fine, absorbable stitches. The aim is to preserve as much of the original fallopian tube as possible, enhancing fertility prospects in the future.