Comprehensive Guide to Trigger Finger: Causes, Types, and Prevention Strategies
This article explores trigger finger, a condition causing fingers or thumbs to become stuck or snap. It covers types, causes, and prevention tips, emphasizing the importance of healthy habits and medical care to manage and prevent this common issue.

Comprehensive Guide to Trigger Finger: Causes, Types, and Prevention Strategies
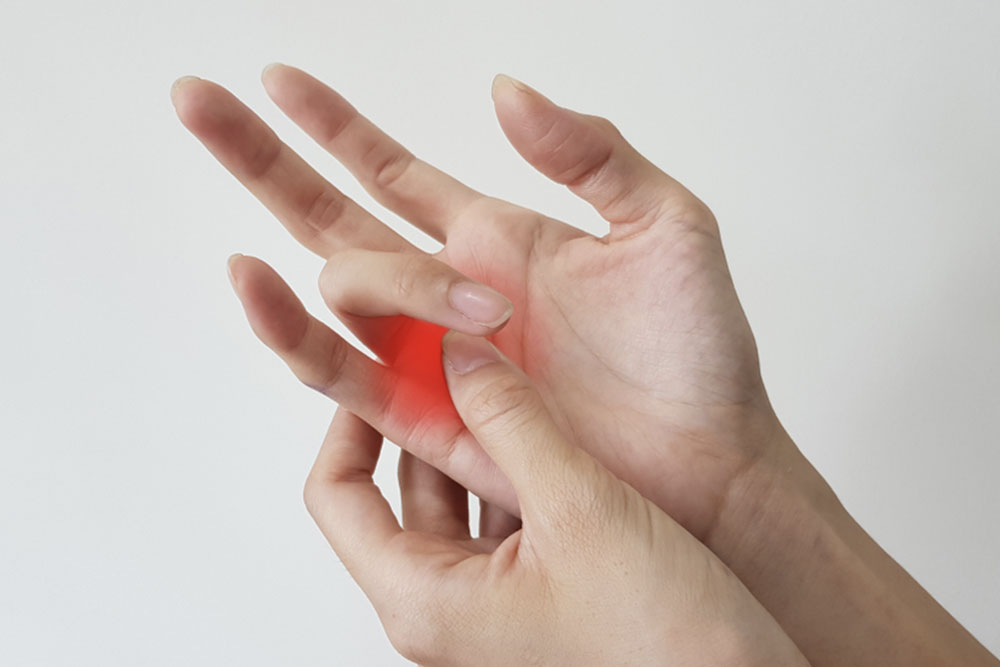
Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, is a condition where a finger or thumb gets stuck in a bent position and then suddenly extends, mimicking the action of pulling a trigger. This happens when the tendons that control finger movement become inflamed or thickened, hindering smooth sliding through the sheath. The condition can occur in any finger or thumb, with severity varying. The main types include primary trigger finger, resulting from tendon sheath inflammation, and secondary trigger finger, linked to underlying health issues such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes primarily involve inflammation or thickening of tendons and their sheaths, often due to repetitive movements, injuries, or infections. Factors like age, genetic predispositions, and chronic illnesses also increase risk. In children, trigger finger commonly affects the thumb and may need surgical intervention in severe cases. Prevention focuses on avoiding repetitive strain, performing finger exercises, and allowing adequate rest to preserve flexibility and strength.
Adopting healthy movement habits can help lower the risk of developing trigger finger. It is important to seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.