Proven Methods to Achieve Healthy A1C Targets
Learn effective strategies to lower and maintain your A1C levels, vital for managing diabetes and reducing health risks. This guide emphasizes the importance of regular testing, healthy eating, physical activity, and working with healthcare professionals to achieve optimal blood sugar control.

Proven Methods to Achieve Healthy A1C Targets
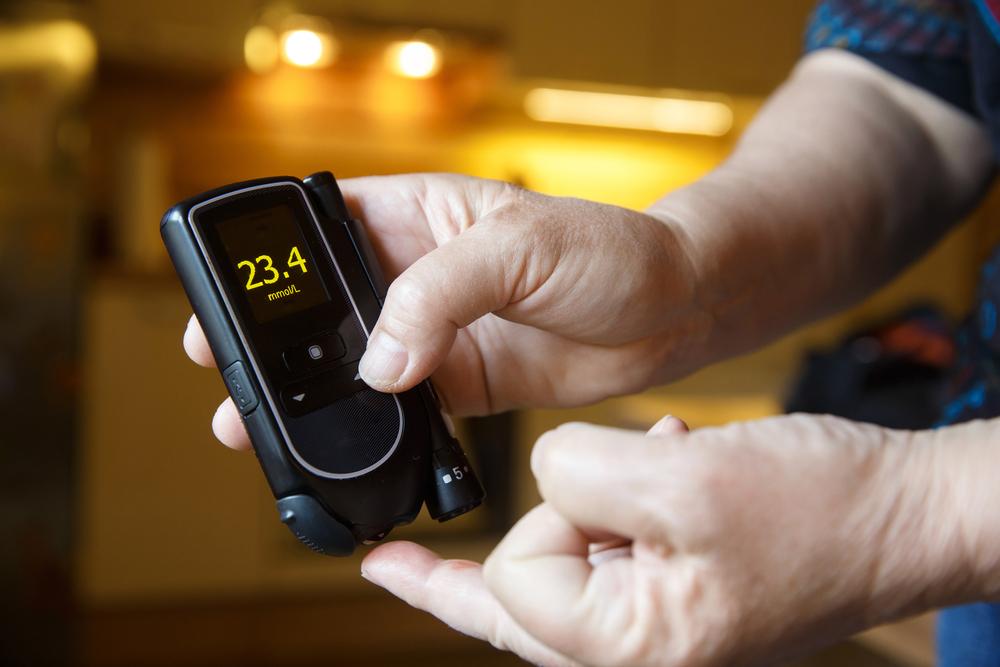
Effective blood sugar management is essential for diabetes control and prevention of complications. The A1C test provides an overview of average blood glucose levels over two to three months. Regular testing allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring better disease management.
What Does the A1C Test Signify?
The A1C test measures the percentage of hemoglobin with sugar attached, reflecting long-term glucose control. Higher percentages indicate poorer blood sugar regulation.
Interpreting A1C Results
A normal A1C level is below 5.7%. Values between 5.7% and 6.4% point to prediabetes, increasing the chance of developing type 2 diabetes. An A1C of 6.5% or higher confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
Maintaining an A1C below 7% can significantly reduce health risks for those with diabetes.
Strategies to Lower A1C Include:
Managing weight effectively
Staying physically active regularly
Eating a balanced diet rich in vegetables and whole foods
Managing stress effectively
Develop a comprehensive management plan covering:
Medical treatment guidelines
Medications
Blood glucose targets
Emergency contact information
Response plans for hypoglycemia
Prioritize a diet high in vegetables, fruits, healthy fats, proteins, and complex carbohydrates like potatoes and whole grains. Limit processed foods and sugary drinks. Portion control is key.
Coordinate with your healthcare provider to monitor blood sugar levels and adjust your plan as needed.
Understanding and actively working to lower your A1C is vital for optimal diabetes management. Always seek professional advice tailored to your health needs.